Muscle Insider
New member
While the squat remains the number one exercise for building powerful quads, the leg press is right up there. The leg press is a terrific alternative exercise if you can’t do squats due to your structure, mechanics, or inherent weaknesses. And, if you can squat, following it with a few sets of heavy leg presses will help you build power and mass in your quads.
In this article, we will uncover several leg press variations that will allow you to better target your quads for power. Most of these changes involve your foot positioning. As you’re about to discover, where you put your feet on the platform can make all the difference when it comes to targeting different muscle groups.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press is a compound exercise because it operates through two joints — the knee and hips. You are performing hip flexion when you lower the weight to bring your knees back. Then, when you push back to the start position, you perform knee extension.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
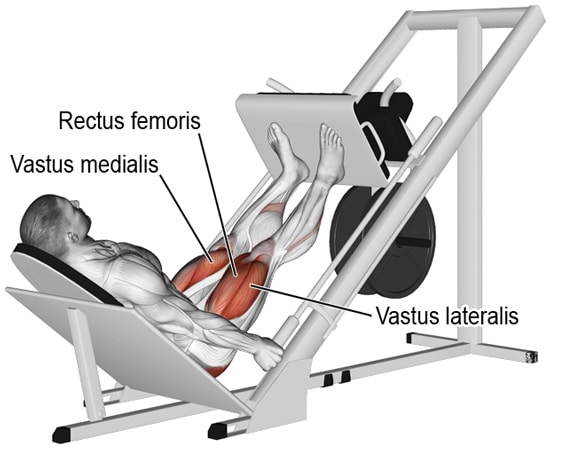
The leg press mainly works the quadriceps, which is a four-headed muscle group. These four muscles are:
Rectus femoris: This is the only quad muscle that crosses the hip joint. It originates at the base of the spine, running down the front of the quads to attach to the kneecap. This muscle plays a part in knee extension and hip flexion. A wider leg press stance will put more focus on the rectus femoris.
Vastus lateralis: It originates at the top of the upper leg bone (femur) and runs down the outside of the quads to attach to the kneecap. A wide stance will better activate this muscle.
Vastus intermedius: This muscle runs down the middle of the quads, from the top of the femur to the kneecap.
Vastus medialis: This muscle lies on the inner side of the quads, again running from the femur to the kneecap. Adopting a narrow leg press stance will maximally engage the vastus medialis.
The other muscles engaged when you do the leg press are the glutes, calves, and hamstrings.
Leg Press Benefits
Before we delve into the variations that will allow you to ramp up the intensity on the leg press, let’s consider three reasons why adding this exercise to your leg day workout in the first place makes sense.
Stable Environment
A major benefit of the leg press is that it allows you to work your legs in a stable environment. When you do exercises such as squats and lunges that don’t lock you into a fixed movement pattern, many things can go wrong, especially when working with heavy weights.
Built-in Safety
Because your back is supported when doing the leg press, you can concentrate 100% of your focus and energy on pressing the weight. The machine also has a built-in safety mechanism; with a simple twist of the handles, you can activate the locks that secure the weights in place. That means you can go extra heavy on this exercise without needing a spotter.
Greater Quad Focus
Your range of motion for the leg press is typically shorter than if you were doing squats. If you’re trying to develop quad mass and power, that’s actually a good thing. That’s because it keeps the focus on your quads rather than transferring it to your glutes and hamstrings.
Which Type of Leg Press Should You Use?
There are two types of leg press machines commonly found in gyms:
Horizontal
45-degree
With a horizontal leg press, you push your legs directly out in front of you. On the other hand, the 45-degree version has you pressing your legs at an angle.
So, which is best?
There is no definitive answer to this question. At this stage, no studies have directly compared the effectiveness of the two versions of the exercise in terms of building quad power. However, we can be informed by simple physics on this subject.
When doing the 45-degree leg press, the weight you load on the machine is spread out over the diagonal plane of the leg press machine. This creates a wide moment arm, which is the distance between the line of action and the pivot point, which in this case is the hip joint. The wider the moment arm, the lower the force needed to lift the weight.
But when you do the horizontal leg press, the weight is spread out directly in front of your hips, creating a shorter moment arm. A shorter moment arm means you’ll need more force to lift the weight.
That’s why you’ll find it harder to light the same weight on the horizontal leg press than on the 45-degree leg press.
As a general guide, you should be able to lift about 30% more weight on the 45-degree leg press. But simply being able to lift more weight will not make your quads stronger if the physics of the machine have made it easier.
The fact that it’s easier to lift a weight on the 45-degree leg press doesn’t mean that you should only use the horizontal machine. But if you’ve got access to both machines, you should compensate when using the 45-degree machine by adding extra weight to make up for the longer moment arm. If you don’t, you won’t be pushing your weight limit, and you’re likely to plateau your quad power.
Leg Press Form Tips
Whether using a horizontal or a 45-degree leg press machine, ensure that your lower back and glutes are pressed hard against the pads.
Do not use a weight that is too heavy. This will restrict your range of movement. Don’t be that guy who loads up seven or eight 45s on each side and then moves just a few inches.
Slow down. When you go too fast, your knees tend to cave in, and you may even bounce the weight using momentum at the bottom.
Don’t lock your knees at the top of the rep. Stopping just short of lock-out keeps the tension on your quads.
Consciously think about keeping the weight evenly distributed between both legs.
Should Your Knees Go Over Your Toes?
The knees-over-toes debate is usually associated with the squat, But the same applies to the leg press. For decades, lifters were told not to allow their knees to track over the toes because it would damage the knee joint. Recent research, however, has thrown that argument out the window.
One study showed that allowing your knees to track over your toes during the squat led to significantly improved activation of the vastus medialis head of the quadriceps. This part of the quads is often known as the ‘teardrop’ because of its appearance on a developed bodybuilder with low body fat levels. Furthermore, there was no adverse effect on the knee joint reported. [1]
It should be noted that this study specifically looked at the muscle stimulation of the quads during the squat. It is reasonable to speculate that the same thing applies to the leg press but, to date, there are no studies specifically testing the leg press in this regard.
