Tag: muscle growth
HGH Men
“HGH Men Discover the powerful benefits. This article explores common dosages and durations for beginners, intermediates, and advanced athletes, as well as the role of HGH in anti-aging. Learn how HGH can enhance muscle growth, promote fat loss, aid in recovery, and optimize performance for male athletes.”

SARMS FOR SALE
SARMS for Sale: Unlocking the Potential of Ostarine MK-2866, Cardarine, and RAD-140 by SARM Sciences When it comes to SARMS (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators), SARM Sciences stands as a trusted brand offering high-quality products. In this article, we will explore the benefits of three popular SARMS sold by SARM Sciences: Ostarine MK-2866, Cardarine, and RAD-140….
Steroids Forums at MuscleChemistry Informative and Secure
Steroids Forums at MuscleChemistry MuscleChemistry.com stands as a leading platform in the bodybuilding community, offering a secure and private space for individuals to discuss and share knowledge about anabolic steroids. With its offshore dedicated servers, MuscleChemistry.com ensures a high level of privacy and security for its members. In this article, we will delve into the…
IGF-1 Insulin-Like Growth Factors in Bodybuilding
Unleash the power of IGF-1 in bodybuilding to maximize your muscle growth, recovery, and performance. Discover the benefits of IGF-1 LR3, the recommended dosages for beginners, intermediate, and advanced bodybuilders, and how to safely incorporate this potent growth factor into your bodybuilding journey. Unlock your full potential and achieve optimal results with the help of IGF-1.
Does Alcohol Affect Muscle Growth?
Alcohol is part of many people’s life. From the occasional celebratory drink to regular weekend-long benders, a large percentage of the population enjoys consuming alcohol. Of course, some people prefer to abstain and don’t drink alcohol at all. But this article is not for them!
Whether you limit yourself to a couple of drinks a month or are a regular happy hour attendee, you probably want to know if and how drinking alcohol affects muscle growth.
The bad news is that alcohol can hurt your gains, especially when consumed regularly and to excess.
In this article, we reveal how alcohol affects muscle growth.
Alcohol and Muscle Protein Synthesis
Muscle is constantly being broken down and rebuilt. This is called muscle protein synthesis, or MPS for short. Your workouts cause increased muscle breakdown, and your diet provides the amino acids your body needs to repair and build your muscles and make them bigger and stronger. Try our Protein Intake Calculator.
So, to increase muscle size, muscle building must exceed muscle breakdown.
Unfortunately, studies show that drinking alcohol, especially in large quantities, can decrease muscle protein synthesis (1). It seems that alcohol disrupts the signaling pathways that tell the body how to build muscle. Alcohol consumption can reduce MPS by as much as 37% compared to not drinking alcohol after training.
So, while you can still drink alcohol and build muscle, your rate of progress is likely to be significantly slower. As such, you should avoid consuming alcohol after training and for the next 24-48 hours, which is when MPS tends to be highest.
Alcohol and Testosterone Production
Testosterone is one of the prime anabolic or muscle-building hormones. Working alongside human growth hormone and insulin growth factor-1, testosterone directly and indirectly drives muscle growth.
Testosterone Molecular Structure
Men produce testosterone in their testes, while women make it in their ovaries, and men typically have ten times more testosterone than women. This is why men are generally more muscular than women and find it easier to build muscle mass.
Testosterone is such a potent muscle builder that some athletes and bodybuilders use exogenous testosterone to raise their levels abnormally high. Most anabolic steroids are testosterone derivatives.
Unfortunately, alcohol is bad for testosterone production, and excess consumption can significantly lower your testosterone levels. It appears that, in large quantities, alcohol is toxic to the testes.
While 1-2 drinks won’t have much, if any, impact on your testosterone levels, consuming 4-8 drinks can lower testosterone levels by as much as 40% (2). Regular heavy drinking can even result in testicular atrophy or shrinkage.
Needless to say, this is a literal kick in the balls for muscle growth!
The good news is that this testosterone-lowering effect only lasts a day or so, meaning the occasional big night out won’t hurt your gains too much. However, frequent overconsumption of alcohol will significantly undermine your muscle-building efforts.
