In the last couple of years, there has been a significant increase in wanting to increase growth hormone production – and for good reason. With promises of improved health, fat loss, muscle growth, and improved bone density, who wouldn’t want to increase their growth hormone levels?
However, as with everything in life, there are choices. Growth Hormone synthesis can be improved through various mechanisms, and GH release isn’t strictly reliant on your own endocrine system anymore. With the invention of the growth hormone-releasing hormone and growth hormone-releasing peptide you no longer need to rely solely on your pituitary gland.
But which is best – CJC 1295 or GHRP 6? Or, should you be creating a GHRP6 CJC 1295 Stack?
Well, in this article, we’ll be telling you all about each compound and why stacking is perhaps the best thing you could be doing.
Key Takeaways
- CJC-1295, or more specifically CJC-1295 without DAC (Drug Affinity Complex), is a synthetic peptide that belongs to the growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) analog class
- GHRP-6, or Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-6, is a synthetic peptide that belongs to the growth hormone secretagogue class
- Both CJC and GHRP are effective, but their ability to increase growth hormone production is significantly higher when used in conjunction with one another
Overview of GHRP6 CJC 1295 Stack
The combination of GHRP-6 and CJC-1295 (without DAC) is a common practice in some circles, and it’s believed that the synergistic effect of these peptides can enhance the stimulation of growth hormone release.
The combination of GHRP-6 and CJC-1295 is thought to have a synergistic effect on increasing growth hormone levels. GHRP-6 stimulates a rapid release, while CJC-1295 provides a sustained release, potentially leading to a more natural pulsatile secretion. Users of this combination suggest that it may lead to more pronounced benefits such as increased muscle mass, improved fat metabolism, and enhanced recovery compared to using each peptide individually.
Role of the Pituitary Gland in Hormone Regulation
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” plays a central role in the intricate system of hormone regulation within the human body. Nestled at the base of the brain, the pituitary gland acts as a crucial interface between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Comprising two distinct lobes—the anterior and posterior—the pituitary gland synthesizes and secretes an array of hormones that orchestrate various physiological processes.
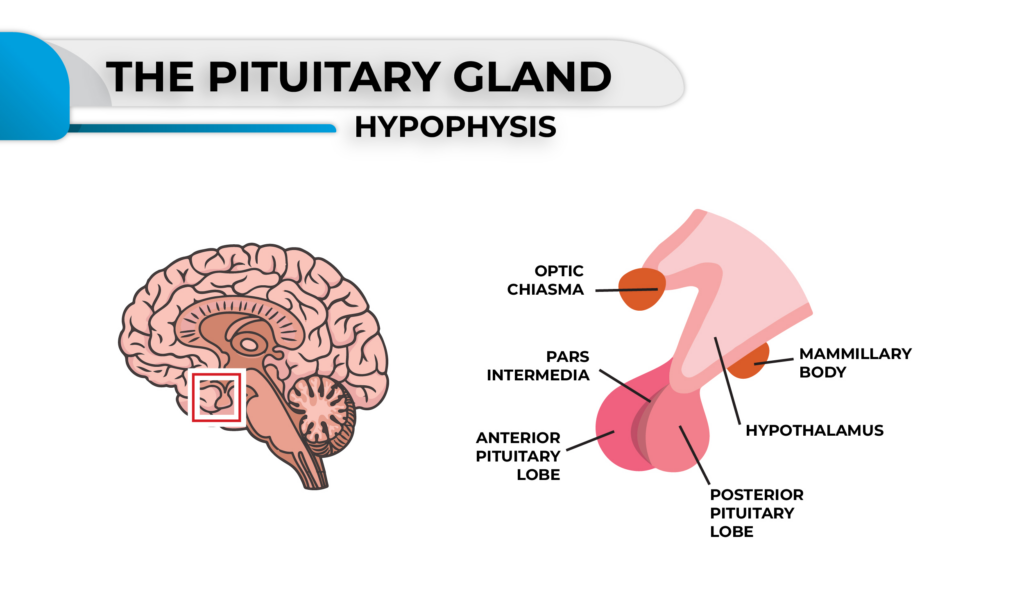
The anterior lobe produces hormones like growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), each exerting control over specific target organs. GH influences growth and metabolism, TSH regulates the thyroid gland, and ACTH governs the adrenal cortex. The posterior lobe releases oxytocin and vasopressin, impacting reproductive functions and water balance, respectively.