The leg press foot platform is generally a large area. That gives you the freedom to vary your foot placement from very wide to very narrow. Where you choose to palace your feet on the platform will work your muscles differently. Here’s an overview of the different foot placements and what areas each one targets:
1. High & Wide
When you place your feet high and wide on the platform, you will target your hamstrings. You want to place your legs as high and wide on the platform as possible without your hips coming off the seat pad. Your toes should actually be off the edge of the platform’s top and angled outward. To accentuate the hamstrings, push your heels into the platform on the descent.
In the high and wide position, your feet should be about one and a half times your hip width.
2. Low & Close
Putting your feet low and close together on the platform will emphasize your quads. Your heels should be almost, but not quite, hanging off the bottom of the platform, with your feet about six inches apart.
When pressing, think of pushing your quads out and over your knees. Think also about keeping the weight distributed over the balls of your feet. This position is going to really blow up your quads, but only if you go deep on the descent. So don’t let your ego get in the way of a full range of motion.
As we’ve seen, the more your knees can track over your toes, the greater the quad activation, especially on the vastus medialis head. One way to increase this effect is to wear elevated-heel weightlifting shoes when doing the narrow stance leg press. This is especially beneficial if you have poor ankle flexibility and find your heel coming off the platform in the bottom position of the leg press.
3. Neutral
A neutral stance is where your feet will naturally go on the platform if you’re not thinking about it. Find your most comfortable position with your feet hip distance apart. This position will provide an even distribution across the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
A neutral foot placement will help you lift the most weight. Focus on a slow descent, bringing your knees down to the outside of your shoulders, and then push the heels through the platform on the ascent. Drive your lower back into the seat pad the whole time.
4. Heels Elevated
An adaptation of the neutral position may place extra emphasis on the quads. This involves wearing weightlifting shoes with elevated heels. The increased angle this creates puts more load on the vastus medialis quad muscle that runs into the knee joint.
5. Toes Elevated
To assume a toes elevated position, you need to place a pair of small weight plates or a squat wedge under your toes on the foot platform. Your feet should otherwise be in a neutral stance. This will shift the emphasis to your hamstrings.
Single Leg Press
The single-leg press allows you to work each quad independently. It helps correct quad strength imbalance, where one leg is stronger than the other.
When you do the two-legged leg press, your dominant side will take a disproportionate percentage of the weight. Doing the single-leg press forces each leg to carry its own weight, which will eventually help balance the strength between your quads.
Place your foot low and inside hip width to target the quads with the single-leg press. Place the other foot firmly on the ground. Unrack the weight and slowly bring the platform back toward you. Concentrate on the knee traveling back and out as you descend. This will lengthen your range of motion so that you don’t hit your knee into your ribcage.
Come back until your leg forms a right angle at the knee, and then push your heel into the platform to return to the start position. Don’t lock out at the top but move smoothly into the next rep.
Do not allow your heel to lift off during the descent. If you do, you’ll transfer the force from your quad to your knee. You must also not allow your hips to roll up off the pad in the bottom position.
A Leg Press Workout For Power Quads
Now that we’ve identified the best ways to do the leg press to target the quads, we can put them together to create a mini quad workout on the leg press machine. We’ll be doing the following three leg press variations:
Neutral-stance leg press
Low and close stance leg press
Single-leg press
The first two exercises will be done as a mechanical drop set. This is when you do a drop set without changing the weight by shifting your foot position. We’ll start with the low and close stance version, as this is the one that most directly targets the quads. After pumping out eight reps, you quickly rack the weight and shift to a neutral stance. Then immediately unrack and do another eight reps.
Because you’re strongest in the neutral stance, following a set of narrow stance reps with eight more neutral stance reps will tap deep into your quad’s strength reserves, allowing you to eke out every ounce of benefit from the set. The key to getting the most out of a mechanical drop set like this is minimizing the downtime between the two phases — it should only take a few seconds.
Once you’ve completed your 16 reps on the mechanical drop set, get out of the machine, shake your legs out, and then take half the weight off the machine. Now get straight back on and start pumping out single-leg presses. This transition should take you less than 30 seconds.
Your goal is to get 16 reps on each leg on the single-leg press. At that point, your quads will be on fire. Rest for two minutes, and then do the whole thing over again. Work up to doing three total sets. Here’s what it will look like:
Set One:
Narrow-stance leg press: 8 reps
Neutral stance leg press: 8 reps
Single-leg press (right leg): 16 reps
Single-leg press (left leg): 16 reps
Rest for two minutes and then repeat for another two sets.
Wrap Up
The leg press is an effective quad power and mass builder. You can target different areas of your upper legs depending on where you place your feet on the platform. The best way to target your quads is with a low, narrow stance. You can target the quads even more by elevating your heels using weightlifting shoes.
The next best foot stance to hit the quads is the neutral stance. This is also the version you can lift the most weight with. Our final quad-centric leg press move for power is the single-leg press with a low stance.
Combine these three exercises into a killer mechanical drop set followed by a unilateral quad isolation workout. You can either do this as the first part of your quad workout and follow it up with leg extensions and lunges or, if you’re game, do four sets of squats first and then jump into your leg press workout.
Just don’t expect to be able to walk the next day!
References
Escamilla, R. F., Fleisig, G. S., Zheng, N., Lander, J. E., Barrentine, S. W., Andrews, J. R., & Bergemann, B. W. (2001). Effects of technique variations on knee biomechanics during the squat and leg press. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 33(9), 1552-1566.
While the squat remains the number one exercise for building powerful quads, the leg press is right up there. The leg press is a terrific alternative exercise if you can’t do squats due to your structure, mechanics, or inherent weaknesses. And, if you can squat, following it with a few sets of heavy leg presses will help you build power and mass in your quads.