Related: Seven Ways to Boost Your Testosterone Naturally
Alcohol and Insulin Resistance
Insulin is another anabolic hormone that plays a crucial role in muscle building. The main function of insulin is transporting nutrients into your muscle cells. It drives both glucose and protein into your muscles, facilitating recovery and growth.
Consuming large quantities of alcohol has been shown to increase whole-body insulin resistance, essentially blocking the flow of nutrients into your muscles (3). This will impair post-workout recovery and, in turn, undermine muscle growth.
In addition, insulin resistance often goes hand in hand with fat gain. This is because the nutrients that should be entering the muscles end up being diverted to the fat cells. So, smaller muscles and a higher body fat percentage – talk about a terrible combination!
Alcohol and Cortisol
Where testosterone and human growth hormone are anabolic or muscle-building substances, cortisol is catabolic, meaning it causes muscle breakdown. Cortisol is often produced in response to stress. However, high alcohol consumption is also linked to elevated cortisol levels (4).
A little cortisol is no bad thing, as it’s one of the triggers of anabolism and muscle growth. However, too much cortisol, or prolonged elevation, will impede muscle growth.
Alcohol and Sleep
Sleep is critical for muscle growth; it’s when your body gets busy repairing the muscle damage caused by your workouts. Anabolic hormone levels tend to rise while you sleep, as does muscle protein synthesis. So, while you’re pushing out the zzzs, your body is busy repairing and rebuilding your muscles. As such, most people should try and score 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
While alcohol can make you drowsy and may even help you drop off to sleep faster, alcohol-fueled sleep is often of poor quality, disrupted, and not especially restful (5). Poor sleep can have a significant impact on your training performance, recovery, and muscle growth.
Interrupted and insufficient sleep can cause cortisol levels to rise, testosterone and growth hormone levels to fall, and insulin resistance to increase. In addition, sleep deprivation can lower your motivation to train and impair your recovery.
This all means that alcohol-fueled sleep is not good and won’t help you build muscle.
Alcohol and Motivation
Let’s face it – building muscle is hard work. It takes consistent effort and determination to push yourself through workouts that are often uncomfortable and even painful. If you aren’t motivated, you will probably miss more workouts than you complete, significantly undermining your progress.
Motivation can be intrinsic or extrinsic, but ultimately, YOU must drag your butt to the gym and do the work required to build muscle.
Regular alcohol consumption, especially when you feel hungover the next day, can severally undermine your motivation to train (6). You’re much more likely to skip workouts, and your motivation to eat well will probably also take a dive.
The bottom line is if you want to stay motivated and skip fewer workouts, you should limit your alcohol intake.
Alcohol and Nutrition
Successful muscle building has as much to do with your diet as it does your workout. Your diet supplies the calories and nutrients your body needs to fuel your training and repair and build your muscles.
While alcohol contains calories, weighing in at seven calories per gram, it doesn’t have any other beneficial nutrients. In fact, alcohol is an anti-nutrient, meaning it uses resources but doesn’t provide any.
Drinking alcohol, especially to excess, can cause you to make improper food choices and reduce your motivation to eat healthily (7). A poor diet will undermine your workouts and impede your muscle-building progress.
How Much Alcohol is Okay for Muscle Growth?
It’s often said that drinking alcohol in moderation is okay and might even be good for you. However, there are no proven benefits associated with regular alcohol consumption – sorry! That said, a couple of drinks now and then probably won’t hurt you (8).
But what does a moderate alcohol intake look like? And will it interfere with your fitness and muscle-building progress?
According to research (1), consuming 0.5g/kg of alcohol or less won’t affect muscle recovery following exercise. So, for someone who weighs 180 lbs., that’s about 2-3 standard-sized drinks. However, consuming 1.5g/kg of alcohol or 8 drinks will significantly impact muscle protein synthesis and undermine your ability to recover and grow.
So, if you want to drink alcohol without derailing your gains, you should limit yourself to no more than a couple of drinks at a time and have a few dry days per week when you don’t drink alcohol at all. You should also avoid binge drinking, where you consume multiple drinks in short succession.
Alcohol Affect Muscle Growth – Closing Thoughts
While some people prefer not to drink, alcohol can be part of a healthy diet. However, when consumed to excess, alcohol can hurt your gains and undermine your health. This is especially true for habitual and binge drinking.
