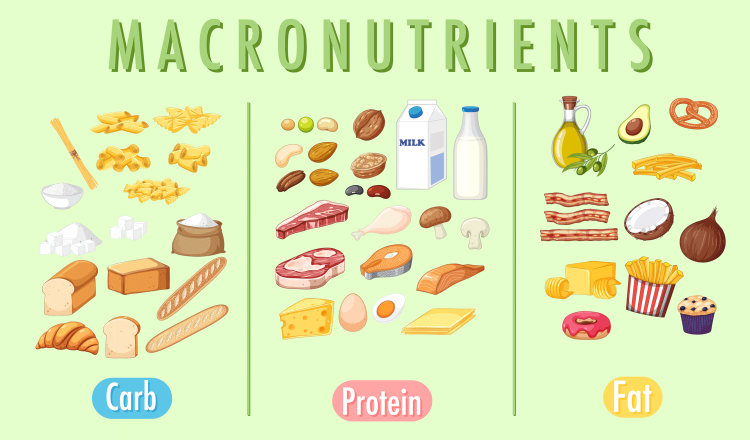
Tag: Macronutrient

Best Vegan Bodybuilding Meal Plan For Bulking and Cutting
Over the past few years, one of the biggest nutritional movements has been a massive shift to vegetarianism and veganism. That trend has affected all sectors of society. Bodybuilders have been especially keen to embrace the vegetarian lifestyle. Going meatless, of course, flies in the face of the traditional bodybuilding diet of chicken, eggs, and tuna. So, how can you still pack on quality muscle when you can’t eat meat?
This article answers that question by laying out a seven-day vegan bodybuilding meal plan for bulking and cutting. It will also address the benefits and drawbacks of vegan bodybuilding, consider the best sources of the key macronutrients and address the most frequently asked questions about vegan bodybuilding.
What is Vegan Bodybuilding?
Vegan bodybuilding involves developing your body to enhance lean muscle mass and minimize body fat while eliminating all animal-based foods from your diet. Veganism is a stricter form of animal-based food exclusion than vegetarianism, which excludes meat, fish, and seafood.
Vegans avoid animal products. This includes everything vegetarians avoid but adds dairy products such as milk and cheese, eggs, honey, gelatin, and food additives derived from animal sources.
Vegans fall into two categories — raw-food vegans and whole-food vegans, who only consume unprocessed or minimally processed plant-based foods.
A vegan bodybuilding meal plan differs from a standard vegan meal plan in its macronutrient content. Bodybuilders require more proteins and fats to build muscle and provide energy. The carbohydrate counts will be about the same.
Read also: 12 Vegan Bodybuilders That Will Motivate You To Go Plant-Based
Vegan Dieting for Muscle Gain & Fat Loss
Whether you are following a vegan or carnivore diet, calorie intake is a key consideration. To build muscle, you must create a caloric surplus, where you take in more calories than you expend. Conversely, to lose body fat, you need a caloric deficit so that your caloric intake is less than your body’s energy needs. This forces your body to use stored energy (body fat) to meet its daily energy needs.
The first step to determining your caloric needs is to determine your maintenance calorie level. You must consume this number of calories daily to meet your energy needs. Check out this calculator to determine your ideal daily calorie intake.
You should consume 10-15% more than your maintenance level to build lean muscle mass. So, if you require 2,500 calories per day to meet your energy needs, you should aim for between 2,750 and 2,875 calories per day to add muscle mass.
To lose body fat, consume 10-15% fewer calories than your maintenance level. At a 2,500-calorie maintenance level, you should consume between 2,125 and 2,250 daily calories.
Vegan foods are generally less calorie dense than animal-sourced foods. That means vegans may have to eat more to reach their daily calorie goal. Rather than eating three huge meals, I recommend having five or six smaller meals spread approximately three hours apart over the course of the day.
Vegan Bodybuilding Protein Sources
Vegan proteins are derived from plants. The category ‘plants’ include everything from vegetables like corn and spinach to legumes like nuts and seeds and wholegrains such as oats and rice. In fact, provided that the protein source is not an animal, it is considered a plant protein.
The Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for protein is 0.8 grams per pound of body weight. That is fine for sedentary people. However, gym goers require more than that, depending on their goals. If your goal is to build muscle mass, you should increase your protein intake to between 1.2 and 1.5 grams per pound of body weight. [1]
Benefits of Plant-Based Proteins
The biggest adjustment you’ll have to make when you turn vegan is to find new protein sources. Getting complete amino acid profiles from vegan protein sources is more challenging. Here are three reasons why it may be well worth the effort:
Weight Loss
Some research suggests that plant-based proteins are more effective than animal-based proteins at encouraging weight loss. One study published in the 2016 Journal of General Internal Medicine found that following a general vegetarian diet, including vegan protein powders, was more effective in achieving weight loss goals than non-vegetarian weight loss diets. [2]
Protein, in general, is excellent for encouraging weight loss. It is the most satiating macronutrient and takes the most energy to digest. Plant-based proteins are even better for weight loss because they have far less saturated fat and fewer calories. [3]
General Health
Many people, especially young guys, who are determined to bulk up, eat too many animal proteins. This can lead to an increased risk of heart disease and kidney complications. Another problem with too much animal protein is that it is rich in heme iron. Too much of this iron can cause oxidative stress and free radical damage.
When you choose plant-based proteins, you reduce the risk of these complications. In addition, plant proteins supply your body with important phytonutrients. These natural chemicals help prevent disease, strengthen the immune system, and help offset the natural health declines associated with aging.
Environmental Friendliness
Switching to plant-based proteins is a smart move in terms of helping the environment. Reducing animal product consumption helps reduce the carbon footprint, saves precious water, and creates far less waste.
Best Plant Protein Sources
Black Bean: 15 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Chickpeas: 15 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Edamame: 17 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Tempeh: 31 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Tofu: 20 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Lentis: 18 grams of protein per 1 cooked cup
Plant-Based Protein Powders
Although most plant-based sources of protein do not contain all of the essential amino acids, many plant-based protein powders include a blend of sources that work together to provide you with your full complement of the essential amino acids. Of all the plant-based protein powders, brown rice protein powder is one of the best. It includes peptides that boost weight loss more than white rice or soy protein. It has also been shown to reduce the glycemic index response and improve liver function.
Related: Best Vegan Protein Powders Reviewed
Vegan Bodybuilding Carbohydrate Sources
Carbohydrate sources for vegan bodybuilders will not differ significantly from those of a meat-eating bodybuilder. That’s because the best sources of healthy, muscle-building carbohydrates for bodybuilders are rice, fruits, and vegetables.