The pituitary gland’s regulatory functions are finely tuned through intricate feedback loops, ensuring a delicate balance of hormone secretion to maintain homeostasis. Disturbances in pituitary function can lead to a cascade of hormonal imbalances, affecting growth, metabolism, and overall physiological harmony.
Mechanism of Action of Growth Hormone
Growth hormone, also known as somatotropin, is synthesized and secreted by specialized cells called somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of GH is tightly regulated by the hypothalamus and influenced by various factors.
The hypothalamus releases growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) and somatostatin, which stimulate and inhibit GH secretion, respectively. In response to GHRH, somatotrophs release GH into the bloodstream.
GH exerts its effects on target tissues, and one of its prominent actions is on adipose (fat) tissue. GH stimulates lipolysis, the breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids. This process involves the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) in adipocytes.
GH enhances the availability of free fatty acids, making them accessible for energy production. This increased lipid mobilization is particularly important during periods of fasting or stress, providing the body with an alternative energy source.
GH influences muscle growth indirectly through the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). GH stimulates the liver and other tissues to produce IGF-1 in response to GH signaling. IGF-1 is a crucial mediator of GH’s anabolic effects on skeletal muscle.
It promotes protein synthesis, increases amino acid uptake, and inhibits protein degradation, all contributing to muscle growth (hypertrophy). IGF-1 also enhances the proliferation and differentiation of muscle cells (myocytes), fostering the development of new muscle fibers.
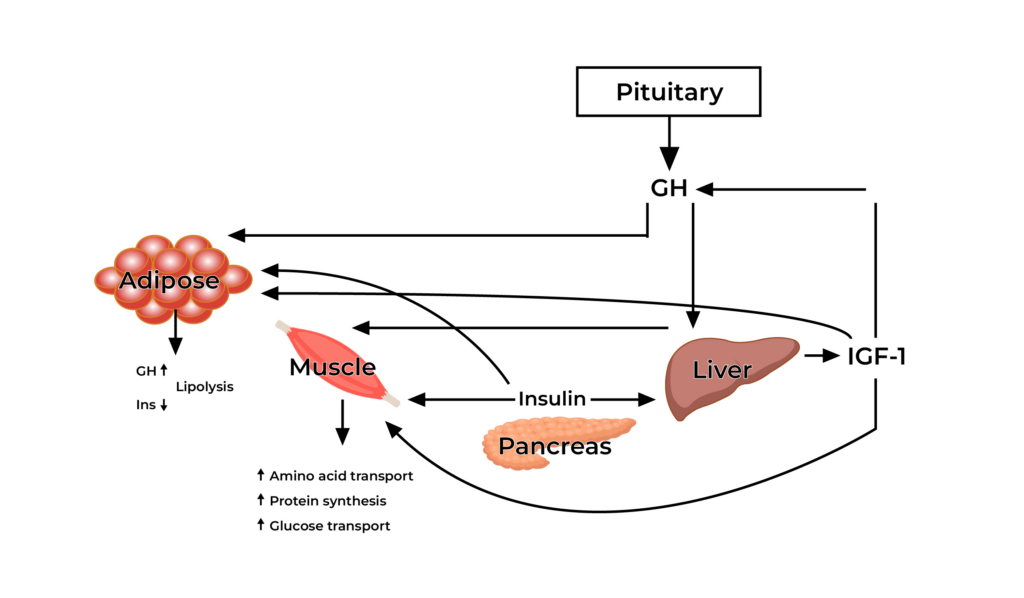
The cascade from GH secretion to lipolysis and subsequent IGF-1-mediated muscle growth highlights the intricate interplay of hormones in regulating metabolic and anabolic processes. This hormonal axis is crucial for maintaining energy balance, promoting tissue repair, and supporting overall growth and development.