Your body views and treats alcohol as a toxic substance and reacts very negatively to its presence. Consuming alcohol can impair muscle protein synthesis, reduce your testosterone, increase cortisol, and undermine your motivation to train and eat healthily. It also hammers your liver.
Building muscle is hard enough without sabotaging yourself with alcohol!
So, by all means, have the occasional drink if you wish, but if you are serious about building muscle, keep your intake to a minimum, or don’t imbibe it at all.
References:
1 – Parr EB, Camera DM, Areta JL, Burke LM, Phillips SM, Hawley JA, Coffey VG. Alcohol ingestion impairs maximal post-exercise rates of myofibrillar protein synthesis following a single bout of concurrent training. PLoS One. 2014 Feb 12;9(2):e88384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088384. PMID: 24533082; PMCID: PMC3922864. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24533082/
2 – Vingren JL, Hill DW, Buddhadev H, Duplanty A. Postresistance exercise ethanol ingestion and acute testosterone bioavailability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013 Sep;45(9):1825-32. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e31828d3767. PMID: 23470309. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23470309/
3 – Lindtner C, Scherer T, Zielinski E, Filatova N, Fasshauer M, Tonks NK, Puchowicz M, Buettner C. Binge drinking induces whole-body insulin resistance by impairing hypothalamic insulin action. Sci Transl Med. 2013 Jan 30;5(170):170ra14. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005123. PMID: 23363978; PMCID: PMC3740748. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3740748/
4 – Badrick E, Bobak M, Britton A, Kirschbaum C, Marmot M, Kumari M. The relationship between alcohol consumption and cortisol secretion in an aging cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Mar;93(3):750-7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0737. Epub 2007 Dec 11. PMID: 18073316; PMCID: PMC2266962. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2266962/
5 – Park SY, Oh MK, Lee BS, Kim HG, Lee WJ, Lee JH, Lim JT, Kim JY. The Effects of Alcohol on Quality of Sleep. Korean J Fam Med. 2015 Nov;36(6):294-9. doi: 10.4082/kjfm.2015.36.6.294. Epub 2015 Nov 20. PMID: 26634095; PMCID: PMC4666864. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4666864/
6 – Shamloo ZS, Cox WM. The relationship between motivational structure, sense of control, intrinsic motivation, and university students’ alcohol consumption. Addict Behav. 2010 Feb;35(2):140-6. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.09.021. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID: 19836901. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19836901/
7 – Fawehinmi TO, Ilomäki J, Voutilainen S, Kauhanen J. Alcohol consumption and dietary patterns: the FinDrink study. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038607. Epub 2012 Jun 12. PMID: 22719905; PMCID: PMC3373562. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22719905/
8 – Chiva-Blanch G, Badimon L. Benefits and risks of moderate alcohol consumption on cardiovascular disease: current findings and controversies. Nutrients. 2019 Dec 30;12(1):108. doi: 10.3390/nu12010108. PMID: 31906033; PMCID: PMC7020057. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7020057/

7 Benefits of Collagen for Muscle Growth: Unlock Your Muscle-Building Potential
We all know that protein is the key macronutrient for muscle growth. And when it comes to a protein supplement, most people immediately think of whey. Yet, while it’s the most popular protein supplement, whey isn’t the only one — and it may not even be the best.
Collagen represents the most abundant protein in your body. It is available in several supplement forms, including as a powder that can be added to shakes. So, how good is it for muscle growth? In this article, we discover whether collagen supplementation can help you pack muscle tissue.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most common protein in the body, representing between 25-35% of your total protein. The connective tissue that constructs your muscles, ligaments, skin, and tendons is made from it.
Collagen is made from the following three amino acids:
Proline
Glycine
Hydroxyproline
Depending on their configuration, these amino acids will produce one of 28 different collagen forms. The four most common forms are:
Type I
Type II
Type III
Type IV
Type I collagen represents 90% of the total collagen in your body. This dense form of collagen is responsible for the structure, support, and strength of your skin, bones, ligaments, and tendons.
Type II collagen is found in joint ligaments, where it enhances elasticity. It is also part of the intervertebral disc material that cushions the spine.
Type III collagen is contained in muscle, skin, and blood vessels.