Unlike other types of food, carbohydrates become immediately available as energy as soon you put them into your mouth. If we don’t require the energy immediately, it is stored for later use. The body stores carbs as glycogen in the muscles and the liver as a source of energy for movement and daily function. [4]
However, the human body can only hold around 100 grams of glucose in the liver and about 400 grams in the muscles. When energy intake is abundant with very little energy output, the muscle and liver stores rapidly fill up, and the excess is stored as body fat.
Carbs prevent the breakdown of muscle tissue. They do this by promoting an anabolic environment, thanks to their ability to stimulate insulin release. This helps counter the catabolic state you get into when you train heavy with weights. [5]
By eating the right sorts of carbs at the right times, you can prevent muscle tissue loss and keep your metabolism revved up for optimal anabolic response and fat loss. High-intensity activity, such as weight training, is fueled by carbs through a process called glycolysis. In fact, carbs are the body’s preferred energy source for vigorous exercise. It will help you to most efficiently generate adequate energy by promoting ATP production, which is the body’s primary energy system.
When you work out, you quickly use up your body’s limited glycogen stores. Taking in carbs after your workout will restore these levels, providing the energy you need to recover and rebuild your body.
Here are some exceptional carbs sources for vegan bodybuilders:
Rice
Sweet Potatoes
Yams
Cereals
Grains
Broccoli
Asparagus
Cauliflower
Spinach
Lettuce
Brussels sprouts
Related: Carbohydrate Calculator
Vegan Bodybuilding Fat Sources
Fats are an important macronutrient for bodybuilders. Containing more than double the number of calories per gram than proteins or carbs, they represent a nutrient-dense way to up your calorie count when bulking. Fats are involved in the production of many hormones, including testosterone. They’re also a concentrated energy source, providing long-lasting energy for workouts lasting more than an hour.
Fats can be classified into three groups:
Saturated
Unsaturated
Trans Fats
By far, the worst of the three is trans fats. These have been shown to raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while, at the same time, reducing HDL (good) cholesterol. You can eat saturated fats in moderation, but the show’s real star is the unsaturated kind. These healthy fats have been shown to act in just the opposite way to trans fats — they increase HDL and lower LDL cholesterol. The more unsaturated fats you get into your day, the healthier you will be. [6]
Switch Up Your Oils
One of the best ways to add healthy fats to your meals is to remove your old cooking oil and replace it with olive oil. The active ingredient in olive oil is oleic acid, which has been shown to produce a whole host of health benefits, including reducing inflammation and fighting free radical damage.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a superstar when it comes to healthy fats. They will benefit your body and your brain, having the ability to bring down triglyceride levels, improve the symptoms of many diseases such as arthritis and Parkinson’s and improve memory and cognitive ability. The best source of omega-3 is fatty fish. You can also get them from avocados, chia seeds, walnuts, and flaxseeds. To ensure a steady daily supply of omega-3s, you can also take them in supplement form. [7]
Here are half a dozen healthy fats to include in your vegan meal plan:
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds
Avocado
Coconut oil
Nut butter
Plant-based oils
Olive oil
Related: Fat Intake Calculator
7-Day Vegan Bodybuilding Meal Plan for Bulking
Here is the seven-day vegan meal plan for bulking:
Day 1:
Meal
Foods
Protein (g)
Carbs (g)
Fats (g)
Calories
Meal 1 (8:00 AM)
Vegan protein pancakes with maple syrup and a side of fruit
30
60
10
550
Meal 2 (11:00 AM)
Tofu scramble with vegetables, whole wheat bread, and avocado
25
40
20
450
Meal 3 (2:00 PM)
Quinoa and black bean bowl with mixed veggies and guacamole
30
60
15
600
Meal 4 (5:00 PM)
Vegan protein smoothie with almond milk, banana, and peanut butter
25
50
15
500
Meal 5 (8:00 PM)
Lentil curry with brown rice and steamed vegetables
40
70
10
700
Meal 6 (11:00 PM)
Chickpea salad with mixed greens, veggies, and tahini dressing
20
30
15
350
Total
170
310
85
3,150
Day 2-7: Follow a similar pattern as Day 1, adjusting the food choices and portion sizes as desired.
Here are some food options for each meal:
Meal 1 (8:00 AM): Vegan protein pancakes made with plant-based protein powder, oats, almond milk, and topped with maple syrup. Serve with a side of fresh fruit.
Meal 2 (11:00 AM): Tofu scramble cooked with vegetables (such as bell peppers, spinach, and onions), served with whole wheat bread and sliced avocado.
Meal 3 (2:00 PM): Quinoa and black bean bowl with a variety of mixed vegetables (such as roasted sweet potatoes, corn, and bell peppers) and a dollop of guacamole.
Meal 4 (5:00 PM): Vegan protein smoothie made with almond milk, a ripe banana, plant-based protein powder, and a spoonful of peanut butter.
Meal 5 (8:00 PM): Hearty lentil curry prepared with coconut milk and spices and served with brown rice and steamed vegetables (such as broccoli, cauliflower, and carrots).
Meal 6 (11:00 PM): Chickpea salad with mixed greens, colorful vegetables (such as cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers), and a creamy tahini dressing
Related: Bulking Calculator
7-Day Vegan Bodybuilding Meal Plan for Cutting
Use the following meal plan to get peeled:
Day 1:
Meal
Foods
Protein (g)
Carbs (g)
Fats (g)
Calories
Meal 1 (8:00 AM)
Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, and berries
20
50
10
400
Meal 2 (11:00 AM)
Whole wheat toast with avocado and tomato slices
10
30
15
300
Meal 3 (2:00 PM)
Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables and chickpeas
25
40
10
450
Meal 4 (5:00 PM)
Rice cakes with almond butter and sliced banana
10
40
15
350
Meal 5 (8:00 PM)
Tofu stir-fry with broccoli, bell peppers, and brown rice
30
50
15
500
Meal 6 (11:00 PM)
Mixed nuts and seeds
15
10
20
250
Total
110
220
85
2,250
Day 2-7: Follow a similar pattern as Day 1, adjusting the food choices and portion sizes as desired.
Here are some food options for each meal:
Meal 1 (8:00 AM): Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, berries, and a sprinkle of nuts.
Meal 2 (11:00 AM): Whole wheat toast topped with mashed avocado, tomato slices, and a drizzle of lemon juice.
Meal 3 (2:00 PM): Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables (such as cucumber, bell peppers, and cherry tomatoes), chickpeas, and a light dressing.
Meal 4 (5:00 PM): Rice cakes spread with almond butter and topped with sliced banana.
Meal 5 (8:00 PM): Tofu stir-fry with broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, and brown rice, seasoned with low-sodium soy sauce or other preferred spices.
