Tag: Keto

Can You Consume Alcohol While Intermittent Fasting? Everything You Need to Know
Intermittent fasting is one of the few modern fitness trends that has consistently provided positive results for many people. This is because intermittent fasting is based on scientific principles and offers people flexibility when it comes to fasting in general.
One of the biggest advantages of intermittent fasting diets is that they do not focus on what people consume but on when they consume it. Additionally, intermittent fasting diets are very lenient in terms of allowed food items compared to other weight loss diets. You can drink coffee, tea, lemon juice, low-calorie electrolyte drinks, etc., during the fasting period.
But is it ok to drink alcohol while fasting? This is a popular question amongst dieters. Let’s dive into this topic and understand how alcohol affects your body, whether it can break your fast, and the best alcohol for intermittent fasting.
How Does Intermittent Fasting Work
Intermittent fasting works by tapping our stored energy. Your body relies on glucose for energy. But when it exhausts glucose, it starts utilizing fat. This metabolic shift occurs when you fast for a prolonged period.
Intermittent fasting involves restricting calorie intake to a specific period in the day, called the ‘feeding window.’ The fasting time is known as the ‘fasting window.’
The fasting window leads to the depletion of stored glucose in the liver. Hence, to maintain homeostasis and provide energy to the cells, stored fat is converted into energy by a process called ketosis. Intermittent fasting generally depends on regular ketosis for fat loss, which also results in several other fasting-related health benefits. [1]
It is vital to undergo a prolonged fasting period to trigger ketosis. This is why most intermittent fasting diets require people to fast for at least 12 to 16 hours regularly. Water or zero-calorie drinks like black coffee, tea, lemon juice, etc., do not trigger blood glucose levels, which is why such beverages are allowed while intermittent fasting. But what about alcohol?
Alcohol While Intermittent Fasting
For starters, we must remember that alcohol and alcoholic drinks are generally high in calories. According to the NHS, 1 gram of alcohol contains approximately 7 calories, which is higher than other food items. This is why alcohol should not only be avoided by people who are fasting but also by people looking to lose weight in general. [2]
Still not convinced? Here are some other problems related to alcohol consumption during intermittent fasting:
Alcohol Adds Empty Calories
Since alcohol is high in empty calories, consuming alcohol and trying to lose weight can not be done together. In most cases, alcohol is a mix of sugary drinks with no nutritional value. Consuming alcohol is akin to consuming empty calories without any nutritional value.
Alcohol Makes You More Hungry
Research studies have revealed that alcoholic drinks can increase appetite, leading to overeating. Fasting can be challenging with regular alcohol consumption. [3]
Alcohol Causes Dehydration
Alcohol can lead to dehydration and further complications if consumed on an empty stomach. Hence, while consuming such beverages, you must stay hydrated.
This does not mean that people who like an occasional drink cannot practice intermittent fasting. As mentioned earlier, one of the biggest advantages of intermittent fasting is that it allows flexibility. Hence, you can enjoy an occasional glass of wine or any other alcoholic drink while practicing intermittent fasting.
However, moderation is key, and it is also important to note that one should never break a fast with alcohol. The best time to consume alcohol while intermittent fasting is in the eating window.
Read also: Does Alcohol Break a Fast?
Let’s look into the effects of alcohol on the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Fat Oxidation
Fat oxidation is one of the primary benefits of intermittent fasting, as prolonged fasting periods help the body break down stored fat to produce energy. [4]
Several studies suggest that alcohol inhibits fat oxidation. Furthermore, people tend to eat more due to alcohol consumption, which can lead to weight gain. [5]
Inflammation
Inflammation is our body’s way of reacting to various diseases or infections. Though it is a part of our natural immune system, high levels of inflammatory markers can lead to autoimmune diseases. Inflammation also increases free radicals in your bloodstream resulting in several health complications. [6]
Studies indicate intermittent fasting can reduce inflammation levels and help flush out harmful free radicals from the bloodstream. [7]
Excess alcohol consumption not only increases inflammation in your body but also causes releases toxins into the bloodstream. This can be mitigated with moderate alcohol consumption. [8]
Brain Health
Ketones released during intermittent fasting are an efficient fuel for your brain. They help improve your brain health and overall performance. Further studies have revealed that intermittent fasting is closely related to the synthesis of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) hormone. Low BDNF levels can lead to depression and anxiety. And excessive alcohol consumption is linked to brain damage. [9][10]
Cellular Health
Fasting for prolonged periods can promote cellular autophagy, a process through which your body replaces old and diseased cells with newer, healthier cells. It leads to the formation of newer, healthier cells. On the other hand, excessive alcohol consumption can cause DNA damage. [11]
Liver Health
Intermittent fasting boosts liver function, which helps remove toxins from our bloodstream. However, excessive alcohol consumption can introduce more toxins into the bloodstream, which can overwhelm the liver. [12]
A Case For Alcohol During Intermittent Fasting
Now that we have looked at the adverse effects of alcohol consumption during intermittent fasting, it is important to note that some alcohol products are not entirely bad, and alcohol consumption is believed to have some health benefits.