In this article, we will uncover several leg press variations that will allow you to better target your quads for power. Most of these changes involve your foot positioning. As you’re about to discover, where you put your feet on the platform can make all the difference when it comes to targeting different muscle groups.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press is a compound exercise because it operates through two joints — the knee and hips. You are performing hip flexion when you lower the weight to bring your knees back. Then, when you push back to the start position, you perform knee extension.
 Leg Press Muscles Worked
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press mainly works the quadriceps, which is a four-headed muscle group. These four muscles are:
Leg Press Benefits
Before we delve into the variations that will allow you to ramp up the intensity on the leg press, let’s consider three reasons why adding this exercise to your leg day workout in the first place makes sense.
Stable Environment
A major benefit of the leg press is that it allows you to work your legs in a stable environment. When you do exercises such as squats and lunges that don’t lock you into a fixed movement pattern, many things can go wrong, especially when working with heavy weights.
Built-in Safety
Because your back is supported when doing the leg press, you can concentrate 100% of your focus and energy on pressing the weight. The machine also has a built-in safety mechanism; with a simple twist of the handles, you can activate the locks that secure the weights in place. That means you can go extra heavy on this exercise without needing a spotter.
Greater Quad Focus
Your range of motion for the leg press is typically shorter than if you were doing squats. If you’re trying to develop quad mass and power, that’s actually a good thing. That’s because it keeps the focus on your quads rather than transferring it to your glutes and hamstrings.
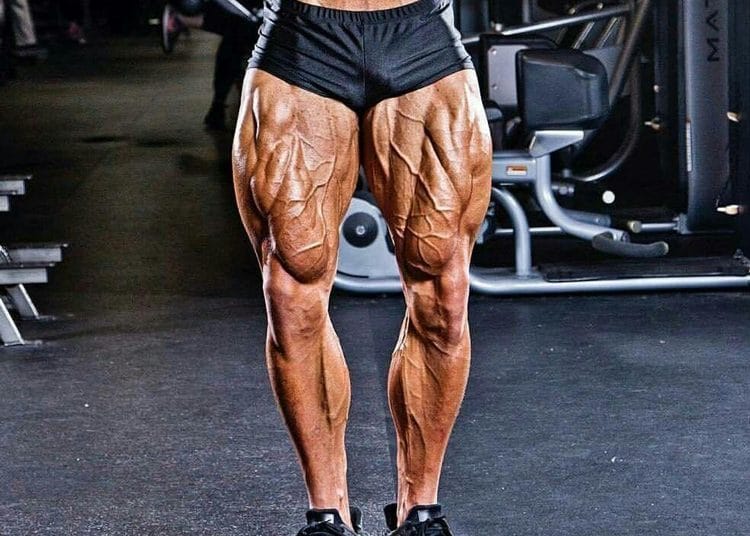


Which Type of Leg Press Should You Use?
There are two types of leg press machines commonly found in gyms:
So, which is best?
There is no definitive answer to this question. At this stage, no studies have directly compared the effectiveness of the two versions of the exercise in terms of building quad power. However, we can be informed by simple physics on this subject.
When doing the 45-degree leg press, the weight you load on the machine is spread out over the diagonal plane of the leg press machine. This creates a wide moment arm, which is the distance between the line of action and the pivot point, which in this case is the hip joint. The wider the moment arm, the lower the force needed to lift the weight.
But when you do the horizontal leg press, the weight is spread out directly in front of your hips, creating a shorter moment arm. A shorter moment arm means you’ll need more force to lift the weight.
That’s why you’ll find it harder to light the same weight on the horizontal leg press than on the 45-degree leg press.
As a general guide, you should be able to lift about 30% more weight on the 45-degree leg press. But simply being able to lift more weight will not make your quads stronger if the physics of the machine have made it easier.
The fact that it’s easier to lift a weight on the 45-degree leg press doesn’t mean that you should only use the horizontal machine. But if you’ve got access to both machines, you should compensate when using the 45-degree machine by adding extra weight to make up for the longer moment arm. If you don’t, you won’t be pushing your weight limit, and you’re likely to plateau your quad power.
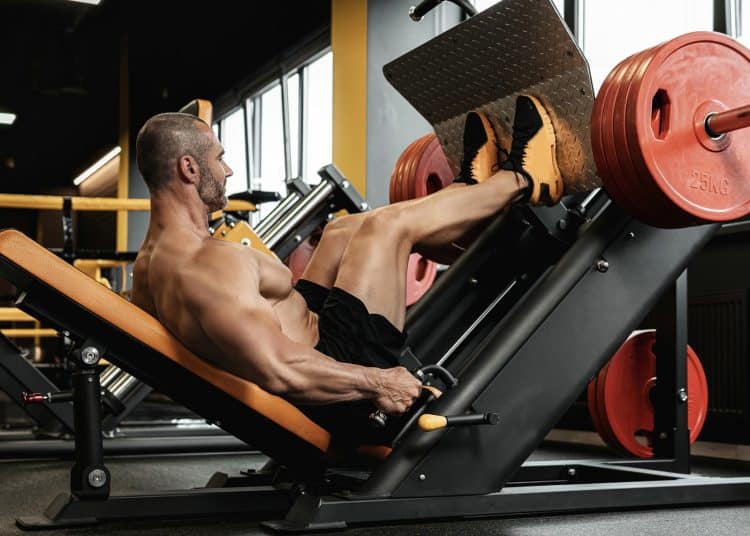


Leg Press Form Tips
[*]Whether using a horizontal or a 45-degree leg press machine, ensure that your lower back and glutes are pressed hard against the pads.
[*]Do not use a weight that is too heavy. This will restrict your range of movement. Don’t be that guy who loads up seven or eight 45s on each side and then moves just a few inches.
[*]Slow down. When you go too fast, your knees tend to cave in, and you may even bounce the weight using momentum at the bottom.
[*]Don’t lock your knees at the top of the rep. Stopping just short of lock-out keeps the tension on your quads.