Meal 6 (11:00 PM): A handful of mixed nuts and seeds (such as almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds).
Related: Weight Loss Calculator
Vegan Bodybuilding Pros
Many people turn to a vegan lifestyle for ethical reasons. There are, though, some very practical benefits that come with adopting a vegan bodybuilding lifestyle. Here are four benefits of becoming a vegan bodybuilder:
Nutrient Density
A diet built around plant-based foods will overflow with essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals. Eating such a wealth of health-giving compounds daily will fortify your immune system, boost your natural energy reserves and keep you running on all cylinders.
Low Saturated Fats
Foods sourced from animals are much higher in saturated fats than plant-based foods. By eliminating meats and dairy products from your diet, you will reduce your LDL cholesterol level while promoting low body fat levels. Cutting out unhealthy fats will also benefit your cardiovascular system.
High Fiber Content
Plant-based foods tend to have high levels of fiber. This helps fill you up, making you less likely to snack between meals. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels, cleaning the digestive system.
Reduced Disease Risk
Several studies have shown that a vegan diet can reduce a person’s risk of contracting chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Certain types of cancer risk may even be reduced when you follow a vegan diet. [8]
Vegan Bodybuilding Cons
Along with the benefits of going vegan for bodybuilders, several potential drawbacks exist. Here are four challenges that vegan bodybuilders face.
Vegan Diets are Low in Vitamin B12 & Iron
Vitamin B12 is essential for health and vitality. It affects our energy level, mood, thinking, and even memory. When we are Vitamin B12 deficient, we will suffer from fatigue. Yet plant sources are largely deficient in B12. Those said to contain them, such as seaweed, fermented soy, and spirulina, actually include analogs of B12 known as carbamides. These actually block the absorption of B12.
It’s hardly surprising that studies consistently show a Vitamin B12 deficiency among vegans. To maintain healthy B12 levels, you must eat animal food sources or supplements.
Getting iron from plant sources is another problem. Iron derived from plants is not as well absorbed as that from animal meats. This is another contributor to low energy levels among vegans.
Vegan Diets Provide Lesser Quality Proteins
The amino acids in proteins are the body’s building blocks. The nine amino acids the human body cannot manufacture are essential and must be derived from the diet. Unlike animal protein sources, few plant sources provide all nine of them. Even with those few that do, the amino acids are not absorbed by the body like animal proteins. To absorb the essential amino acids, your body needs all of them in the same amounts and at the same time. In plants, many essential amino acids are not loaded to the quantities required for efficient absorption by the body.
A vegan’s body will compensate for the lower quality of amino acids entering the system by wasting less protein and recycling proteins. This makes the body work a lot harder. People actively trying to gain muscle mass or improve strength levels will be negatively affected by the lesser quality of proteins that are part and parcel of a vegan diet.
Vegan Diets Are Low in Vitamin K2
Calcium is required for strong bones. But few people appreciate the importance of Vitamin K2. It transports the calcium to the bones. That means that, without sufficient quantities of this vitamin, all the calcium you consume will never reach your bones. With nowhere to go, it will pile up in your arteries.
You cannot get Vitamin K2 from plants, with the exception of a fermented soybean product called natto. Unfortunately, most people cannot stand the taste of it. To get a healthy dose of K2, you must eat animal fat sources like egg yolks, milk, and cheese.
Vegan Diets Rely on Soy
Although vegan diet options have diversified in recent times, soy is still regarded as a key player. Soy has been recognized as being problematic due to its phytoestrogen content. By mimicking estrogen, phytoestrogen causes a cascade of hormonal imbalances. Among other things, this will escalate your estrogen levels dramatically. In one study, infants fed soy formula were seen to have estrogen levels between 13,000 and 22,000 times higher than those fed cow’s milk formula.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can vegans get complete protein sources?
Yes, vegans can get complete protein sources that contain all nine essential amino acids. This can be accomplished by adding the following complete plant-based protein sources to your diet:
Quinoa
Soy products
Buckwheat
Chia Seeds
Vegans can also consume two or more complementary protein sources at one meal to ensure they get all the required amino acids. For example, they can combine legumes with whole grains.
Can I retain my existing muscle if I switch to a vegan diet?
Yes, it is possible to retain your existing muscle when you switch to a vegan diet. Many bodybuilders have found they can keep their current muscle mass and add new lean muscle tissue after turning vegan. To do so, however, you need to pay careful attention to your protein intake, ensuring that you get a plentiful supply of complete proteins through protein complementing or focusing on complete proteins such as soy, quinoa, and chia seeds.
You must also ensure that you eat a caloric surplus to provide your body with the building material for new muscle. This can be challenging because plant-based foods tend to have fewer calories and fill you up faster due to their high fiber content.
How much protein do I need on a vegan bodybuilding diet?
To build muscle on a vegan bodybuilding diet, you should consume at least a gram of protein per pound of body weight. A 180-pound person should aim for around 180 grams of protein per day. If this is spread out over six meals, that averages 30 grams of protein per meal.
Is it easier to get lean on a vegan bodybuilding diet?
Many bodybuilders who have switched to a vegan diet find it easier to get lean than when eating animal-sourced products. Plant-based foods have a higher fiber content, providing a satiating effect that fills you up and helps reduce snacking and cravings between meals when you’re dieting. Vegan-friendly foods are also much lower in saturated fats than animal foods. This helps with fat control and improves your cardiovascular health. Finally, vegan-friendly foods generally have a much lower calorie density, allowing you to eat to satisfaction while still maintaining a low caloric intake.
How does a vegan bodybuilding diet differ from a standard vegan diet?
The main differences between a vegan bodybuilding diet and a standard vegan diet are that the bodybuilding diet is higher in proteins and fats, and the caloric intake is targeted to create either a caloric surplus or deficit based on a person’s training goals. Vegan bodybuilders are also likely to follow a precise nutrient timing protocol. They increase protein and carbohydrate intake around their workouts for optimal protein synthesis and muscle glycogen replenishment.
Wrap-Up
By following a high-quality vegan bodybuilding plan, you can maximize your muscle-building potential while ensuring your body receives only the best plant-based foods. This will make it easier to stay lean while optimizing your energy output and enhancing your overall well-being.
Follow either one of the seven-day vegan bodybuilding meal plans, depending on whether you are in a bulking or cutting phase. Then, use it as a template and general guide, substituting your favorite plant-based foods to add variety and taste. After 12 weeks, transition into the opposite phase (cutting or bulking), adjusting your training accordingly and switching to the other seven-day vegan bodybuilding meal plan provided above. Follow this plan for another 12 weeks, again substituting your favorite vegan meals. Combine your vegan bodybuilding meal plans with consistent, hard training and plenty of rest and recovery, and you’ll be well on your way to realizing your goal physique.