Type IV collagen is found in the layers of the skin and ears, and kidneys.
Collagen is part of what is called the extracellular matrix. As such, it involves the construction and structure of every cell in your body.
As we age, our bodies produce less collagen. This decline begins in our late 20s or early 30s and is a major contributor to the wrinkles, joint stiffness, and sagging skin that are the hallmarks of aging. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, smoking, and excessive exposure to the sun may exacerbate age-related collagen loss.
Collagen supplementation has become popular over the last decade or so to replace the amounts we naturally lose and for its claimed health benefits. Collagen supplements come in various forms, including collagen peptides, which are usually sold in powder form, collagen capsules, liquid collagen, and collagen chewable or gummies.
There are four main sources of collagen for use in supplements:
Bovine (cow)
Porcine (pig)
Marine (fish)
Poultry (chicken)
Benefits of Collagen Supplementation
Collagen supplementation has been shown to provide the following health benefits:
Improves Skin Health
Collagen is well-known as a skin rejuvenator and is used in most skin health products to help reduce wrinkles and replenish skin health. There is some solid science backing up collagen’s ability to enhance skin health. One study involved 114 women aged between 45 and 65. Over eight weeks, the women took either 2.5 grams of collagen or a placebo. At the end of the study period, the collagen group had reduced their wrinkles by 20%.
The researchers found that the supplementation increased elastin production and stimulated the body to produce its own collagen. As the anime suggests, elastin boosts the skin’s elasticity to help prevent wrinkles. [1]
Eases Joint Pain
Joint pain is often a result of degenerative bone disease or a breakdown of bone cartilage. Collagen supplementation can help by building up your protein stores to rebuild cartilage. It also stimulates the body to produce more natural collagen to contribute to this building process.
In one study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 80 people with severe joint pain were given either 2 grams of collagen daily or a placebo for 70 days. The collagen group experienced a decrease in joint pain from Day 35 onwards. The pain progressively decreased up to Day 70. [2]
Hormonal Balance
Collagen plays a big part in modulating hormones, especially estrogen. Once more, glycine is the key player here. This amino acid helps to activate estrogen receptors. This helps to channel the free estrogen floating around in your system and use it effectively. Doing so will help to prevent such problems as water retention and oxidative damage.
Promotes Better Sleep
One of the main reasons that people have trouble sleeping is that they are overheated. The most abundant amino acid in collagen is glycine, which has been shown to be able to cool the body. It does this by acting upon the NMDA receptor, which relaxes the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more effectively through the body. This helps to cool the body down.
Glycine also inhibits a neuropeptide called orexin, which stimulates arousal and wakefulness. So taking collagen can help diminish its effects, helping us attain the relaxed, calm state needed to fall asleep.
Improves Liver Function
The glycine that makes up collagen assists in creating bile, the body’s main fat emulsifier. If we cannot produce enough bile, we will feel bloated and sick after eating a fatty meal. By supplementing with collagen, you can get the glycine you need to kickstart the bile production process. [3]
Collagen also helps offset liver inflammation resulting from excessive alcohol consumption.
Promotes Muscle Recovery
Collagen has been shown to improve muscle recovery after an injury. In one study, researchers found that collagen taken directly after a muscle rupture was able to significantly improve muscle recovery. It was noted that, following the injury, the body was, in effect, screaming out for more collagen. The researchers identified that the injury site needed more Type III collagen straight away; however, weeks later, there was still a demand for more collagen, but this time the Type I version.
Enhances Brain Functioning
Collagen helps support a healthy brain-blood barrier by exchanging compounds between the blood and the brain. The anti-inflammatory effects of collagen also protect the brain. There is also emerging research that suggests that collagen may play a part in neurogenesis, the formation of new brain cells.
Can Collagen Increase Muscle Mass?
Being the most abundant protein in the body, you’d think that collagen must have a role to play in building muscle, which is made of protein. And you’d be right — at least in people with sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss). Sarcopenia affects all men once they reach the age of around 30, with a loss of about 3-5% of total muscle mass every decade from 30 onward.
