cloudstrife1218
MuscleChemistry Registered Member
[h=2]WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW:[/h]What is an intramuscular injection?
An intramuscular (IM) injection is a shot of medicine given into a muscle. Certain medicines need to be given into the muscle for them to work correctly.
[h=2]What should I know about the syringe?[/h]There are 3 parts to a syringe: the needle, the barrel, and the plunger. The needle goes into your muscle. The barrel holds the medicine and has markings on it like a ruler. The markings are in milliliters (mL). The plunger is used to get medicine into and out of the syringe.
[h=2]Where can I give an intramuscular injection?[/h]The following are safe areas to give an IM injection:
[h=2]What are the risks of an intramuscular injection?[/h]An intramuscular injection could cause an infection, bleeding, numbness, or pain.
[h=2]When should I contact a caregiver?[/h]Contact a caregiver if:
An intramuscular (IM) injection is a shot of medicine given into a muscle. Certain medicines need to be given into the muscle for them to work correctly.
[h=2]What should I know about the syringe?[/h]There are 3 parts to a syringe: the needle, the barrel, and the plunger. The needle goes into your muscle. The barrel holds the medicine and has markings on it like a ruler. The markings are in milliliters (mL). The plunger is used to get medicine into and out of the syringe.
[h=2]Where can I give an intramuscular injection?[/h]The following are safe areas to give an IM injection:
- Vastus Lateralis Muscle (Thigh): Look at your thigh and divide it into 3 equal parts. The middle third is where the injection will go. The thigh is a good place to give yourself an injection because it is easy to see. It is also a good spot for children younger than 3 years old.
- Ventrogluteal Muscle (Hip): Have the person getting the injection lie on his or her side. To find the correct location, place the heel of your hand on the upper, outer part of the thigh where it meets the buttocks. Point your thumb at the groin and your fingers toward the person's head. Form a V with your fingers by separating your first finger from the other 3 fingers. You will feel the edge of a bone along the tips of your little and ring fingers. The place to give the injection is in the middle of the V. The hip is a good place for an injection for adults and children older than 7 months.
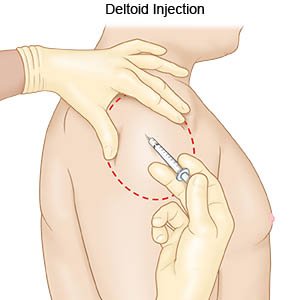
- Deltoid Muscle (Upper arm muscle): Completely expose the upper arm. You will give the injection in the center of an upside down triangle. Feel for the bone that goes across the top of the upper arm. This bone is called the acromion process. The bottom of it will form the base of the triangle. The point of the triangle is directly below the middle of the base at about the level of the armpit. The correct area to give an injection is in the center of the triangle, 1 to 2 inches below the acromion process. This site should not be used if the person is very thin or the muscle is very small.
<tbody>
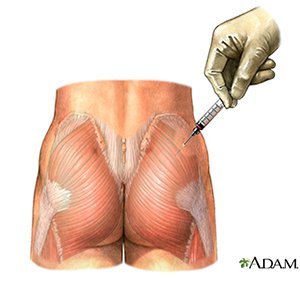
</tbody> - Dorsogluteal Muscle (buttocks): Expose one side of the buttocks. With an alcohol wipe draw a line from the top of the crack between the buttocks to the side of the body. Find the middle of that line and go up 3 inches. From that point, draw another line down and across the first line, ending about halfway down the buttock. You should have drawn a cross. In the upper outer square you will feel a curved bone. The injection will go in the upper outer square below the curved bone. Do not use this site for infants or children younger than 3 years old. Their muscles are not developed enough.
<tbody>
</tbody>
- Keep track of where the injections are given: Make a list of the sites you use. Write down the date, time, and the site each time you give an injection.
- Change sites for the injections: It is important to use a different site each time you give an injection. This helps prevent scars and skin changes. The sites where injections are given should be at least 1 inch away from each other. Ask your caregiver if you need to inject the medicine in a certain site.
- One alcohol wipe
- One sterile 2 x 2 gauze pad
- A new needle and syringe that are the correct size
- Disposable gloves, if you have them
- Open the alcohol wipe: Wipe the area where you plan to give the injection. Let the area dry. Do not touch this area until you give the injection.
- Prepare the needle: Hold the syringe with your writing hand and pull the cover off with your other hand. Place the syringe between your thumb and first finger. Let the barrel of the syringe rest on your second finger.
- Hold the skin around where you will give the injection: With your free hand, gently press on and pull the skin so that it is slightly tight.
- Insert the needle into the muscle: Hold the syringe barrel tightly and use your wrist to inject the needle through the skin and into the muscle at a 90 degree angle.
- Check the needle: Let go of the skin with your other hand. Hold the syringe so it stays pointed straight in. Pull back on the plunger a little to make sure you did not hit a blood vessel. If blood comes back, remove the needle immediately. Do not inject the medicine. Dispose of both the syringe and the medicine. Get more medicine in a new syringe. When you give the second injection, give it on the other side.
- Inject the medicine: Push down on the plunger to inject the medicine. Do not force the medicine by pushing hard. Some medicines hurt. You can inject the medicine slowly to reduce the pain.
- Remove the needle: Once the medicine is injected, remove the needle at the same angle as it went in. Place gauze over the area where you gave the injection.
[h=2]What are the risks of an intramuscular injection?[/h]An intramuscular injection could cause an infection, bleeding, numbness, or pain.
[h=2]When should I contact a caregiver?[/h]Contact a caregiver if:
- A fever, sneezing, or coughing develops after the injection.
- There is a lump, swelling, or bruising where the injection was given that does not go away.
- You have questions about how to give an injection.
- A rash or itching develops after the injection is given.
- Shortness of breath develops after the injection is given.
- The mouth, lips, or face swells after the injection is given.