References
Schoenfeld BJ, Aragon AA. How much protein can the body use in a single meal for muscle-building? Implications for daily protein distribution. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Feb 27;15:10. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0215-1. PMID: 29497353; PMCID: PMC5828430.
Huang RY, Huang CC, Hu FB, Chavarro JE. Vegetarian Diets and Weight Reduction: a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Gen Intern Med. 2016 Jan;31(1):109-16. doi: 10.1007/s11606-015-3390-7. PMID: 26138004; PMCID: PMC4699995.
Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Nieuwenhuizen A, Tomé D, Soenen S, Westerterp KR. Dietary protein, weight loss, and weight maintenance. Annu Rev Nutr. 2009;29:21-41. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-080508-141056. PMID: 19400750.
Schneeman BO. Carbohydrates: significance for energy balance and gastrointestinal function. J Nutr. 1994 Sep;124(9 Suppl):1747S-1753S. doi: 10.1093/jn/124.suppl_9.1747S. PMID: 8089744.
Alghannam AF, Gonzalez JT, Betts JA. Restoration of Muscle Glycogen and Functional Capacity: Role of Post-Exercise Carbohydrate and Protein Co-Ingestion. Nutrients. 2018 Feb 23;10(2):253. doi: 10.3390/nu10020253. PMID: 29473893; PMCID: PMC5852829.
Harrison S, Lemieux S, Lamarche B. Assessing the impact of replacing foods high in saturated fats with foods high in unsaturated fats on dietary fat intake among Canadians. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Mar 4;115(3):877-885. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab420. PMID: 34958344; PMCID: PMC8895210.
Simopoulos AP. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002 Oct;56(8):365-79. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(02)00253-6. PMID: 12442909.
Hever J, Cronise RJ. Plant-based nutrition for healthcare professionals: implementing diet as a primary modality in the prevention and treatment of chronic disease. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2017 May;14(5):355-368. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.05.012. PMID: 28630615; PMCID: PMC5466942.
Calories Per Gram Calculator
Are you looking to convert the amount of macronutrients from grams to calories? Look no further! Our Grams to Calories Calculator is a simple and convenient tool that allows you to convert the grams of macronutrients into their corresponding calorie values. Whether you want to track your daily intake, maintain a healthy diet, or achieve your weight goals, this calculator will be your go-to resource.
Calories Per Gram Calculator
Calculate
Clear
Calories Breakdown
Macronutrient
Grams
Calories
Carbohydrates
0
0
Proteins
0
0
Fats
0
0
Total Calories
0
0
Protein and carbohydrates provide 4 calories per gram, while fats offer a substantial 9 calories per gram. This user-friendly macronutrient calculator is here to assist you in computing the total calories derived from proteins, fats, and carbs in any given meal, ensuring an accurate overall calorie count.
Understanding the Conversion: Grams to Calories
Food labels often provide information about the total calories and grams of macronutrients present, but they rarely mention the specific calorie breakdown for each macronutrient. That’s where our calculator comes in handy. By using it, you can easily understand the relationship between grams and calories and learn the conversion rules.
Let’s take a closer look at the calorie content of each macronutrient:
How Many Calories in a Gram of Carbohydrates?
In general, carbohydrates provide approximately 4 kilocalories (kcal) per gram. Simple sugars offer around 3.87 kcal per gram, while complex carbohydrates range from 3.57 to 4.12 kcal per gram. For simplicity, the conversion is often rounded to 4 kcal per gram.
Try Carbohydrate Intake Calculator!
How Many Calories in a Gram of Protein?
Protein also provides around 4 kcal per gram. It plays a vital role in cell structure and function, and you must obtain it from your diet since the human body cannot synthesize all necessary amino acids.
Try Protein Intake Calculator!
How Many Calories in a Gram of Fat?
Among the macronutrients, fat has the highest calorie content. Each gram of fat provides 9 kcal. Fats are essential for various bodily functions, including maintaining cell membranes, regulating body temperature, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Try Fat Intake Calculator!
How Many Calories in Alcohol?
Alcohol contains 7 kcal per gram. To calculate the calories from alcohol, multiply the amount of alcohol in grams by 7. For example, if you have 50 mL of vodka with an alcohol content of 40%, the calculation would be 7 kcal/g × 50 mL × 0.40 × 0.78924 g/mL = 110 kcal.
Gram to Calorie Conversion Table
Convert the macro’s nutritional values by the this calculator precisely.
Gram
Calories
1g
7.7162 kcal
2g
15.43 kcal
3g
7.7162 kcal
4g
23.15 kcal
5g
30.86 kcal
6g
38.58 kcal
7g
46.3 kcal
8g
54.01 kcal
9g
61.73 kcal
10g
69.45 kcal
15g
108.03 kcal
20g
146.61 kcal
25g
185.19 kcal
30g
223.77 kcal
35g
262.35 kcal
40g
300.93 kcal
Understanding Calories: Calorie vs. Kilocalorie
When discussing calories, it’s important to note that there are two main definitions:
Small calorie or gram calorie (cal): This is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius.
Large calorie, food calorie, or kilocalorie (Cal, calorie, or kcal): This is the unit commonly used in nutrition to express the energy value of food and drinks. It’s equivalent to 1,000 small calories.
In the context of nutrition, the terms “calories” and “kilocalories” are often used interchangeably. So, when using our grams to calories calculator, you may come across both terms referring to the same conversion.
Practical Example: Converting Grams to Calories
Let’s walk through a practical example to understand how to convert grams to calories using our calculator. Suppose we have the following nutritional information for a food product:
Carbohydrates: 25 grams
Protein: 10 grams
Fat: 10 grams
To calculate the total calories in this food product, we apply the appropriate conversion rate for each macronutrient:
Carbohydrates: 4 kcal/g × 25 g = 100 kcal
Protein: 4 kcal/g × 10 g = 40 kcal
Fat: 9 kcal/g × 10 g = 90 kcal
Total: 100 kcal + 40 kcal + 90 kcal = 230 kcal
Therefore, this particular food product contains 230 calories.
Benefits and Applications
Now that you understand how to use the Grams to Calories Calculator,
let’s explore some practical applications:
Following a Healthy Diet: The calculator helps you maintain a balanced and nutritious diet by tracking the calorie content of macronutrients. By knowing the calorie breakdown of your meals, you can make informed choices and meet your energy requirements effectively.
Monitoring Energy Intake: Whether you’re trying to lose, maintain, or gain weight, understanding the calories you consume is crucial. Our calculator enables you to monitor your energy intake accurately and helps you make adjustments to achieve your weight goals.