Wine
Fruits and berries are a rich source of polyphenols that show antioxidant properties. Studies have revealed that polyphenols help prevent diseases by reducing oxidative stress. Wine is prepared from grapes along with its skin and seeds and is believed to have a high amount of polyphenols. If you consume wine after food, it helps in digestion and avoids any spike in glucose levels. [13]
Whiskey
Whiskey is also filled with polyphenols. It is prepared by fermenting mashed grains. When consumed in moderation, whiskey is believed to reduce cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease. [14]
Beer
Beer is made by brewing and fermenting hop flowers. It contains a high amount of water and polyphenols, which add antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. When consumed in low to moderate amounts, beer helps reduce cholesterol content in your body and improve cardiac health. [15]
Frequently Asked Questions
Does alcohol affect intermittent fasting?
Yes, alcohol contains calories, and it breaks your fast if consumed during the fasting window. When consumed in excess, it can lead to weight gain, inflammation, and cell damage. However, you could drink alcohol during your eating window.
How many hours does it take for your body to clear alcohol from your system?
This may vary based on how much you consume and your metabolism. When you consume alcohol, your body focuses on metabolizing it. Generally, it takes 12 to 36 hours for your body to clear alcohol from your system and start burning fat. How long does alcohol stop fat burning?
Can you drink alcohol on a 16-hour fast?
In a 16-hour fast, you can drink alcohol in moderation during the eight-hour eating window. You may experience adverse health effects and weight gain if you consume excessive alcohol, hampering your intermittent fasting benefits.
Final Words
Combining intermittent fasting and alcohol can be challenging. Alcohol breaks your fast and adds empty calories to your diet. However, low to moderate alcohol consumption can be considered with regular monitoring of your eating habits to avoid weight gain.
According to the CDC, alcohol consumption should be limited to two drinks or less per day for men and one drink or less per day for women. You can limit your alcohol intake to practice intermittent fasting and reap its benefits.
Also, alcohol consumption causes dehydration, and during intermittent fasting, you need to focus on your water and electrolyte intake. Do not break your fast with alcohol or plan to drink while on an empty stomach. When it comes to alcohol, it is essential to choose wisely and carefully plan your fasting routine.
References
Lichtash, C., Fung, J., Ostoich, K. C., & Ramos, M. (2020, July 7). Case report: Therapeutic use of intermittent fasting and ketogenic diet as an alternative treatment for type 2 diabetes in a normal weight woman: a 14-month case study. PubMed Central (PMC).
Calories in alcohol. (n.d.). Nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/alcohol-advice/calories-in-alcohol/
Short term effects of alcohol on appetite in humans. Effects of context and restrained eating – PubMed. (2010, December 1). PubMed.
Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism – PubMed. (2005, January 1). PubMed.
Is alcohol consumption a risk factor for weight gain and obesity? – PubMed. (2005, January 1). PubMed.
H., Pizzino, G., Irrera, N., Cucinotta, M., Pallio, G., Mannino, F., Arcoraci, V., Squadrito, F., Altavilla, D., & Bitto, A. (2017, July 27). Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health.
Intermittent fasting during Ramadan attenuates proinflammatory cytokines and immune cells in healthy subjects – PubMed. (2012, December 1). PubMed.
Effect of alcohol consumption on systemic markers of inflammation – PubMed. (2001, March 10). PubMed.
Björkholm, C., & Monteggia, L. M. (2015, November 11). BDNF — a key transducer of antidepressant effects. PubMed Central (PMC).
The neuropathology of alcohol-related brain damage – PubMed. (2009, April 1). PubMed.
DNA damage, DNA repair, and alcohol toxicity–a review – PubMed. (1997, September 1). PubMed.
Wang, H. J., Zakhari, S., & Jung, M. K. (2010, March 21). Alcohol, inflammation, and gut-liver-brain interactions in tissue damage and disease development. PubMed Central (PMC).
Phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in sparkling wines: Modulation by the aging on lees. (2013, August 29). Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity in Sparkling Wines: Modulation by the Ageing on Lees – ScienceDirect.
Duthie, G., Pedersen, M., Gardner, P., Morrice, P., Jenkinson, A., McPhail, D., & Steele, G. (1998, September 30). The effect of whisky and wine consumption on total phenol content and antioxidant capacity of plasma from healthy volunteers – European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Nature.
Marcos, Ascensión, et al. “Moderate Consumption of Beer and Its Effects on Cardiovascular and Metabolic Health: An Updated Review of Recent Scientific Evidence.” PubMed Central (PMC), 9 Mar. 2021

Intermittent Fasting and Collagen Production: How Fasting Can Enhance Your Skin and Health!
Intermittent fasting is fast becoming the go-to diet for achieving different health goals, most importantly, weight loss. Many celebrities, business tycoons, and famous entrepreneurs have endorsed this transformative fasting strategy as the sure-shot way to a healthier mind and body.