In a study by Zdzieblik et al., 53 men with an average age of 72 were put on a 12-week resistance training program. Half of them were given a daily dose of 15 grams of collagen, while the other half were given a placebo. Post-study testing revealed that the collagen group had a significantly greater increase in fat-free mass (4.2 kg average compared with 2.9 kg for the placebo group). Muscle strength gain and fat loss were also greater in the collagen group. [4]
Scientists believe that a key mechanism by which collagen boosts muscle growth when combined with resistance training is that it improves muscle protein synthesis and acts as a stimulus for muscle repair and growth after a strenuous workout.
Collagen has been shown to be especially good at inducing protein synthesis in people on a low-protein diet. Of course, most people trying to add muscle are just the opposite, but if you are on a keto diet or follow an intermittent fasting protocol, your protein intake will probably be lower than normal.
Collagen is an excellent source of the amino acids glycine and arginine, both of which are ingredients in creatine. So, when you take a collagen supplement, you are also ingesting two key building blocks of creatine. Creatine synthesizes ATP from the moment you start your workout. It’s what powers you through the initial seconds of your workout. In other words, a collagen supplement will help you generate maximum strength at the start of your workout. That is why the elderly men in the study cited above had an increase in muscle strength while those on a placebo did not.
Is Collagen Better Than Whey for Muscle Gain?
When it comes to supplements, many people have an either-or mentality. They need to know if this is better than that so that they can choose one over the other. The reality is that, in many cases, supplements are complementary. That is certainly the case when it comes to whey and collagen protein.
Whey could be considered a ‘better’ source of protein for muscle growth than casein because it contains more BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids). The three BCAAs – leucine, valine, and isoleucine — are the key drivers of protein synthesis.
Whey protein is a by-product of the cheese-making process. Whey liquid is dehydrated to form a powder. Whey protein is valued because it contains all nine essential amino acids and is fast digesting. Collagen, in contrast, is not an essential amino acid. Though high in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, it is relatively low in tryptophan, methionine, and histidine.
A 2018 study directly compared whey and collagen’s ability to build muscle. Eight men were given either 22 grams of whey or collagen protein 45 minutes before exercising, 22 grams intra-workout, and another 22 grams post-workout. The workout consisted of a 75-minute intensive cycle session. The post-study analysis revealed that the whey group had significantly greater protein synthesis levels. This was attributed to the higher levels of BCAAs in whey protein. [5]
A 2009 study by Hays et al. compared the nitrogen balance that results from whey and collagen supplementation. Nitrogen balance relates to the relationship between the level of nitrogen that enters the body through the diet and the levels that the body excretes. Positive nitrogen balance is needed to build new muscle. In this study, nine healthy women were given a whey protein supplement for 15 days. After a one-week washout period, they were given the same amount of collagen for 15 days. The analysis showed that the women had significantly higher levels of positive nitrogen balance during the collagen trial. [6]
The researchers also noted that, while collagen has a lower protein digestibility, on a per-gram basis, those proteins contained more nitrogen. This boosts the level of available nitrogen in the body, meaning that you can be in a higher nitrogen balance with less protein intake than you’d need if you were taking another protein source such as whey.
These studies confirm that collagen plays a vital role in building muscle. It boosts protein synthesis and promotes positive nitrogen balance. This is different from the muscle-building potential of whey protein, which is mainly based on its high levels of BCAAs. Ideally, you should take both collagen and whey protein supplements to maximize your muscle-building potential. In other words, you get more bang for your buck from collagen when it comes to maintaining a positive nitrogen balance.
Collagen Dose for Muscle Growth
The best way to determine the effective dosage for a supplement is to consider the dosages used in clinical studies. In the case of collagen, the study dosages range from 2 to 15 grams per day. If you’re training hard to build muscle, you should err on the higher side because your stressed muscle will have a higher demand for nutrients.
We recommend taking 15 grams of collagen daily for muscle growth.
Side Effects
While collagen supplementation is safe for most people, some may experience unpleasant effects due to intolerance or excessive dosage. Collagen supplements may be manufactured from fish and eggs, so people with an intolerance or allergy to these foods should look for an alternative source that is safer for them.