[*]Consciously think about keeping the weight evenly distributed between both legs.
Should Your Knees Go Over Your Toes?
The knees-over-toes debate is usually associated with the squat, But the same applies to the leg press. For decades, lifters were told not to allow their knees to track over the toes because it would damage the knee joint. Recent research, however, has thrown that argument out the window.
One study showed that allowing your knees to track over your toes during the squat led to significantly improved activation of the vastus medialis head of the quadriceps. This part of the quads is often known as the ‘teardrop’ because of its appearance on a developed bodybuilder with low body fat levels. Furthermore, there was no adverse effect on the knee joint reported. [1]
It should be noted that this study specifically looked at the muscle stimulation of the quads during the squat. It is reasonable to speculate that the same thing applies to the leg press but, to date, there are no studies specifically testing the leg press in this regard.
The leg press foot platform is generally a large area. That gives you the freedom to vary your foot placement from very wide to very narrow. Where you choose to palace your feet on the platform will work your muscles differently. Here’s an overview of the different foot placements and what areas each one targets:
1. High & Wide
When you place your feet high and wide on the platform, you will target your hamstrings. You want to place your legs as high and wide on the platform as possible without your hips coming off the seat pad. Your toes should actually be off the edge of the platform’s top and angled outward. To accentuate the hamstrings, push your heels into the platform on the descent.
In the high and wide position, your feet should be about one and a half times your hip width.
2. Low & Close
Putting your feet low and close together on the platform will emphasize your quads. Your heels should be almost, but not quite, hanging off the bottom of the platform, with your feet about six inches apart.
When pressing, think of pushing your quads out and over your knees. Think also about keeping the weight distributed over the balls of your feet. This position is going to really blow up your quads, but only if you go deep on the descent. So don’t let your ego get in the way of a full range of motion.
As we’ve seen, the more your knees can track over your toes, the greater the quad activation, especially on the vastus medialis head. One way to increase this effect is to wear elevated-heel weightlifting shoes when doing the narrow stance leg press. This is especially beneficial if you have poor ankle flexibility and find your heel coming off the platform in the bottom position of the leg press.
3. Neutral
A neutral stance is where your feet will naturally go on the platform if you’re not thinking about it. Find your most comfortable position with your feet hip distance apart. This position will provide an even distribution across the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
A neutral foot placement will help you lift the most weight. Focus on a slow descent, bringing your knees down to the outside of your shoulders, and then push the heels through the platform on the ascent. Drive your lower back into the seat pad the whole time.
4. Heels Elevated
An adaptation of the neutral position may place extra emphasis on the quads. This involves wearing weightlifting shoes with elevated heels. The increased angle this creates puts more load on the vastus medialis quad muscle that runs into the knee joint.
5. Toes Elevated
To assume a toes elevated position, you need to place a pair of small weight plates or a squat wedge under your toes on the foot platform. Your feet should otherwise be in a neutral stance. This will shift the emphasis to your hamstrings.
Single Leg Press
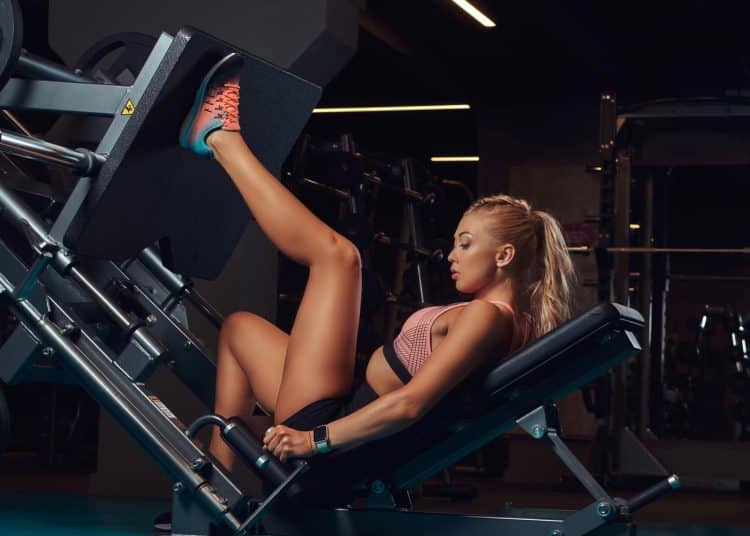


The single-leg press allows you to work each quad independently. It helps correct quad strength imbalance, where one leg is stronger than the other.
When you do the two-legged leg press, your dominant side will take a disproportionate percentage of the weight. Doing the single-leg press forces each leg to carry its own weight, which will eventually help balance the strength between your quads.
Place your foot low and inside hip width to target the quads with the single-leg press. Place the other foot firmly on the ground. Unrack the weight and slowly bring the platform back toward you. Concentrate on the knee traveling back and out as you descend. This will lengthen your range of motion so that you don’t hit your knee into your ribcage.
Come back until your leg forms a right angle at the knee, and then push your heel into the platform to return to the start position. Don’t lock out at the top but move smoothly into the next rep.
Do not allow your heel to lift off during the descent. If you do, you’ll transfer the force from your quad to your knee. You must also not allow your hips to roll up off the pad in the bottom position.