Supporting a Healthy Lifestyle: By being aware of the calorie content in your food, you can make conscious decisions about your eating habits. Additionally, the calculator provides insights into the calorie content of alcohol, which can be beneficial for those interested in mindful drinking.
FAQs about Grams to Calories Conversion
How many calories are in a pint of beer?
The calorie content of a pint of beer typically ranges from 160 to 180 kcal, depending on the beer type. This estimate takes into account the calories derived from the alcohol content (7 kcal/g) as well as the calories contributed by carbohydrates (4 kcal/g). For example, a pint of 5% beer contains approximately 130 kcal from alcohol and 40 kcal from carbohydrates.
How many grams are in 200 calories?
For carbohydrates and proteins, approximately 50 grams are equivalent to 200 calories. However, for fats, 200 calories would be approximately 22.2 grams.
Why does fat have 9 calories?
Fat contains a higher number of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The bonds within these atoms store more energy, resulting in a higher calorie content. As a result, fats provide 9 calories per gram.
What is the calorie content of 1 pound of fat?
One pound of body fat is estimated to contain approximately 3,500 calories. Therefore, to lose 1 pound of body fat, you need to create a calorie deficit of 3,500 calories. It’s recommended to aim for a healthy calorie deficit of around 500 calories per day to achieve gradual and sustainable weight loss.
Which macronutrient has the most calories per gram?
Fats have the highest calorie content per gram, providing approximately 9 calories per gram. In comparison, both carbohydrates and proteins offer around 4 calories per gram. However, it’s important to consume fats in moderation and choose healthier sources of fat, such as unsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish.
Related Calculators:
Wrapping Up
In summary, our Grams to Calories Calculator is a valuable tool that simplifies the conversion of macronutrients from grams to calories. By utilizing this calculator, you can easily understand the calorie content of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and even alcohol. Start tracking your macronutrient intake, achieve a healthy weight, and make informed dietary choices today!

‘Bodybuilding’s Kendall Jenner’ Vladislava Galagan Reveals Her Daily Protein & Carbs Intake
Vladislava Galagan has been making headlines in the fitness space for her resemblance to American media personality and socialite Kendall Jenner. The difference is she’s much more muscular than the Keeping Up with the Kardashians star. In a recent interview uploaded on YouTube, Galagan revealed her daily macro intake to maintain her jacked physique.
Social media platforms provide a convenient way to amass fame and fortune online given one manages to build a following. There have been various different kinds of audiences that influencers have found. Liver King is one of the most popular names who went viral for eating raw cuts of meat and insane workout routines. Joey Swoll is another recognizable figure in the fitness community who found success on such platforms. He promotes making gyms a safe space for everyone and has a positive crowd that pushes back on the rise in toxic gym culture.
Vladislava Galagan went viral for her unreal muscle mass, size, and similarity to Kendall Jenner earlier this month. The Russian model found a passion for fitness and working out in her teen years about a decade ago. She boasts a pretty feminine face with an incredibly jacked physique that often leaves people stunned at first view. She even faced accusations of faking her build using CGI technology or Photoshop.
Galagan admitted to taking steroids to achieve her physique but insisted the importance of proper nutrition and training could not be neglected.
The 27-year-old has a large audience of a million on Instagram and maintains an active OnlyFans account, which has proven to be a lucrative opportunity for her. She disclosed she earns an eye-watering $10,000 each month by uploading racy content showing off her gigantic arms and washboard six-pack abs. She tends to stay away from the more x-rated requests and reported having success with arm wrestling clips.
‘Bodybuilding’s Kendall Jenner’ Vladislava Galagan reveals her daily macro intake
In a recent YouTube video, Vladislava Galagan revealed her daily macro intake.
Galagan’s daily macro breakdown: 120g protein, 180g carbs, and 80g fats.
Vladislava Galagan / Instagram
Vladislava Galagan continued to improve her personal fitness after making her bodybuilding debut in 2018. She consumes four meals a day with her protein sources coming from meats like beef, chicken, and fish. She follows a strict training plan hitting the gym six days a week for about 90 minutes each, targeting every muscle group twice with three sessions reserved for cardio.
Galagan has shown no signs of slowing down anytime soon. Considering she’s only in her twenties, it will be interesting to see how her physique changes over the next years.
You can watch the full video below.
Related: Calculate your optimal daily protein intake with the best protein calculator
Published: 20 May, 2023 | 12:08 PM EDT
Female Muscle Growth: Unleash Your True Potential
Traditionally, muscle and women haven’t gone together. The overriding view has been that muscle will make a woman look manly, less athletic, and less feminine. Thankfully, we are entering into a more enlightened age. Millions of ladies around the world have discovered the truth about what eating and exercising to add muscle to their physique can do for them. Building muscle can help women:
Improve their figure
Eliminate body fat
Improve aesthetics
Boost strength, self-confidence, and inner conviction
As a personal trainer, I’ve spent 35+ years introducing women to the benefits of muscle training and working with them to get serious about weight training and nutrition to create a toned, athletic, muscular body.
In this article, I lay out a complete beginner’s guide to female muscle growth.
Taking Stock
When you start on a journey, you need a roadmap. It’s the same thing with building muscle. That roadmap begins with an assessment of where you are starting from. To find that out, you need to take some vital statistics.
Take the following body measurements:
To do this, you’ll need a smart scale. You can pick up a good one for around $80. These scales pair to a phone app to provide you with important data, including your lean body mass and body fat percentage.
To take your body measurements, you will need a tape measure.
Measure the following body parts:
Upper arm (flexed)
Chest
Stomach (around the belly button)
Hips
Mid Thigh
Take these body measurements once every week to assess your progress. Be aware, though, that you will be reshaping your body by both losing fat and adding muscle. Because muscle is heavier than fat, you may not lose as much weight on the scale as expected. The key parameters to focus on are your body fat percentage and lean body mass.
How Should Women Train?
The idea that women are delicate beings persists. As the saying goes, they are the weaker sex – the rose to the man’s thorn. Men are meant to be the strong ones. It may be sexist and stereotypical, but it’s still stuck in our collective mindset.
That’s why you can still walk into any gym and see the racks of heavy iron on one side, all dark and imposing – and then the tiny, cute pink dumbbells on the other. That’s the women’s side. Well, it’s time to blast the notion that men and women, with the same goal, need to train differently out of the water once and for all.
Muscle is Muscle
Women do not need to train differently than men to build muscle. Until one of us – men or women – starts restructuring our cell’s molecular composition or growing new types of muscle fiber, we all need to train in the same manner. You see, whether a muscle belongs to a man or a woman, it will react to stress in the same way. It will need the same type of stimulus to grow, the same form of fuel to repair itself, and an identical amount of rest to recuperate. So, fundamentally men and women should train the same.