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern where you fast for a certain number of hours a day and reserve calorie intake to a small eating window. When you do this, in the fasting period, your body uses up the glycogen stores it utilizes for energy and undergoes a “metabolic switch.” With this metabolic switch, the body enters a state known as ketosis, where the liver produces ketones from the stored fat reserves to use as an energy source.
There are several intermittent fasting techniques, the most common being 16/8, where you fast for 16 hours and eat calories in the eight-hour feeding window. Some fasters like to do the 5/2 fasting schedule, where they eat normally for five days of the week, and on two non-consecutive days, they limit calorie intake to 500-600 calories. Yet more advanced fasters prefer to go for OMAD fasting (one meal a day), 36-hour fasts, and monk fasts, with extreme fasters also taking it as far as a 60-hour fast.
Many variants of intermittent fasting exist, like water fasting and fat fasting, each with its own special benefits. People also work out towards the end of the fasting period to lose fat and gain muscle simultaneously.
Despite its growing popularity, one of the most overlooked benefits of intermittent fasting is its significant impact on collagen production within the body. We need collagen, a protein, for healthy skin, nails, joints, and hair. Recent research suggests that intermittent fasting can assist in stimulating the body’s production of collagen. This article examines the relationship between intermittent fasting and collagen production, supporting the theory with scientific studies and research. Keep reading to discover the connection between intermittent fasting and collagen synthesis.
What is Collagen?
Among the different kinds of proteins in the human body, collagen is the most abundant, accounting for 30% of the total protein composition. It is a building block for muscles, skin, tendons, bones, ligaments, and other kinds of connective tissue. You can also find collagen in the blood, intestinal lining, and organs.
All proteins are made from amino acids, and collagen is no exception. Proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline are collagen’s main amino acids. These three amino acids are grouped to form protein fibrils in the famous triple helix structure.
Role of Collagen in the Body
The main role of collagen is to provide strength, structure, and support to the body. Its specific roles are:
Helping the formation of fibroblasts in the dermis, thereby helping the formation of new skin cells.
Replacement of dead skin cells.
Giving a protective covering to the different vital organs in the body.
Providing skin strength, structure, and elasticity.
Blood clotting.
What are the Different Types of Collagen in the Body?
To date, researchers have identified 28 types of collagen. The differentiation is based on the molecule assembly, the cell components, and the location of the collagen in the body. All these different collagen fibrils consist of a triple helix structure.
Here are the main types of collagen as well as their various functions:
Type I: This consists of 90% of the collagen in the body, and it is densely packed, providing structure to ligaments, tendons, bones, and skin.
Type II: It is found in the elastic cartilage that supports joints.
Type III: It is found in organs, arteries, and muscles.
Type IV: This can be found in the different layers of the skin.
Type V: It is found in the cornea, some skin layers, and the hair and tissue of the placenta.
What Factors Affect Collagen Production?
Here are the different factors that can affect collagen production in the body:
Age: With age, collagen production naturally diminishes, which leads to sagging skin, wrinkles, as well as pain in the joints.
Nutrition: Consumption of proteins and vitamin C can help produce collagen in the body.
Sun Exposure: Collagen fibers can get damaged from prolonged exposure to UV rays, which can cause skin damage and premature aging.
Smoking: Collagen production reduces if you smoke, causing skin damage and premature aging.
Stress: Chronic stress causes increased production of the stress hormone cortisol, which can potentially inhibit collagen production.
Exercise: If you exercise regularly, collagen production increases.
Sleep: If you can get enough quality sleep, your body’s production of collagen increases. This is because the body repairs and regenerates itself when you sleep.
Apart from these factors, it has also been found that fasting, especially intermittent fasting, can increase collagen production. We shall take a look at this phenomenon now.
What is the Relationship Between Intermittent Fasting and Collagen Production in the Body?
Intermittent fasting can stimulate collagen synthesis in multiple ways. Check them out here:
Intermittent Fasting Increases Human Growth Hormone Secretion
It has been proven that intermittent fasting can increase and enhance the secretion of an important hormone, Human Growth Hormone (HGH). HGH is a very important regulator of collagen production in the body. HGH stimulates collagen production in two ways. Firstly, it helps the fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts, cells that produce collagen. Secondly, HGH upregulates collagen gene expression.
A study published in the Nutrition Research journal revealed that 24-hour intermittent fasting led to an immense increase in HGH levels in both women and men [1]. Another study proved that a 37.5-hour fast elevated basal HGH concentration by 10-fold and additionally reduced the metabolic clearance of HGH. [2]
As we know, HGH is essential for collagen synthesis. This increase in HGH levels during intermittent fasting suggests that the latter is a very useful tool for increasing collagen production in the human body.
Intermittent Fasting Induces Autophagy
Cancer.gov defines autophagy as “ A process by which a cell breaks down and destroys old, damaged, or abnormal proteins and other substances in its cytoplasm (the fluid inside a cell). The breakdown products are then recycled for important cell functions, especially during periods of stress or starvation.”