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) and Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide (GHRP)
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) and Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide (GHRP) are distinct classes of compounds that influence the secretion of growth hormone, but they operate through different mechanisms. GHRH, a natural hormone produced in the hypothalamus, stimulates the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. It acts as a signaling molecule, triggering the synthesis and release of growth hormone in a pulsatile manner.
In contrast, GHRPs are synthetic peptides designed to mimic the action of ghrelin, a hunger hormone. GHRPs, such as GHRP-6 or GHRP-2, directly bind to the ghrelin receptor, stimulating the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. While GHRH primarily influences the pulsatile release of growth hormone, GHRPs have a more immediate effect, inducing a rapid and robust secretion. Combining GHRH and GHRP is a common strategy to capitalize on their synergistic action, aiming for a more natural and sustained elevation of growth hormone levels.
GHRP6 and CJC 1295 in Isolation
GHRP6: Characteristics and Functions
GHRP-6, or Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide 6, is a synthetic peptide that belongs to the growth hormone secretagogue class. It is designed to stimulate the release of growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland. While GHRP-6 has been primarily explored in research settings, there is limited evidence and ongoing studies suggesting potential therapeutic applications. Some aspects of its potential therapeutic use include:
- Stimulation of Growth Hormone Release: GHRP-6 has been investigated for its ability to stimulate the release of growth hormone. This makes it potentially useful in conditions where growth hormone deficiency or impaired GH secretion is a concern.
- Muscle Wasting Disorders: Research has explored the potential of GHRP-6 in conditions characterized by muscle wasting, such as cachexia in cancer patients. The aim is to counteract muscle loss and promote muscle growth through increased GH release.
- Metabolic Disorders: GHRP-6 may have applications in addressing metabolic disorders. By enhancing GH secretion, it could influence metabolism, including the utilization of fats and sugars, potentially benefiting individuals with metabolic imbalances.
- Wound Healing: Some studies have investigated the role of GHRP-6 in wound healing. The peptide’s potential to accelerate tissue repair and regeneration, including collagen synthesis, has been explored in preclinical and clinical studies.
- Growth Hormone Deficiency: GHRP-6, along with other growth hormone secretagogues, may be considered in the management of individuals with growth hormone deficiency, especially in cases where traditional growth hormone replacement therapy is not suitable or available.
CJC 1295: Characteristics and Functions
CJC-1295 For Sale
CJC 1295 is a synthetic peptide known for its ability to stimulate the secretion of growth hormone (GH) in the body, which it achieves by acting as a mimic of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), a natural hormone produced in the hypothalamus.
CJC 1295 consists of 29 amino acids and is utilized to enhance GH production in a controlled and sustained manner.
By binding to and activating the GHRH receptors in the pituitary gland, CJC 1295 prompts an increase in the release of GH into the bloodstream, playing a crucial role in various physiological processes, including muscle growth, fat metabolism, tissue repair, and overall health and vitality.
CJC 1295’s capacity to elevate GH levels makes it a popular choice among athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking to improve their physical performance and appearance.
It can promote muscle development, reduce body fat, and accelerate recovery from injuries. Additionally, CJC 1295 has been explored for its potential anti-aging effects and its ability to enhance overall well-being.
It can be a valuable tool for individuals looking to optimize their hormonal balance and achieve specific health and fitness goals.
CJC-1295 Overview
 Top Benefits: Skin elasticity, muscle growth, fat loss, and improved recovery
Top Benefits: Skin elasticity, muscle growth, fat loss, and improved recovery Form: Lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder form, reconstituted with bacteriostatic water before injection
Form: Lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder form, reconstituted with bacteriostatic water before injection Max Time Used: 8 to 12 weeks
Max Time Used: 8 to 12 weeks Average Cost: $52
Average Cost: $52 Side Effects: May include injection site reactions, water retention, and potential impact on insulin sensitivity.
Side Effects: May include injection site reactions, water retention, and potential impact on insulin sensitivity. Dangers: Overuse or misuse of CJC 1295 may lead to unwanted side effects.