Differing Goals
Weights are a tool. What we want to achieve from the tool will dictate how we use it. Some female weight trainers desire muscular size and strength gains, while others are after a toned, shapely look. Those goals require different workout plans.
For size and strength, you’ll train super heavy with lots of sets to failure and relatively low reps. Those more intent on defining and shaping the muscle should perform sets in the 8-30 rep range and include isolation exercises. Notice, though, that it is the goal and not the gender that determines the nature of the weight training. After all, there are many women out there who do desire larger, stronger muscles. These women will train just like men to achieve their goals.
Meet Your Muscles
The first step toward adding lean muscle mass to your body is to become aware of the different muscles that make up your amazing body.
Here’s an overview:
Shoulders
The shoulders consist of three muscles — the front, side, and rear deltoids. The shoulders pull the humerus (upper arm bone) out to the side (middle delt), out to the front (front delt), and behind the body (rear delt). Here are shoulder workouts for designed for women.
Chest
There are two parts to your chest muscles — the pectoralis major and minor. The pec major sits on top of the pec minor. The main job of the chest is to push your arms away from your body and towards its center line.
Trapezius
The trapezius, or traps, is a kite-shaped muscle that covers the area from your neck to the mid-spine. It allows the scapular bones to move up and down and in and out.
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi (or lats) is a large muscle that originates at the ribs and inserts at the top of the humerus. Well-developed lats give a pleasing ‘V’ shape to the torso.
Erector Spinae
The erector spinae are the muscles at the base of the spine. They run all the way from the pelvis up to the neck. Its main job is to extend or pull back the spine.
Biceps
The biceps are a two-headed muscle. Their main function is to flex the elbow, bringing the wrist up towards the shoulder. They also assist in wrist supination. Here are three arm workouts specifically designed for women.
Triceps
The triceps, at the back of your upper arm, is a three-headed muscle group. All three heads originate at the shoulder joint and insert on the elbow. The job of the triceps is to straighten the arm through elbow flexion. It is the antagonist (opposite) muscle to the biceps.
Abdominals
The abdominals are a flat muscle band covering the lower front torso. These muscles allow for flexion of the torso, bringing the chest toward the knees.
Quadriceps
The quadriceps comprises four heads, which run from the hip/pelvis to the knee. These muscles combine to perform flexion and extension of the knee, as well as lateral and medial rotation.
Calves
Two muscles make up the calves — the gastrocnemius, which flexes the ankle, and the soleus, which assists in that ankle flexion.
Glutes
There are three parts to your glute (butt) muscles — the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. These muscles combine to allow for hip extension, abduction, and rotation. Additionally, here are three glute workouts specifically tailored for women.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings are sometimes known as the leg biceps. That’s because they do the same job as the biceps, which is to flex and extend the limb’s joint — in this case, the knee. It is the antagonistic muscle group to the quadriceps.
How to Get More Out of Your Muscle Growth Workouts
Building muscle is hard work, and it’s even harder for women than it is for men. That’s because they have less testosterone coursing through their veins. If you want to be successful, you need to be totally locked in when you are on the gym floor. Here are five training tips to help you optimize your workouts:
1. Get Rid of Distractions
When you are in the gym, you need to be in the moment with what you are doing. Every distraction needs to be eliminated so that you can focus like a laser beam on the movement that your body is undergoing.
That means the gym is not a place for your smartphone, social chit-chat, or daydreaming about what you’ll do on the weekend. Leave that to the wannabes who will be spinning their wheels for the next five years.
You also have to turn off the negative voice inside your head that is constantly telling you that you can’t do what you intend to do. We all have that voice. It’s the ones of us who can quash it who are the ones who make real gains. When you can override the voice that tells you to bail out of a set because you could be late for the next appointment or overtrain, you can push your set to the required limit.
2. Two Key Body Position Changes
The positioning of your elbows and your sternum is something that most weight trainers don’t really think about. However, they are vital to optimal performance. Rather than starting a lift with rounded shoulders, think about pulling your shoulders back and extending the chest. You can do this by pulling the shoulder blades back and together while also lifting the sternum.
When you are performing any pulling type of resistance exercise, don’t think about pulling with your hands. Rather focus on pulling from the elbows so as to bring them back and behind your torso. Consider your hands and forearms simply to be the hooks that connect your elbows to the resistance.
4. Put Yourself on the Clock
You’ll recall that earlier I stated that the gym floor is no place for your smartphone. The exemption to that rule is that you can utilize the stopwatch function on your phone to increase the intensity of your training. Of course, you can only do this if you have the discipline not to use any of the social media features of your phone while you’re training. If you can’t, go out and buy a simple stopwatch!
The first thing you can do with your stopwatch is to limit your rest between sets. This could be 30, 60, or 90 seconds, according to your training goals, but the key is to keep it consistent.
You can also use your stopwatch on finishing exercises in order to get the most out of your body-part training. For example, let’s say that you’ve come to the end of your shoulder workout.
Set your stopwatch for 60 seconds and then grab a relatively light pair of dumbbells and hold them out at a 45-degree angle from your body as the stopwatch counts down for 60 seconds. As soon as your time is up, start pressing the weights overhead. Your goal is to get to 50 reps, but you won’t get there. Let’s say you get to 29 reps and then can’t do another one. Now you have to immediately go back to that static hold but this time for 30 seconds. Once that is done, continue your pressing reps. If you get right through to 50 reps, then you are done. But if you fail before 50, you have to do another 30 seconds hold before continuing.
This is a great finisher that can be adapted to any body part.
4. Minimize Energy Links
Many lifters are losing out on a lot of their strength potential by inadvertently causing energy leaks. Often these occur through the core area. In effect, they steal away from the upward-lifting power you exert by using it for horizontal bracing.
You can easily overcome this problem by bracing or tightening your core on every repetition that you perform. You can do this by pulling your lats down while tightening your abs and squeezing your pectoral muscles.
Another important cue that will allow you to stop energy leaks is to forcefully squeeze your glutes at the top of a rep. This will ensure maximum stability.
5. Descending Sets
Descending sets are a great way to extend a set to eke out the last bit of possible movement from the target muscle. It involves performing a set number of reps with a given weight, then dropping the weight slightly, and going for the same number again. Repeat this process for four or five drops until you are working with half of your original weight (though it will feel like twice as much).
As an example, consider the standing overhead shoulder press. Stand in front of a dumbbell rack and grab a pair that will allow you to get a good six reps. Perform your set and then
re-rack the weight. Immediately pick up the next pair and rep out another six reps. Keep going down the rack for another three drops without any rest. Your delts will be on fire, and your gains will be guaranteed.