As the body ages, it gets increasingly exposed to free radicals from the food we eat, the air we breathe, and the different products we use daily. This stresses out the individual cells and causes them to get damaged faster than normal. These damaged cells can linger in connective tissues and organs, causing inflammation and disease. Autophagy removes the task of maintaining these useless and inefficient cells in the body. It frees it to fight inflammation, deter diseases, and line the body up for optimal functioning.
After age 30, the fibroblasts in the skin begin to store more waste, slowing down the collagen-producing and autophagy rates. This then causes a deterioration of the fragility and integrity of the skin and leads to sagging and wrinkled skin. Hence, an increased autophagy rate will help clean the fibroblasts, removing unwanted cellular debris and slowing down the signs of skin aging.
A study found that intermittent fasting induced autophagy in mice, helping remove dead and damaged cells and produce healthy and new cells. [3]
As we know, autophagy is crucial for collagen synthesis, and increased autophagy rates brought about by intermittent fasting lead to improved and increased collagen synthesis by inference.
Intermittent Fasting Reduces Inflammation
Intermittent fasting can reduce body inflammation in many ways. It reduces oxidative stress by producing antioxidants, promotes autophagy, lowers insulin levels, activates anti-inflammatory pathways, and modulates the gut microbiome, all contributing to reduced inflammation.
A study found that intermittent fasting reduces chronic inflammation in mice by activating an anti-inflammatory pathway known as the Nrf2 pathway. [4]
As we know, inflammation is a big cause of collagen breakdown. Hence, the above reduction in inflammation in the mice suggests that intermittent fasting can help protect collagen.
Intermittent Fasting Improves Gut Microbiome
There are several ways in which intermittent fasting can improve gut health. Firstly, it improves the motility of the gut, helping the digestive system move food through the GI tract. Secondly, it improves the gut microbiota, modulating the composition of the trillions of microorganisms residing in the gut. Thirdly, it refines the gut barrier function by increasing mucus formation, reducing inflammation, and finally enhancing the absorption of nutrients from the gut.
A study has conclusively shown that intermittent fasting improves overall gut health. [5]
Now, the gut is where most of the nutrients necessary for collagen synthesis get absorbed. Hence, a healthy gut can ensure that the body has all the ingredients it needs for the production of collagen, and this can be made possible through intermittent fasting.
Can I Use Collagen as a Protein Source While Fasting For Weight Loss?
Collagen is a great way to help you achieve your weight loss goals, but you’re probably using it wrong. When used correctly, it can help prevent snacking, reduce cravings, and help you get to your weight loss goals.
The biggest mistake that you are making is that you are using collagen as your main protein source. If you do this, you will lose weight, but it will be in the form of a loss in muscle and bone mass, leading to a decrease in metabolism, which you do not want.
To achieve healthy weight loss, use collagen supplements in tandem with a rich protein source. Suppose you are making a collagen supplement smoothie. We suggest you reinforce this smoothie with a rich source of protein, like Greek yogurt or even another protein supplement.
If you use bone broth, you can sip on it but do not use it as a replacement for protein. Rather, use it as an add-on to a meal. For example, you can sip on bone broth while relishing a chicken salad. This gives you collagen and a complex protein.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will collagen intake interrupt my fast?
Strictly speaking, yes. Collagen intake during fasting periods will break your fast. Even if you eat hydrolyzed and unflavored collagen peptides, remember that each scoop of collagen contains 30 calories.
2. What slows down the production of collagen in our body?
The collagen tissues in our body are responsible for forming tendons, ligaments, and bones. However, you can lose collagen in your body if you are exposed to UV rays, if you consume tobacco, or if you take excessive sugar, as well as with age. Additionally, chronic stress can make you lose collagen.
3. How long does it take to generate collagen?
It has been observed that new collagen growth can take anywhere from 4 to 12 weeks to complete.
4. Why is collagen important for weight loss?
Collagen supplements can make you feel satiated. This helps with weight loss and the prevention of hunger pangs when you are doing intermittent fasting. Collagen has this effect because it is a form of protein.
5. Which foods are rich in collagen?
The top foods rich in collagen are bone broth, eggs, meat, fish, and spirulina.
Conclusion
The link between intermittent fasting and collagen production is multi-faceted and complex. Collagen is a crucial protein that is indispensable to the human body as it maintains the function and structure of different organs and tissues. Studies have shown that fasting can increase the secretion of human growth hormone and promote the process of autophagy, both of which directly or indirectly influence the production of collagen.
The intricate relationship between collagen synthesis and intermittent fasting impacts longevity and health. If we can increase collagen production by fasting intermittently, it could help arrest age-related issues with skin, joint health, and the density of our bones. Again, nowadays, collagen supplements are quite popular, and their efficacy can be increased if we better understand the relationship between fasting and collagen production.