A Leg Press Workout For Power Quads
Now that we’ve identified the best ways to do the leg press to target the quads, we can put them together to create a mini quad workout on the leg press machine. We’ll be doing the following three leg press variations:
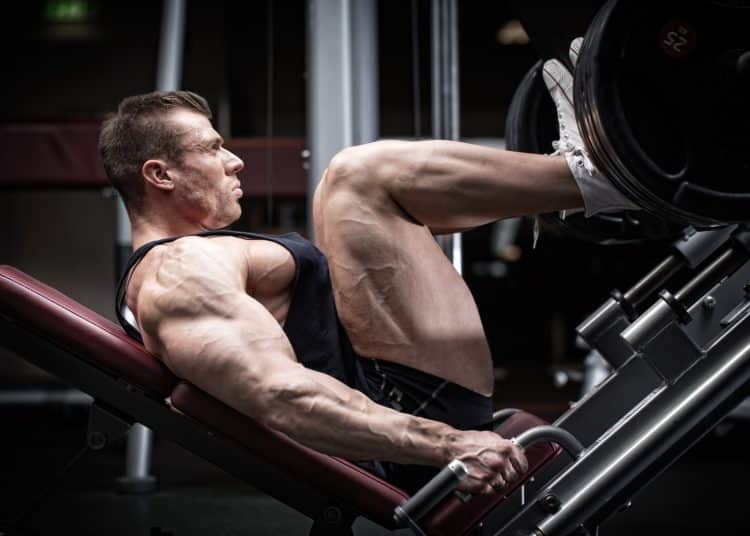


The first two exercises will be done as a mechanical drop set. This is when you do a drop set without changing the weight by shifting your foot position. We’ll start with the low and close stance version, as this is the one that most directly targets the quads. After pumping out eight reps, you quickly rack the weight and shift to a neutral stance. Then immediately unrack and do another eight reps.
Because you’re strongest in the neutral stance, following a set of narrow stance reps with eight more neutral stance reps will tap deep into your quad’s strength reserves, allowing you to eke out every ounce of benefit from the set. The key to getting the most out of a mechanical drop set like this is minimizing the downtime between the two phases — it should only take a few seconds.
Once you’ve completed your 16 reps on the mechanical drop set, get out of the machine, shake your legs out, and then take half the weight off the machine. Now get straight back on and start pumping out single-leg presses. This transition should take you less than 30 seconds.
Your goal is to get 16 reps on each leg on the single-leg press. At that point, your quads will be on fire. Rest for two minutes, and then do the whole thing over again. Work up to doing three total sets. Here’s what it will look like:
Set One:
Wrap Up
The leg press is an effective quad power and mass builder. You can target different areas of your upper legs depending on where you place your feet on the platform. The best way to target your quads is with a low, narrow stance. You can target the quads even more by elevating your heels using weightlifting shoes.
The next best foot stance to hit the quads is the neutral stance. This is also the version you can lift the most weight with. Our final quad-centric leg press move for power is the single-leg press with a low stance.
Combine these three exercises into a killer mechanical drop set followed by a unilateral quad isolation workout. You can either do this as the first part of your quad workout and follow it up with leg extensions and lunges or, if you’re game, do four sets of squats first and then jump into your leg press workout.
Just don’t expect to be able to walk the next day!
References
[*]Escamilla, R. F., Fleisig, G. S., Zheng, N., Lander, J. E., Barrentine, S. W., Andrews, J. R., & Bergemann, B. W. (2001). Effects of technique variations on knee biomechanics during the squat and leg press. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 33(9), 1552-1566.
Click here to view the article.
In this article, we will uncover several leg press variations that will allow you to better target your quads for power. Most of these changes involve your foot positioning. As you’re about to discover, where you put your feet on the platform can make all the difference when it comes to targeting different muscle groups.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press is a compound exercise because it operates through two joints — the knee and hips. You are performing hip flexion when you lower the weight to bring your knees back. Then, when you push back to the start position, you perform knee extension.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press mainly works the quadriceps, which is a four-headed muscle group. These four muscles are:
Rectus femoris: This is the only quad muscle that crosses the hip joint. It originates at the base of the spine, running down the front of the quads to attach to the kneecap. This muscle plays a part in knee extension and hip flexion. A wider leg press stance will put more focus on the rectus femoris.
Vastus lateralis: It originates at the top of the upper leg bone (femur) and runs down the outside of the quads to attach to the kneecap. A wide stance will better activate this muscle.
Vastus intermedius: This muscle runs down the middle of the quads, from the top of the femur to the kneecap.
Vastus medialis: This muscle lies on the inner side of the quads, again running from the femur to the kneecap. Adopting a narrow leg press stance will maximally engage the vastus medialis.
The other muscles engaged when you do the leg press are the glutes, calves, and hamstrings.
Leg Press Benefits
Before we delve into the variations that will allow you to ramp up the intensity on the leg press, let’s consider three reasons why adding this exercise to your leg day workout in the first place makes sense.
Stable Environment
A major benefit of the leg press is that it allows you to work your legs in a stable environment. When you do exercises such as squats and lunges that don’t lock you into a fixed movement pattern, many things can go wrong, especially when working with heavy weights.
Built-in Safety
Because your back is supported when doing the leg press, you can concentrate 100% of your focus and energy on pressing the weight. The machine also has a built-in safety mechanism; with a simple twist of the handles, you can activate the locks that secure the weights in place. That means you can go extra heavy on this exercise without needing a spotter.
Greater Quad Focus
Your range of motion for the leg press is typically shorter than if you were doing squats. If you’re trying to develop quad mass and power, that’s actually a good thing. That’s because it keeps the focus on your quads rather than transferring it to your glutes and hamstrings.
Which Type of Leg Press Should You Use?
There are two types of leg press machines commonly found in gyms:
Horizontal
45-degree
With a horizontal leg press, you push your legs directly out in front of you. On the other hand, the 45-degree version has you pressing your legs at an angle.
So, which is best?
There is no definitive answer to this question. At this stage, no studies have directly compared the effectiveness of the two versions of the exercise in terms of building quad power. However, we can be informed by simple physics on this subject.
When doing the 45-degree leg press, the weight you load on the machine is spread out over the diagonal plane of the leg press machine. This creates a wide moment arm, which is the distance between the line of action and the pivot point, which in this case is the hip joint. The wider the moment arm, the lower the force needed to lift the weight.
But when you do the horizontal leg press, the weight is spread out directly in front of your hips, creating a shorter moment arm. A shorter moment arm means you’ll need more force to lift the weight.
That’s why you’ll find it harder to light the same weight on the horizontal leg press than on the 45-degree leg press.