What Really Happens When You Work Out?
You’re at war with the weight when you’re in the gym. You imagine that the weight is mocking you, laughing at your inability to lift it. So, you throw yourself against it with maximum intensity. You leave nothing on the gym floor. When you walk out of there, your muscles are quivering and pumped to the max.
And, yet, you haven’t built one ounce of muscle.
In fact, you’ve done just the opposite. Your intense training has broken your muscles. The immense challenge of lifting all that weight has caused minute tears in their
fiber. When you walk out of the gym, you are in a catabolic (muscle-depleting) state.
It’s what happens after the workout that determines whether or not you build any mass. That’s because growth happens during the recovery phase, not during the training phase.
The Importance of Recovery
Your workout has paved the way for muscle growth. What is needed now is muscle recovery, which involves re-feeding, resting, and recuperating. By doing these things, you can
repair the microfiber damage that has been done to the muscle fiber. If you provide it with the correct nutrients and sufficient recovery time, your muscle will grow bigger and stronger.
If you don’t recover sufficiently, however, the opposite will happen. Rather than getting bigger and stronger, your muscles will get smaller and weaker. That’s because you won’t be giving it
the opportunity to repair the damage you’ve inflicted upon it during your workout.
Here are four tips to help you to optimize your workout recovery:
Know When to Stop
We’ve all heard the phrase, “No pain, no gain,” right?
Well, many trainers lack the experience to understand the difference between beneficial muscle extension and contraction pain that engorges the muscle cell with blood and lactic acid and the pain that is actually harming their body.
As a result, they slip into an overtrained state, which dramatically impairs their recovery ability.
You don’t want to push your body to the limit in every single workout. Sure, there’s a place for taking your training to the limit, but there’s also a place for pushing just a little beyond your comfort zone.
Make it your goal to do a little bit more than you did last workout, not to destroy the muscle.
Take Stretching Seriously
Most people who work out don’t take stretching seriously. If they do it at all, it’s usually just a few seconds that mimics the exercises they’re about to do. Stretching, though, is an important part of the muscle-building and recovery equation.
A stretched muscle is a more flexible muscle. Stretching the muscle allows you to perform your exercises through a complete range of motion. However, stretching after your workout is even more important.
During your training, you have built up a great deal of muscular tension. Incorporating stretching as part of your cool-down routine will reduce this tension while lessening post-workout muscle soreness.
Improve the Quality and Quantity of Your Sleep
Sleep is an underrated part of recovery. Yet, it is the period when the vast majority of the muscle recovery process occurs.
When you get 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night, your body can go to work to repair and rebuild muscle tissue that has been broken down during your workout. It can do this more effectively because it doesn’t have to carry out the myriad of other daytime functions it is called upon to perform.
During deep sleep, two vital muscle-building hormones are released at maximum levels. These two hormones – testosterone and growth hormone – will greatly boost the muscle repair process.
For the effects of sleep to provide maximum recovery benefits, you need to stick to a regular night-time schedule that gives you 7-8 hours of sleep each night. Take a slow-release casein protein supplement 30 minutes before bed to provide your muscles with the required nutrients for cell repair.
Stay Hydrated
Your entire body performs better when you drink water. You will be able to absorb nutrients more quickly and effectively, which will help you get crucial amino acids into the muscle cell more quickly.
Aim to drink half a gallon (around 2 liters) of water daily.
Nutrition for Female Muscle Growth
What you eat is the most important factor for adding muscle to your body. Food provides the nutrients that fuel your muscle cells and the building blocks to create new muscles. All the training in the world will not bring results unless it is supported by sensible, quality nutrition.
Macros
Food has three main, or macro, nutrients — protein, carbohydrates, and fat.
We measure the energy in foods in calories. There are four calories in one gram of protein and carbs and nine calories in one gram of fat.
All three of the macros are needed by the body. When it comes to building muscle, however, the most important macro is protein. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Carbohydrates are also important as they provide the energy to fuel you through your workouts.
We suggest the following macronutrient ratio:
50% carbs
30% protein
20% fat
Focus on lean protein sources:
In terms of carbohydrates, concentrate on green leafy vegetables, starches such as sweet potatoes and yams, rolled oats as well as fruits like bananas and apples.
Supplements for Female Muscle Growth
Working out places a lot of stress on the body. To meet those demands and undertake the needed bodily repair and recovery, you need more nutrients than sedentary people. Even when you are following a healthy, balanced diet, there are several nutrients you probably won’t get in sufficient quantity to meet your body’s needs. That’s where supplements come in.
Here are seven proven muscle-building supplements that you should consider:
1. Beta-Alanine
During your workout, when insulin levels are high, beta-alanine rushes into the muscle fiber, where it combines with the amino acid histidine to form carnosine. Carnosine helps buffer the acidity level inside muscle fibers so they can contract with more strength for longer periods.
Research shows that supplementing with beta-alanine increases muscle strength, power, and endurance. [1]
Ideal dosage for females: 2-4 g
2. Creatine
Several studies have shown that creatine can improve power and strength when combined with resistance training. It delivers the extra phosphocreatine your body needs to restore its ATP (adenosine triphosphate) stores. ATP is the body’s main energy source. Yet, after around 10 seconds of intense exercise, your body will exhaust its ATP supplies. Creatine will provide the boost you need to complete those last couple of muscle-stimulating reps. [2]
Many people choose to take their creatine separately from their pre-workout.
3. Tyrosine
The amino acid tyrosine has been clinically proven to increase training endurance without any jittery side effects. It also improves stamina and focus. The body uses it as a precursor to the key neurotransmitters epinephrine and dopamine. [3]
Ideal dosage for females: 1-3 g
4. B Vitamins
The B-complex vitamins, especially B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cobalamin), are vital for the body’s energy-producing process. Their main job is to convert food into energy. Other B-complex vitamins to look out for are thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), and folate (B9). [4]
Ideal dosage for females: B6 (50-100 mg); B12 (50-400) mcg [micrograms]
5. Caffeine
We all know that caffeine is a powerful central nervous system booster. However, the voluminous research on the world’s most popular stimulant has also been shown to be a powerful strength and muscle builder and a blunter of muscle pain. Look for the anhydrous form of caffeine, which has been shown to be the most effective. Be sure to stay under the maximum recommended dosage to avoid a dramatic energy crash and jittery reaction. [5]
6. Citrulline
The body takes citrulline and converts it into arginine. It then becomes nitric oxide (NO). To achieve a pump in the gym, you need to boost your NO levels. NO is a vasodilator that expands the blood vessels to allow more blood to surge into the muscle.