The following side effects may be experienced:
Skin rash
Acne
Inflamed skin
Scar tissue (fibrosis) in the liver
Kidney stones
Stomach upset
Diarrhea
Constipation
Heartburn
Abnormal heart rhythm
How Long To Take It
Collagen takes a relatively long period to be synthesized in the body and deliver noticeable results. Don’t expect results any sooner than six-eight weeks after beginning collagen supplementation.
The average length of collagen studies is about eight weeks. There have been no reported negative effects of long-term collagen use.
Alternatives
Collagen contains a unique chemical makeup, so finding a like-for-like substitute is not easy. Keratin, which is another form of protein found in hair, nails, and skin, has been promoted as a collagen substitute, but the existing research does not support its ability to replicate the benefits of collagen supplementation. [7]
There have been attempts to cater to vegans wanting to supplement with collagen. By adding human collagen genes to yeast, it can produce its own form of collagen.
You could also purchase individual supplements that contain the three key amino acids in collagen production; glycine, lysine, and proline.
Wrap Up
Several studies support collagen’s ability to promote muscle growth. It appears to simulate both muscle protein synthesis and the positive nitrogen balance needed for it to occur. When you combine this with the other research-backed benefits of taking collagen, it appears that taking collagen is a smart choice. A great way to get your collagen is in the form of a bone broth. To make bone broth, you simmer animal bones and connective tissue, which releases collagen and other nutrients into the liquid. Bone broth also contains muscle growth-promoting minerals such as magnesium and calcium.
I’ve been taking collagen in the form of bone broth for several years. I take a cup of it about an hour before my workout. Then post-workout, I have a whey protein shake. Combining collagen and whey in this manner gives me the best of both worlds. Whether you take collagen in the form of a powder, bone broth, capsule, or liquid, get into the habit of consuming it daily, and your muscle growth potential will get a serious boost.
References
Proksch E, Schunck M, Zague V, Segger D, Degwert J, Oesser S. Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduces skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27(3):113-9. doi: 10.1159/000355523. Epub 2013 Dec 24. PMID: 24401291.
Schauss AG, Stenehjem J, Park J, Endres JR, Clewell A. Effect of the novel low molecular weight hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract, BioCell Collagen, on improving osteoarthritis-related symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Apr 25;60(16):4096-101. doi: 10.1021/jf205295u. Epub 2012 Apr 16. PMID: 22486722.
Yamashina S, Ikejima K, Enomoto N, Takei Y, Sato N. Glycine as a therapeutic immuno-nutrient for alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):162S-5S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189281.82523.6c. PMID: 16344603.
Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Baumstark MW, Gollhofer A, König D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomized controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2015 Oct 28;114(8):1237-45. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002810. Epub 2015 Sep 10. PMID: 26353786; PMCID: PMC4594048.
Impey SG, Hammond KM, Naughton R, Langan-Evans C, Shepherd SO, Sharples AP, Cegielski J, Smith K, Jeromson S, Hamilton DL, Close GL, Morton JP. Whey Protein Augments Leucinemia and Postexercise p70S6K1 Activity Compared With a Hydrolyzed Collagen Blend When in Recovery From Training With Low Carbohydrate Availability. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018 Nov 1;28(6):651-659. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2018-0054. Epub 2018 Oct 1. PMID: 29757056.
Hays NP, Kim H, Wells AM, Kajkenova O, Evans WJ. Effects of whey and fortified collagen hydrolysate protein supplements on nitrogen balance and body composition in older women. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009 Jun;109(6):1082-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.03.003. PMID: 19465192.
Mokrejs P, Hutta M, Pavlackova J, Egner P, Benicek L. The cosmetic and dermatological potential of keratin hydrolysate. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017 Dec;16(4):e21-e27. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12319. Epub 2017 Feb 6. PMID: 28164425.

The Best Time to Work Out for Muscle Growth
Building muscle takes time, energy, and dedication, and your diet must be on point, too. Even then, unless you are very genetically blessed, increasing muscle size is a slow and laborious process.
Most people are lucky if they gain a pound of muscle per month.
Because of this, it makes sense to try and make your workouts as effective and efficient as possible. Supplements like creatine and pre-workout can help, and following a hypertrophy-specific training program is obviously a must.
There may also be an optimal time to work out for muscle growth. We investigate how your workout time may affect your muscle-building gains.