As a general guide, you should be able to lift about 30% more weight on the 45-degree leg press. But simply being able to lift more weight will not make your quads stronger if the physics of the machine have made it easier.
The fact that it’s easier to lift a weight on the 45-degree leg press doesn’t mean that you should only use the horizontal machine. But if you’ve got access to both machines, you should compensate when using the 45-degree machine by adding extra weight to make up for the longer moment arm. If you don’t, you won’t be pushing your weight limit, and you’re likely to plateau your quad power.
Leg Press Form Tips
Whether using a horizontal or a 45-degree leg press machine, ensure that your lower back and glutes are pressed hard against the pads.
Do not use a weight that is too heavy. This will restrict your range of movement. Don’t be that guy who loads up seven or eight 45s on each side and then moves just a few inches.
Slow down. When you go too fast, your knees tend to cave in, and you may even bounce the weight using momentum at the bottom.
Don’t lock your knees at the top of the rep. Stopping just short of lock-out keeps the tension on your quads.
Consciously think about keeping the weight evenly distributed between both legs.
Should Your Knees Go Over Your Toes?
The knees-over-toes debate is usually associated with the squat, But the same applies to the leg press. For decades, lifters were told not to allow their knees to track over the toes because it would damage the knee joint. Recent research, however, has thrown that argument out the window.
One study showed that allowing your knees to track over your toes during the squat led to significantly improved activation of the vastus medialis head of the quadriceps. This part of the quads is often known as the ‘teardrop’ because of its appearance on a developed bodybuilder with low body fat levels. Furthermore, there was no adverse effect on the knee joint reported. [1]
It should be noted that this study specifically looked at the muscle stimulation of the quads during the squat. It is reasonable to speculate that the same thing applies to the leg press but, to date, there are no studies specifically testing the leg press in this regard.
The leg press foot platform is generally a large area. That gives you the freedom to vary your foot placement from very wide to very narrow. Where you choose to palace your feet on the platform will work your muscles differently. Here’s an overview of the different foot placements and what areas each one targets:
1. High & Wide
When you place your feet high and wide on the platform, you will target your hamstrings. You want to place your legs as high and wide on the platform as possible without your hips coming off the seat pad. Your toes should actually be off the edge of the platform’s top and angled outward. To accentuate the hamstrings, push your heels into the platform on the descent.
In the high and wide position, your feet should be about one and a half times your hip width.
2. Low & Close
Putting your feet low and close together on the platform will emphasize your quads. Your heels should be almost, but not quite, hanging off the bottom of the platform, with your feet about six inches apart.
When pressing, think of pushing your quads out and over your knees. Think also about keeping the weight distributed over the balls of your feet. This position is going to really blow up your quads, but only if you go deep on the descent. So don’t let your ego get in the way of a full range of motion.
As we’ve seen, the more your knees can track over your toes, the greater the quad activation, especially on the vastus medialis head. One way to increase this effect is to wear elevated-heel weightlifting shoes when doing the narrow stance leg press. This is especially beneficial if you have poor ankle flexibility and find your heel coming off the platform in the bottom position of the leg press.
3. Neutral
A neutral stance is where your feet will naturally go on the platform if you’re not thinking about it. Find your most comfortable position with your feet hip distance apart. This position will provide an even distribution across the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
A neutral foot placement will help you lift the most weight. Focus on a slow descent, bringing your knees down to the outside of your shoulders, and then push the heels through the platform on the ascent. Drive your lower back into the seat pad the whole time.
4. Heels Elevated
An adaptation of the neutral position may place extra emphasis on the quads. This involves wearing weightlifting shoes with elevated heels. The increased angle this creates puts more load on the vastus medialis quad muscle that runs into the knee joint.
5. Toes Elevated
To assume a toes elevated position, you need to place a pair of small weight plates or a squat wedge under your toes on the foot platform. Your feet should otherwise be in a neutral stance. This will shift the emphasis to your hamstrings.
Single Leg Press
The single-leg press allows you to work each quad independently. It helps correct quad strength imbalance, where one leg is stronger than the other.
When you do the two-legged leg press, your dominant side will take a disproportionate percentage of the weight. Doing the single-leg press forces each leg to carry its own weight, which will eventually help balance the strength between your quads.
Place your foot low and inside hip width to target the quads with the single-leg press. Place the other foot firmly on the ground. Unrack the weight and slowly bring the platform back toward you. Concentrate on the knee traveling back and out as you descend. This will lengthen your range of motion so that you don’t hit your knee into your ribcage.
Come back until your leg forms a right angle at the knee, and then push your heel into the platform to return to the start position. Don’t lock out at the top but move smoothly into the next rep.
Do not allow your heel to lift off during the descent. If you do, you’ll transfer the force from your quad to your knee. You must also not allow your hips to roll up off the pad in the bottom position.
A Leg Press Workout For Power Quads
Now that we’ve identified the best ways to do the leg press to target the quads, we can put them together to create a mini quad workout on the leg press machine. We’ll be doing the following three leg press variations:
Neutral-stance leg press
Low and close stance leg press
Single-leg press
The first two exercises will be done as a mechanical drop set. This is when you do a drop set without changing the weight by shifting your foot position. We’ll start with the low and close stance version, as this is the one that most directly targets the quads. After pumping out eight reps, you quickly rack the weight and shift to a neutral stance. Then immediately unrack and do another eight reps.
Because you’re strongest in the neutral stance, following a set of narrow stance reps with eight more neutral stance reps will tap deep into your quad’s strength reserves, allowing you to eke out every ounce of benefit from the set. The key to getting the most out of a mechanical drop set like this is minimizing the downtime between the two phases — it should only take a few seconds.
Once you’ve completed your 16 reps on the mechanical drop set, get out of the machine, shake your legs out, and then take half the weight off the machine. Now get straight back on and start pumping out single-leg presses. This transition should take you less than 30 seconds.