Taking citrulline before arginine will boost the body’s blood levels of arginine. Arginine taken directly will see a lot of it taken up by the intestines. [6]
Ideal dosage for females: 3-6 g
7. Arginine
Arginine converts directly to nitric oxide in the bloodstream. To get as much arginine as possible, look for alternatives to L–arginine as arginine-AKG or arginine-HCL. [7]
Ideal dosage for females: 3-5 g
6 Myths About Women & Weights — Busted!
Weight training has come a long way in the last few decades. Years ago, even men were told that lifting weights would make them slow and muscle-bound; that athletes would lose their edge; and that, really, there was very little benefit to the whole thing.
Today, we know that none of those things are true! But when it comes to women and weights, many myths still prevent women from getting the figures they want in the gym.
It’s time to set the record straight once and for all with six of the most common misconceptions about women, weight training, and muscle.
1. Weight Training Will Make Women Look Masculine
Dana Linn Bailey via @danalinnbailey
Let’s get this right from the outset: women will never develop the muscles of a man unless they take a whole lot of artificial testosterone (i.e., steroids). Women simply do not have enough of it naturally. Testosterone, the main driver of muscle growth, is a male hormone, meaning women have between 90 and 95 percent less of it than a guy.
The result of lower testosterone levels is that women will have to work very hard and with a lot of determined focus to add every pound of muscle to their bodies. They won’t get bulky by accident!
The great thing about weight training is that it is a tool that allows you to shape your body the way you want. If you want to achieve a slightly bulkier body like Dana Linn Bailey, you can do that. However, if your goal is to end up with a lean, athletic body like three-time Bikini Olympia champion Ashley Kaltwasser, then you can do that, too!
2. Women Should Train Differently From Men
Of course, there are some major anatomical differences between men and women. When it comes to our skeletal muscles, however, we are pretty much identical. There are obviously differences in muscle size, and women have more slow-twitch muscle fibers than men. However, men and women have the same muscle insertion and attachment points, and the fibers travel in the same direction. That’s all that counts when it comes to working out with weights.
Take the quadriceps muscles. You have four of them (hence the name). So does every guy. All four of those quad muscles attach and insert in the same places. That means the exercises that will best strengthen and build the quadriceps for you are the same ones that will strengthen and build the quadriceps for a guy.
The same thing goes for every muscle in your body.
Bottom line: The same exercises are needed for women and men to get bigger and stronger muscles.
3. Olympic Lifting is Too Dangerous for Women
Olympic lifting mainly refers to two specific lifts;
There are several variations of these two moves, which are done in the gym. They are all functional compound movements that will make you get strong fast. They will also help you burn off body fat and improve your muscular and cardiovascular endurance.
Olympic lifting can be dangerous, but so can running on the treadmill. So long as you learn the proper technique, warm up properly every time, and progressively increase your resistance, you will benefit immensely by adding Olympic lifts to your routine. Start with just an unloaded bar and go from there.
4. Women Should Use Light Weights & High Reps to Get Toned
There’s no such thing as ‘toning’ a muscle. There is only making it stronger, bigger, and more defined. As we have already discovered, working on your nutrition is key to getting defined muscles. Calorie-burning exercises like full-body compound strength training workouts will also help remove body fat and enhance your muscular definition.
Light weights are beneficial as part of a complete weight training program. Your body has two types of muscle fiber: fast twitch and slow twitch. Doing high reps (as high as 50 reps) and low reps (as low as 6 reps) will help you develop all of your muscle fibers. But concentrating on high reps in the belief that it will get your muscles more defined is a myth that needs to be buried once and for all!
5. Stick to the Treadmill to Get Lean
Getting lean includes:
Stripping off body fat
Developing muscle
When it comes to removing fat from your body, 75 percent of your results depend on what you put in your mouth. To lose fat, you must create a caloric deficit, which requires eating fewer calories daily than your body burns.
You also need to expend more energy throughout the day. The best form of exercise to do that is debatable, but one thing is certain: weight training helps remove fat while strengthening and building muscle. Walking, or even running, on the treadmill will not build muscle.
A smart training plan will combine strength training with a high-intensity form of cardio training called HIIT — exactly like you’ll find in my FitQueen Challenges.
6. Older Women Should Avoid the Weight Room
Nothing could be further from the truth!
A plethora of research over the last few years is establishing strength training as the most important thing people over 50 can do to turn back the signs of aging. In the past, the few seniors who discovered the benefits of strength training in these studies did so as part of their rehab program after an injury or accident. We now know that proactively beginning a strength training program in your 40s or 50s can help prevent accidents or injuries from occurring in the first place.
Studies conducted over the past decade have shown that regular strength training can significantly reduce the symptoms of the following age-related conditions:
Arthritis
Poor balance
Diabetes
Osteoporosis
Obesity
Back pain
Breathing problems
Depression
Dementia
In addition to making you far less likely to suffer from these and other health conditions, strength training will make you more functional in your everyday tasks.
And don’t think that just because you’re in your 60s or 70s, you need to stick to the baby weights. Your muscles, joints, and bones will respond just as well to heavy weights as those of a 20-year-old!
Wrap Up
The days of women working out with pretty pink weights to ‘tone’ their bodies are over. Today’s woman wants an athletic, muscular, lean physique, and she knows that she’s got to get serious in the gym to get it.
In this article, we’ve discovered that you have to train just as hard and heavy as the guys to build muscle. We’ve also seen that what you eat matters. Focus on lean proteins, complex carbs, and the key supplements we identified. Train consistently, eat smartly, and focus on recovery and you will steadily add the lean muscle that you desire.
References
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. beta-Alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00397.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 9. PMID: 17690198.
Cooper R, Naclerio F, Allgrove J, Jimenez A. Creatine supplementation with specific view to exercise/sports performance: an update. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012 Jul 20;9(1):33. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-9-33. PMID: 22817979; PMCID: PMC3407788.
Ipson BR, Green RA, Wilson JT, Watson JN, Faull KF, Fisher AL. Tyrosine aminotransferase is involved in the oxidative stress response by metabolizing meta-tyrosine in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 14;294(24):9536-9554. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004426. Epub 2019 May 1. PMID: 31043480; PMCID: PMC6579467.
Kennedy DO. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients. 2016 Jan 27;8(2):68. doi: 10.3390/nu8020068. PMID: 26828517; PMCID: PMC4772032.
Fisone G, Borgkvist A, Usiello A. Caffeine as a psychomotor stimulant: mechanism of action. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Apr;61(7-8):857-72. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3269-3. PMID: 15095008.
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 9750, Citrulline. Retrieved May 14, 2023.
McConell GK. Effects of L-arginine supplementation on exercise metabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2007 Jan;10(1):46-51. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32801162fa. PMID: 17143054.