Dangers: Overuse or misuse of CJC 1295 may lead to unwanted side effects. Best Peptide Stack: Ipamorelin/GHRP-6/TB-500
Best Peptide Stack: Ipamorelin/GHRP-6/TB-500
⚤ Men/Women: Men and women Go to the Full review
Go to the Full review
- Potentially rapid recovery from injuries
- Potential for muscle growth
- Anti-aging Benefits
- Injection site pain
- Possibility of water retention
- Risk of altered blood sugar levels
CJC-1295, specifically CJC-1295 without DAC (Drug Affinity Complex), is a synthetic peptide belonging to the growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) analog class. While primarily studied in research settings, CJC-1295 has shown potential therapeutic applications, though its clinical use is not widespread. Some aspects of its potential therapeutic use include:
- Stimulation of Growth Hormone Release: CJC-1295 is designed to extend the half-life of endogenous growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), leading to a more sustained release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. This extended-release may offer advantages in certain therapeutic scenarios.
- Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: CJC-1295, like other GHRH analogs, may be considered in the management of individuals with growth hormone deficiency. The extended-release profile could provide a more convenient and potentially effective alternative to traditional growth hormone replacement therapy.
- Muscle Wasting Disorders: Similar to GHRP-6, CJC-1295 has been investigated in conditions characterized by muscle wasting. The goal is to promote muscle growth and counteract muscle loss through increased and sustained GH release.
- Metabolic Disorders: CJC-1295 might have applications in addressing metabolic disorders. By influencing growth hormone release, it could impact metabolism, potentially benefiting individuals with metabolic imbalances.
- Anti-Aging and Wellness: While controversial, some individuals explore the use of CJC-1295 and similar peptides for anti-aging purposes and overall well-being. The idea is that increased growth hormone levels may contribute to improved muscle tone, reduced body fat, and enhanced vitality.
The Synergistic Power of the GHRP6 CJC 1295 Stack
The combination of a Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) with a Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide (GHRP) is often employed to maximize the release of growth hormone (GH) and achieve more favorable results. The mechanism involves a synergistic approach to stimulate GH secretion through different pathways.
Combining GHRP6 and CJC 1295: Rationale
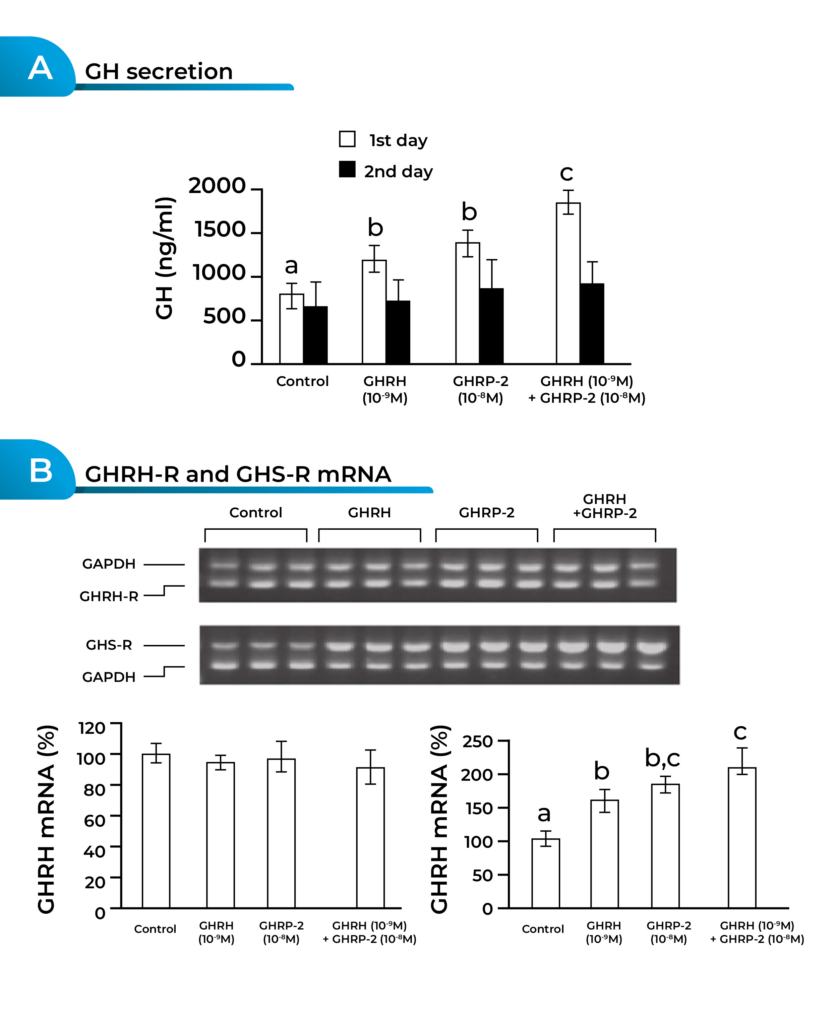
- GHRH Stimulation of GH Release: GHRH, a natural hormone produced in the hypothalamus, signals the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. It acts by binding to specific receptors on the surface of somatotrophs (GH-producing cells) in the anterior pituitary. This interaction triggers the synthesis and pulsatile release of GH into the bloodstream.