Your goal is to get 16 reps on each leg on the single-leg press. At that point, your quads will be on fire. Rest for two minutes, and then do the whole thing over again. Work up to doing three total sets. Here’s what it will look like:
Set One:
Narrow-stance leg press: 8 reps
Neutral stance leg press: 8 reps
Single-leg press (right leg): 16 reps
Single-leg press (left leg): 16 reps
Rest for two minutes and then repeat for another two sets.
Wrap Up
The leg press is an effective quad power and mass builder. You can target different areas of your upper legs depending on where you place your feet on the platform. The best way to target your quads is with a low, narrow stance. You can target the quads even more by elevating your heels using weightlifting shoes.
The next best foot stance to hit the quads is the neutral stance. This is also the version you can lift the most weight with. Our final quad-centric leg press move for power is the single-leg press with a low stance.
Combine these three exercises into a killer mechanical drop set followed by a unilateral quad isolation workout. You can either do this as the first part of your quad workout and follow it up with leg extensions and lunges or, if you’re game, do four sets of squats first and then jump into your leg press workout.
Just don’t expect to be able to walk the next day!
References
Escamilla, R. F., Fleisig, G. S., Zheng, N., Lander, J. E., Barrentine, S. W., Andrews, J. R., & Bergemann, B. W. (2001). Effects of technique variations on knee biomechanics during the squat and leg press. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 33(9), 1552-1566.
While the squat remains the number one exercise for building powerful quads, the leg press is right up there. The leg press is a terrific alternative exercise if you can’t do squats due to your structure, mechanics, or inherent weaknesses. And, if you can squat, following it with a few sets of heavy leg presses will help you build power and mass in your quads.
In this article, we will uncover several leg press variations that will allow you to better target your quads for power. Most of these changes involve your foot positioning. As you’re about to discover, where you put your feet on the platform can make all the difference when it comes to targeting different muscle groups.
Leg Press Muscles Worked
The leg press is a compound exercise because it operates through two joints — the knee and hips. You are performing hip flexion when you lower the weight to bring your knees back. Then, when you push back to the start position, you perform knee extension.

The leg press mainly works the quadriceps, which is a four-headed muscle group. These four muscles are:
- Rectus femoris: This is the only quad muscle that crosses the hip joint. It originates at the base of the spine, running down the front of the quads to attach to the kneecap. This muscle plays a part in knee extension and hip flexion. A wider leg press stance will put more focus on the rectus femoris.
- Vastus lateralis: It originates at the top of the upper leg bone (femur) and runs down the outside of the quads to attach to the kneecap. A wide stance will better activate this muscle.
- Vastus intermedius: This muscle runs down the middle of the quads, from the top of the femur to the kneecap.
- Vastus medialis: This muscle lies on the inner side of the quads, again running from the femur to the kneecap. Adopting a narrow leg press stance will maximally engage the vastus medialis.
Leg Press Benefits
Before we delve into the variations that will allow you to ramp up the intensity on the leg press, let’s consider three reasons why adding this exercise to your leg day workout in the first place makes sense.
Stable Environment
A major benefit of the leg press is that it allows you to work your legs in a stable environment. When you do exercises such as squats and lunges that don’t lock you into a fixed movement pattern, many things can go wrong, especially when working with heavy weights.
Built-in Safety
Because your back is supported when doing the leg press, you can concentrate 100% of your focus and energy on pressing the weight. The machine also has a built-in safety mechanism; with a simple twist of the handles, you can activate the locks that secure the weights in place. That means you can go extra heavy on this exercise without needing a spotter.
Greater Quad Focus
Your range of motion for the leg press is typically shorter than if you were doing squats. If you’re trying to develop quad mass and power, that’s actually a good thing. That’s because it keeps the focus on your quads rather than transferring it to your glutes and hamstrings.


Which Type of Leg Press Should You Use?
There are two types of leg press machines commonly found in gyms:
- Horizontal
- 45-degree
So, which is best?
There is no definitive answer to this question. At this stage, no studies have directly compared the effectiveness of the two versions of the exercise in terms of building quad power. However, we can be informed by simple physics on this subject.
When doing the 45-degree leg press, the weight you load on the machine is spread out over the diagonal plane of the leg press machine. This creates a wide moment arm, which is the distance between the line of action and the pivot point, which in this case is the hip joint. The wider the moment arm, the lower the force needed to lift the weight.
But when you do the horizontal leg press, the weight is spread out directly in front of your hips, creating a shorter moment arm. A shorter moment arm means you’ll need more force to lift the weight.
That’s why you’ll find it harder to light the same weight on the horizontal leg press than on the 45-degree leg press.
As a general guide, you should be able to lift about 30% more weight on the 45-degree leg press. But simply being able to lift more weight will not make your quads stronger if the physics of the machine have made it easier.
The fact that it’s easier to lift a weight on the 45-degree leg press doesn’t mean that you should only use the horizontal machine. But if you’ve got access to both machines, you should compensate when using the 45-degree machine by adding extra weight to make up for the longer moment arm. If you don’t, you won’t be pushing your weight limit, and you’re likely to plateau your quad power.


Leg Press Form Tips
[*]Whether using a horizontal or a 45-degree leg press machine, ensure that your lower back and glutes are pressed hard against the pads.
[*]Do not use a weight that is too heavy. This will restrict your range of movement. Don’t be that guy who loads up seven or eight 45s on each side and then moves just a few inches.
[*]Slow down. When you go too fast, your knees tend to cave in, and you may even bounce the weight using momentum at the bottom.
[*]Don’t lock your knees at the top of the rep. Stopping just short of lock-out keeps the tension on your quads.
[*]Consciously think about keeping the weight evenly distributed between both legs.
Should Your Knees Go Over Your Toes?
The knees-over-toes debate is usually associated with the squat, But the same applies to the leg press. For decades, lifters were told not to allow their knees to track over the toes because it would damage the knee joint. Recent research, however, has thrown that argument out the window.