Collagen production is influenced by various factors, including lifestyle, exercise, and nutrition; intermittent fasting is one of many ways collagen synthesis can be promoted. The fascinating link between intermittent fasting and collagen production needs further exploration and study so that we can come to a better understanding of their complex relationship.
References
Ho, K. Y., et al. “Fasting Enhances Growth Hormone Secretion and Amplifies the Complex Rhythms of Growth Hormone Secretion in Man.” PubMed Central (PMC), https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI113450.
Ho, K. Y., et al. “Fasting Enhances Growth Hormone Secretion and Amplifies the Complex Rhythms of Growth Hormone Secretion in Man.” PubMed Central (PMC), https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI113450.
“Time-restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Postmenopausal Obesity – PubMed.” PubMed, 1 Dec. 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2016.09.006.
Zhang, Yu-Kun Jennifer, et al. “Genetic Activation of Nrf2 Protects Against Fasting-Induced Oxidative Stress in Livers of Mice.” PubMed Central (PMC), 18 Mar. 2013, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059122.
“Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota – PubMed.” PubMed, 3 Oct. 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.019.
Cite this page: Byakodi, D. (2023) ‘Intermittent Fasting and Collagen Production: How Fasting Can Enhance Your Skin and Health!’, Fitness Volt. Available at: https://fitnessvolt.com/intermittent-fasting-collagen-production/ (Accessed: 30 April 2023).

Intermittent Fasting for Shift Workers: Benefits and Challenges
Intermittent fasting has emerged as a popular diet thanks to its purported health benefits. Fasting plans work differently for each individual, as these depend on a score of factors such as lifestyle, sleep patterns, occupation, and existing health conditions. Hence, all these aspects must be considered before starting a fasting regimen. This article aims to…
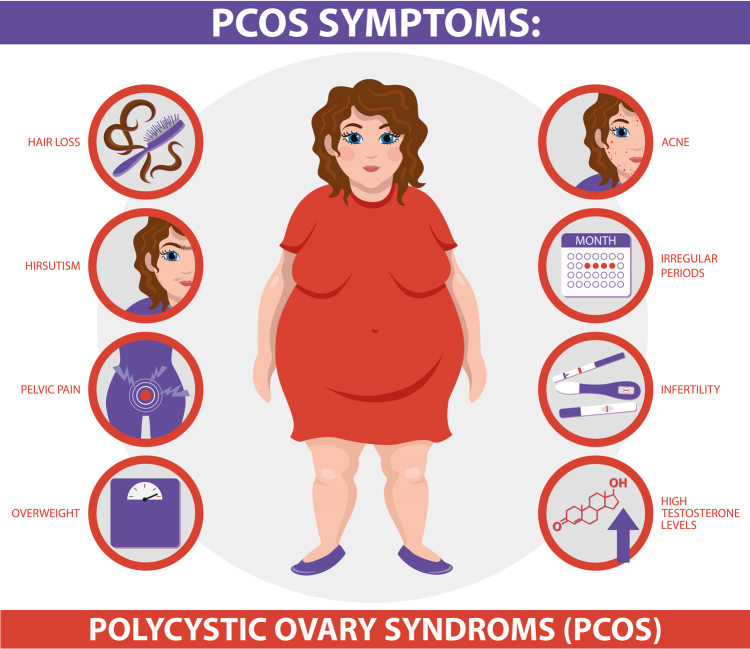
Is Intermittent Fasting a Ray of Hope for PCOS? Evidence-Based Answers
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder in women during their reproductive years. Responsible for various issues such as infertility or subfertility, insulin resistance, obesity, hormonal disorder, and hyperinsulinemia, PCOS exerts enormous mental and physical stress on those with this condition. Amongst the recommended treatments are diabetic and birth control drugs with specified…

Getting Yoked on the Keto Diet
Getting Yoked on the Keto Diet.
It seems that every couple of years a new fad diet pops up and takes the country by storm. Atkins, Paleo, the Mediterranean diet, and now we have the Keto diet, all of which promise incredible results in a short amount of time. The key difference here is that beyond the anecdotal evidence that comes with any new diet craze, the Keto diet has sound science backing it, and truly does seem to be effective in weight loss.
But why is the Keto diet catching on so quickly in bodybuilding culture? Of course people want to shed as much extra fat as they possibly can to show off their hard-won gains, but is the Keto diet effective when trying to build muscle? Here is a quick rundown of how and why ketosis might be one of the best diets out there for getting absolutely shredded.
Understanding How Ketosis Impacts Your Body
The Keto diet is different than a majority of the other diets you run into. The reason for this is that the Keto diet actually changes how your body uses energy as opposed to other diets that simply limit or cut out certain foods. While a diet high in fats might seem counterproductive when you’re trying to lose weight and shed fat, it is actually one of the keys to how ketosis actually works.
Your body loves carbohydrates. The energy contained in carbohydrates is easily accessible to our bodies, and is broken down into glucose or glycogen for immediate use or later storage. When you cut carbs out of your diet, it in a sense “scares” your body into burning fat as an energy source. This process is called ketosis and results in your body breaking fats down into ketones, which replaces glucose as an energy source.