- GHRP Stimulation of GH Release: GHRPs, such as GHRP-6 or GHRP-2, work by directly binding to the ghrelin receptor, which is present on the surface of somatotrophs. This binding stimulates the release of GH independently of GHRH. GHRPs induce a rapid and robust secretion of GH, particularly effective during periods when natural GHRH secretion may be lower.
- Synergistic Effect of Combination: When GHRH and GHRP are used together, their actions complement each other. GHRH provides a pulsatile and more sustained release of GH, while GHRP enhances the immediate and robust secretion. This combination is believed to mimic the natural pulsatile pattern of GH secretion more closely than using either peptide alone.
- Extended Elevation of GH Levels: GHRH and GHRP work together to create a more prolonged elevation of GH levels in the bloodstream. GHRH extends the duration of GH release, and GHRP provides an initial spike, resulting in a more natural and sustained profile compared to using either peptide in isolation.
- Optimizing Physiological Responses: The synergistic action of GHRH and GHRP aims to optimize the physiological responses associated with increased GH levels. These responses include enhanced muscle growth, improved fat metabolism, and potentially other benefits related to tissue repair and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the GHRP-6 CJC-1295 stack offers a strategic and synergistic approach to enhancing growth hormone (GH) stimulation. With an increasing interest in elevating GH levels for health and aesthetic reasons, this combination capitalizes on the unique mechanisms of both GHRH and GHRP peptides. GHRH, represented by CJC-1295, provides a sustained and pulsatile release of GH, while GHRP-6 induces a rapid and robust secretion.
The combination aims to achieve a more natural and extended elevation of GH levels, optimizing physiological responses such as increased muscle mass, improved fat metabolism, and enhanced recovery. As choices abound in the realm of growth hormone synthesis, the GHRP-6 CJC-1295 stack emerges as a promising strategy, offering a nuanced and comprehensive approach to maximizing the benefits associated with heightened GH levels. As the pursuit of improved health, body composition, and overall well-being continues, the GHRP-6 CJC-1295 stack stands out as a noteworthy option in the landscape of growth hormone modulation.
What is the best combination with CJC-1295?
The most commonly used peptide stack with CJC 1295 will have to be Ipamorelin. This will increase human growth hormone the same as CJC 1295 GHRP 6 would, but with even more success. This would lead to even more muscle growth, fat loss, and improved health.
What is the best stack with GHRP-6?
The best stack would be GHRP 6 along with CJC 1295 and Ipamorelin. This might be expensive, but is certainly worth the cost.
Can you take CJC-1295 and HGH together?
It’s not advised. CJC 1295 would pale in comparison, and HGH production would be tanked due to the exogenous growth hormone usage. This would not yield better results.
What is the best time to take GHRP-6?
Any time of the day that hunger is important.