One study showed that allowing your knees to track over your toes during the squat led to significantly improved activation of the vastus medialis head of the quadriceps. This part of the quads is often known as the ‘teardrop’ because of its appearance on a developed bodybuilder with low body fat levels. Furthermore, there was no adverse effect on the knee joint reported. [1]
It should be noted that this study specifically looked at the muscle stimulation of the quads during the squat. It is reasonable to speculate that the same thing applies to the leg press but, to date, there are no studies specifically testing the leg press in this regard.
The leg press foot platform is generally a large area. That gives you the freedom to vary your foot placement from very wide to very narrow. Where you choose to palace your feet on the platform will work your muscles differently. Here’s an overview of the different foot placements and what areas each one targets:
1. High & Wide
When you place your feet high and wide on the platform, you will target your hamstrings. You want to place your legs as high and wide on the platform as possible without your hips coming off the seat pad. Your toes should actually be off the edge of the platform’s top and angled outward. To accentuate the hamstrings, push your heels into the platform on the descent.
In the high and wide position, your feet should be about one and a half times your hip width.
2. Low & Close
Putting your feet low and close together on the platform will emphasize your quads. Your heels should be almost, but not quite, hanging off the bottom of the platform, with your feet about six inches apart.
When pressing, think of pushing your quads out and over your knees. Think also about keeping the weight distributed over the balls of your feet. This position is going to really blow up your quads, but only if you go deep on the descent. So don’t let your ego get in the way of a full range of motion.
As we’ve seen, the more your knees can track over your toes, the greater the quad activation, especially on the vastus medialis head. One way to increase this effect is to wear elevated-heel weightlifting shoes when doing the narrow stance leg press. This is especially beneficial if you have poor ankle flexibility and find your heel coming off the platform in the bottom position of the leg press.
3. Neutral
A neutral stance is where your feet will naturally go on the platform if you’re not thinking about it. Find your most comfortable position with your feet hip distance apart. This position will provide an even distribution across the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
A neutral foot placement will help you lift the most weight. Focus on a slow descent, bringing your knees down to the outside of your shoulders, and then push the heels through the platform on the ascent. Drive your lower back into the seat pad the whole time.
4. Heels Elevated
An adaptation of the neutral position may place extra emphasis on the quads. This involves wearing weightlifting shoes with elevated heels. The increased angle this creates puts more load on the vastus medialis quad muscle that runs into the knee joint.
5. Toes Elevated
To assume a toes elevated position, you need to place a pair of small weight plates or a squat wedge under your toes on the foot platform. Your feet should otherwise be in a neutral stance. This will shift the emphasis to your hamstrings.
Single Leg Press


The single-leg press allows you to work each quad independently. It helps correct quad strength imbalance, where one leg is stronger than the other.
When you do the two-legged leg press, your dominant side will take a disproportionate percentage of the weight. Doing the single-leg press forces each leg to carry its own weight, which will eventually help balance the strength between your quads.
Place your foot low and inside hip width to target the quads with the single-leg press. Place the other foot firmly on the ground. Unrack the weight and slowly bring the platform back toward you. Concentrate on the knee traveling back and out as you descend. This will lengthen your range of motion so that you don’t hit your knee into your ribcage.
Come back until your leg forms a right angle at the knee, and then push your heel into the platform to return to the start position. Don’t lock out at the top but move smoothly into the next rep.
Do not allow your heel to lift off during the descent. If you do, you’ll transfer the force from your quad to your knee. You must also not allow your hips to roll up off the pad in the bottom position.
A Leg Press Workout For Power Quads
Now that we’ve identified the best ways to do the leg press to target the quads, we can put them together to create a mini quad workout on the leg press machine. We’ll be doing the following three leg press variations:
- Neutral-stance leg press
- Low and close stance leg press
- Single-leg press


The first two exercises will be done as a mechanical drop set. This is when you do a drop set without changing the weight by shifting your foot position. We’ll start with the low and close stance version, as this is the one that most directly targets the quads. After pumping out eight reps, you quickly rack the weight and shift to a neutral stance. Then immediately unrack and do another eight reps.
Because you’re strongest in the neutral stance, following a set of narrow stance reps with eight more neutral stance reps will tap deep into your quad’s strength reserves, allowing you to eke out every ounce of benefit from the set. The key to getting the most out of a mechanical drop set like this is minimizing the downtime between the two phases — it should only take a few seconds.
Once you’ve completed your 16 reps on the mechanical drop set, get out of the machine, shake your legs out, and then take half the weight off the machine. Now get straight back on and start pumping out single-leg presses. This transition should take you less than 30 seconds.
Your goal is to get 16 reps on each leg on the single-leg press. At that point, your quads will be on fire. Rest for two minutes, and then do the whole thing over again. Work up to doing three total sets. Here’s what it will look like:
Set One:
- Narrow-stance leg press: 8 reps
- Neutral stance leg press: 8 reps
- Single-leg press (right leg): 16 reps
- Single-leg press (left leg): 16 reps
Wrap Up
The leg press is an effective quad power and mass builder. You can target different areas of your upper legs depending on where you place your feet on the platform. The best way to target your quads is with a low, narrow stance. You can target the quads even more by elevating your heels using weightlifting shoes.
The next best foot stance to hit the quads is the neutral stance. This is also the version you can lift the most weight with. Our final quad-centric leg press move for power is the single-leg press with a low stance.
Combine these three exercises into a killer mechanical drop set followed by a unilateral quad isolation workout. You can either do this as the first part of your quad workout and follow it up with leg extensions and lunges or, if you’re game, do four sets of squats first and then jump into your leg press workout.
Just don’t expect to be able to walk the next day!
References
[*]Escamilla, R. F., Fleisig, G. S., Zheng, N., Lander, J. E., Barrentine, S. W., Andrews, J. R., & Bergemann, B. W. (2001). Effects of technique variations on knee biomechanics during the squat and leg press. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 33(9), 1552-1566.
Click here to view the article.