Now, this switch in how your body acquires energy doesn’t occur right away. First, your body will use all of the remaining glucose available that is stored in the liver before it begins processing stored fats. While there are plenty of testimonials about how effective the Keto diet is, many fail to really hammer home the point that you have to stick with it for an extended period to see real results.
As soon as you introduce more readily accessible energy into your body, ketosis will cease and your body will go back to breaking down carbohydrates. So, how does this whole process affect how we build muscle?
Boosting HGH Naturally
First, it is incredibly important that you consume enough fat while you are on the Keto diet, because if your body doesn’t have fat to process, it effectively goes into starvation mode and begins to break down muscle. Now, if you’re trying to get ripped, this is extremely counterproductive. Luckily, if you follow a strict ketogenic diet, there is an interesting side effect that relates directly to getting absolutely yoked.
Everyone’s body produces Human Growth Hormone, or HGH. The production of it tends to slope off as we get older, but one look at Sylvester Stallone will show you just how effective HGH is to building muscle at any age.
While it is possible to do injections of HGH, the safest course of action is to take steps to increase your HGH production naturally. In order to kickstart your body’s production of HGH, you need to tweak your sleep schedule, diet, and workout routine. The Keto diet by nature will cover the dietary needs for HGH production.
Cutting out sugar and engaging in intermittent fasting are both key to boosting HGH production in your body, both of which are huge components of the Keto diet. Increasing the amount of sleep that you get each night is also critical.
Finally, for an even greater boost to muscle building HGH production, certain foods like steak, yogurt, raw fish, and oats all contain compounds that encourage the production of HGH in your pituitary gland.
Staying Healthy
So, now that you know how the Keto diet helps you lose weight while also increasing your body’s production of HGH, there are some precautions you need to take. The Keto diet can actually be fairly dangerous if you are not careful, and has a slew of side-effects you should be aware of. The reason for this is due to the nature of ketosis; you are essentially rewiring how your body functions at a basic level.
“The Keto Flu” is real. You’ll notice that for the first couple of weeks on starting the Keto diet that you will feel sluggish, irritable, and generally fatigued. This is due to your body struggling to adapt to operating off of ketosis.
This is also followed by another, less pleasant side-effect dubbed “Keto-diarrhea.” This occurs because the gallbladder, which helps to process fat, becomes overloaded, or because when cutting out carbs, an insufficient level of fiber was added to counter the effect.
You may notice that you have a dry mouth and skin, persistent headaches, feeling lightheaded, all of which are warning signs that you are not drinking enough water and becoming dehydrated.
Dehydration is exasperated by a bad case of diarrhea, and many folks are sent to the emergency room due to a misguided thought that if you drink less, you will experience less diarrhea, when the exact opposite is true. Chronic dehydration can damage your circulatory system, not only causing long-term health issues, but harming the insane vascularity you’ve worked so hard for. Drink more water, especially during ketosis!
Finally, on any limited-food diet like the Keto diet, you may have issues getting all of the vitamins and minerals you would normally get through a more varied diet. While the Keto diet does have you eat a decent amount of leafy greens, restrictions on certain vegetables can leave you with a deficiency of vital nutrients.
Yes, you can go through and figure out how much of what to eat in order to obtain those missing vitamins and minerals, but the easier route is to simply supplement your diet with multivitamins. This will keep you healthy while you shed fat and pack on muscle!
For more news and updates, follow Generation Iron on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Ross Cowan lives in Boise, Idaho with his wife and his dog Mosey. He spends his free time camping at Bear Lake, hiking sections of the Idaho Centennial Trail, white water rafting down the Middle Fork of the Salmon River and Hell’s Canyon. You can follow Ross on his Twitter @RossCowanWrites.

Different Diets You Should Try to Build Muscle and Lose Fat
Diets Doing the Rounds in the Fitness World
The advent of the internet has brought a lot of diets you can follow. While there are many diets you can try, in this article, we will focus on some of the most effective diets which can produce the best results.
Keto
The main premise of the ketogenic diet is to eat fats to burn fat. In the keto diet, you follow a high-fat, moderate-protein, carbohydrate-restricted diet designed to make the body burn fat for fuel.
A keto diet can have many physiological benefits like fat loss, improved body composition, reduced inflammation, and increased insulin sensitivity. The different types of keto diets are –
Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD) – The most basic form of keto.
Restricted Ketogenic Diet (RKD) – A calorie-restricted version of the standard keto.
Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) – A keto diet for people who workout regularly.
Cyclic Ketogenic Diet (CKD) – Focused on advanced athletes who need a boost of carbs for fuel during training.
High Protein Ketogenic Diet (HPKD) – Ideal for people who are trying to shed excess fat.
Paleo
If you have always fancied what the prehistoric people ate and dig their diets, the paleo diet is for you. While following the paleolithic diet you will have to skip all the processed food and eat food which occurs in the wild or come straight from the ground.
In paleo, your diet will primarily consist of meat and fish, plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, and nuts and seeds. Dairy products, cereal grains, legumes, starchy vegetables, fatty meats, and foods which are high in salt content are to be avoided.
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean diet is based upon the epidemiological findings that people who live in Greece, Italy, and Spain and consume traditional diets have a better health than the rest of the world.
In this diet, you’ll be eating plant-based foods such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Replacing butter with healthy fats such as olive oil and canola oil. Using herbs and spices instead of salt to flavor foods.
The Mediterranean diet was introduced in attempts to reduce and prevent heart disease. The flexible nature of the Mediterranean diet makes it relatively easy to follow and implement for the long-term.
Intermittent Fasting (IF)
If you’re interested in maintaining a lean and muscular physique but don’t want to give up on your favorite food IF is what you’ve been looking for. Intermittent fasting involves going an extended period of time without consuming any calories.
In the duration of your fast, you can only drink plain water, black coffee or tea. Many variations of IF exist, but the most popular involves fasting for 16 hours, then eating all of your food during an eight-hour window called the “feeding window.” This type of IF is called “16:8” fasting. Combined with a well-adjusted diet, fat-burners can accelerate fat loss by enhancing metabolism, reducing cravings, and increasing intra-workout energy.
The best ones even go the extra mile to protect against muscle breakdown.
The right fat burner can:
Accelerate metabolism
Increase mobilization of stored body fat (to be used as energy)
Fight against hunger and cravings
Reduce muscle breakdown
Improve lean body mass
Keep you healthy overall
During your “feeding window” you need to reach the same calorie and macronutrient goals as per your diet plan, provided you’re following one designed as per your goals. IF is one of the best diets when it comes to fat burning.
Atkins
The Atkins diet used to be known by many as the steak and eggs diet. In the old Atkins diet, you ate as much protein and fats as your body could handle while disregarding carbs and overlooking where your fats were coming from.
The Atkins diet has since changed tracks and now focuses on a well-rounded approach to their dietary guidelines and touting the importance of healthy carbohydrates and fats combined with protein. The Atkins diet consists of four phases –
Phase One – The first phase is the most strict phase and is followed for two weeks. In this phase, you need to include fats and proteins with each meal and restrict your carbs to 20 grams per day.
Phase Two – The second phase, like the first phase, focuses on weight loss. In this phase, you will include 5 grams of carbs per week until you have only 5-10 pounds you want to lose.
Phase Three – Phase three is known as pre-maintenance. Here you will learn how to eat in order to maintain your weight in the future.
Phase Four – This is the maintenance phase where you will have reached your target weight. In phase four you will have arrived at a diet which will help you maintain your weight.
If It Fits Your Macros (IIFYM)
Macros are short for the three major nutrients – carbs, proteins, and fats. In an IIFYM diet, you focus on meeting your daily macro goals instead of counting your calories. The IIFYM approach is based on the principle that the ratio between the number of calories you consume versus how much you burn dictates whether you gain or lose weight.
While following IIFYM, the source of the calories is disregarded. You just need to maintain the proportion of calories you get from each macro and you’re free to feast on your favorite food.
Vegan
Veganism has been one of the most talked about and followed diets of the past few years. Vegans are different from vegetarians in the sense they don’t even consume dairy products while the vegetarians do. Vegans disregard anything that is derived from animals be it dairy, meat or leather products. There are certain benefits to turning vegan.
Veganism is more than a diet, being a vegan is a lifestyle. Veganism started out as a way to stop animal cruelty, but soon its health benefits took over. Now many pro athletes have turned vegan and report having improved their performance because of their new diets.
Have you tried any of these diets? Let us know in the comments below. Also, be sure to follow Generation Iron on Facebook and Twitter.
*Header image courtesy of Envato Elements.

The Personal Keto Diet Experience: Is It The Best Fat Loss Program Out There?
My personal keto experience.
The Ketogenic diet has been gaining a ton of popularity in recent years. While there have been many low carb diets that have influenced the masses as of late, the keto diet has really made a major impact and with good reason. The keto diet works and that’s not just hyperbole. In the past when I needed to cut weight for fights or even now when a fighter needs advice for shaving off those last few pounds, the keto diet has always been the answer.
A Whole New World of Options
So the initial switch from rice, potatoes, beans, and other carb filled products to fats like oils, avocados, and nuts was a bit daunting. You basically throwaway everything that you’ve grown to love and replacing it with foods that just aren’t the same. Being keto means embracing fats which is something so many people seem to get wrong. Fats are demonized mainly because they are so calorie dense, not because they’re horrible for you. Yes, there are the trans fats that you want to avoid at all costs, but coconut oil and avocados will actually do your body good rather than the reverse.
The options you have at your disposal may at first seem limited, but that’s why you have a little thing called a brain. Research is required to do keto the right way. You can easily get caught up in the pitfalls of eating way too much protein while on the diet which will push you right out of the sweet spot of ketosis. Ketosis is when your body switches over from using carbs for fuel to fats. If you spend too much time eating chicken breast and not enough time consuming oils and nuts then you’re probably doing something wrong.
Entering Ketosis
With my experience first entering ketosis I noticed having a very dry sensation. What does that mean? Well, whether you’re drinking a few sips or all the water your body can handle, it always felt as if you’re just constantly dry. For whatever reason, there was a constant feeling of never getting enough water. But that’s only one man’s observation after all. I venture to bet that every person will have a different experience initially.
Energy Levels
In terms of the energy levels, there have been talks that lifting heavy or doing explosive work on a keto diet is ill advised and could be taxing on the body. Considering that the average person gets most of their energy through carbohydrates, switching over to fats as your primary fuel source does feel a bit different. Initially you’re going to feel sluggish, there’s no doubt. After passing the first hurdle however, life gets better and the suffering passes.
A keto diet during fight week and when you’re just living your everyday life can be considerably different. On fight week sodium intake is put in check. That means you’re not going to be slogging down barrels of salt while you’re trying to cut water weight. Sodium holds onto water which means kicking the table salt to the wayside. If you’re simply trying to lose fat however, the sodium intake is less of a worry. That doesn’t mean pour a mountain of salt on your food, but it does mean you don’t have to be nearly as strict as a fighter or bodybuilder getting prepped for competition.
Results
As far the results go, water weight melts off of you like butter (another fat source to be embraced on keto by the way). When you add the high fat, moderate protein, and low carb method to your diet along with vast quantities of water, you’ll watch as your body dumps out the extra fluid. That said, we have to understand that water weight and fat are entirely two different things.
Water weight comes back easily which means if you hop on the keto diet for a week, see crazy results, get lazy and stuff your face with garbage, you can expect to see the pounds come right back.
Whenever I cut weight for a fight it was less about getting fat off forever and more about getting the water out of my system while still holding onto my muscle. Hind sight being twenty-twenty however, putting back all of the water I had lost the week prior over night wasn’t perhaps the smartest approach. In fact, after one massive twenty pound cut within one week, I packed back on the pounds by eating whatever I pleased. I thought to myself “I’ve been disciplined enough for the last several weeks, no big deal in celebrating a bit.” Little did I know that would end up throwing my metabolism off the rails and pack a good deal of fat onto my frame.
If you’re looking to keep the results of your hard work and dedication then you need to stay strict and maintain the diet for an extended period of time. It also means having a plethora of choices at hand so you won’t fall off the wagon due to lack of options. This may be a bit of “broscience” but by sticking to the game plan for a short time and throwing it all out the window, it ensured that the results would go up in smoke. The secret to success on the keto diet is by looking at it as a lifestyle choice rather than just some fad you’re looking to take up. Staying in ketosis for a long range of time will ensure that you’re not just dropping water weight, but that you’re burning fat as well. But that requires something else.
Training on Keto
Can you lose fat and maintain muscle on a keto diet alone? Yes, that’s totally possible. That said, it works even better if you’re training hard to maintain your muscle mass. Staying active, primarily with resistance training, explosive movements like heavy bag work and sprints, while adding some steady state cardio like walking or jogging into the mix will blast fat easily while you’re in ketosis.
Some people believe you can grow weaker while on a keto diet, but really it’s about what you’re fueling up on. If you have some grass-fed ground beef or steak with avocado and nuts, you’ll be surprised just how explosive and powerful you’ll feel on keto. It’s all about training smart and meal planning intelligently if you want to make strength and muscle gains.
Long Term Use
So can you stay on the keto diet long term? Well, I’ll say so far so good. being sure to understand your options is a big deal with this diet so you’ll need to game plan in order to keep up. But just from personal advice, give yourself a refeed day after about two to three weeks of being on the diet. That means reintroducing carbs back into your diet which will both boost your metabolism while at the same time satisfying those urges and cravings you could be having.
If you start a refeed in the first week, it could be a slippery slope which could lead to binging. Instead you should make smart carb choices while sneaking a cheat meal in there somewhere. We’re all human, so we need a little break from things once in awhile.
While you could follow a keto diet indefinitely, it would be a good idea to alternate between a traditional macro approach and a keto diet every other week or at your leisure. Variety is the spice of life after all and being limited to fifty grams of carbs all the time can become a bit unrealistic at times. All in all, it’s an effective diet that requires a lot of diligence and patience to follow, but will get you the results you desire.
For a more scientific in-depth look at how the keto diet can be effective for bodybuilders, make sure to check out Dr. Jacob Wilson’s researched breakdown on the diet and many other insights on bodybuilding nutrition with Generation Iron Plus.
For more news and updates, follow Generation Iron on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Managing Editor at Generation Iron, Jonathan Salmon is a writer, martial arts instructor, and geek culture enthusiast. Check out his Instagram, Twitter and Facebook to keep up with his antics.