Early Morning Workouts for Muscle Growth
Many exercisers like to start their day with a workout, and numerous famous bodybuilders favor morning training, including the Austrian Oak Arnold Schwarzenegger, who still prefers his workouts bright and early.
Training early in the morning offers several advantages and benefits, including:
You make training your priority, getting it done before other tasks can disrupt your day.
Gyms are often quieter first thing in the morning.
It takes less time to get to the gym as the roads are not as busy.
Some people feel more energetic early in the morning.
Early-morning exercisers tend to be more consistent.
Morning workouts leave you free to enjoy the rest of your day.
There are more opportunities for post-workout meals.
You can still train later in the day if you miss your morning workout.
However, there are downsides to early morning workouts, too:
It may take you longer to warm up.
You may not feel as strong or energetic.
Blood glucose and muscle glycogen levels may be lower than usual.
Serum testosterone levels tend to be lower first thing in the morning (1).
A good-sized pre-workout meal may be impractical.
Some exercisers are not “morning people” and are reluctant to get up early.
You’ll need to go to bed early to ensure that you get sufficient sleep.
Developing an early-morning workout habit is not always easy.
But what does the science say about early morning training for muscle building? The answer is not clear-cut, as you can make gains no matter what time of day you train.
That said, some studies suggest that early morning workouts may not be ideal for strength and hypertrophy gains. For example, a 2016 study from Finland determined that strength and endurance training produced better results when performed in the evening and not in the morning (2).
This result was mirrored by an earlier study that found muscle strength and power tended to be lower during early morning workouts (3). However, that same study also suggested that ingesting caffeine could mitigate many of the downsides of early morning training.
Working Out Later in The Day for Muscle Growth
Not a morning person? That’s okay! Many people find the idea of training shortly after waking a nauseating prospect. They’re too sleepy, stiff, and tired to get a good workout. The good news is that there are plenty of benefits to working out later in the day:
Most people feel warmer and more awake.
Strength/power levels tend to be marginally higher (4).
You’ll have eaten several pre-workout meals.
You won’t feel rushed to complete your workout before heading to work or school.
You can go home and relax once your workout is finished.
Your evening meal will also be your post-workout meal.
Gyms tend to more vibrant and energized later in the day.
Of course, there are disadvantages to training later in the day, too:
You may feel tired after a day at school or work.
The gym will be busier, which may disrupt your workout.
The tasks of the day may delay or even prevent you from working out.
There are fewer opportunities to catch up on missed workouts.
Fewer opportunists for post-workout meals.
Training at night can disrupt your sleep.
Training in the evening may mean saying “no” to social engagements.
There are more demands on your time, so you may be more tempted to skip your evening workout, e.g., family dinners, date nights, etc.
Unsurprisingly, the same studies that suggest early morning workouts are less favorable for building muscle and strength also support training later in the day. Most studies recommend a training window of 4 to 8PM.
AM vs. PM Workouts for Muscle Growth
So, while some studies do support PM vs. AM training for muscle growth, evidence also supports morning training. Go to any gym at 6 AM, and you’ll see people who have achieved outstanding results by working out early.
And don’t forget actor Mark Wahlberg and his famous 4 AM workouts! Despite being in his 50s, Wahlberg is in amazing shape and does all of his training at the “wrong” time.
So why do some people get on so well with early morning workouts while others cannot lift a weight before 4 PM?
Good question!
It’s probably because of something called your chronotype, which is the scientific term for whether you are a morning or an evening person. In fact, studies suggest that some people are genetically programmed to respond well to morning workouts (5). Conversely, some people come awake later in the day and are better suited to PM workouts.
So, if early morning workouts ARE less effective than training later in the day, any differences are marginal. In fact, a 2019 meta-analysis comparing the results of 11 training time studies revealed no discernable difference between morning and evening workouts (6).
In all likelihood, the best time to train for muscle growth is the time that suits you. If early morning workouts feel good and fit your schedule, then stick with them. In contrast, if you come alive later in the day and feel stronger in the afternoon and early evening, then that is the time to train.
How do you know if you are an AM or PM person? Try working out at different times of the day and see which you prefer!
However, it’s worth noting that you can acclimate yourself to working out at almost any time of the day (7). It’ll take a few weeks, but you can turn an evening workout habit into a morning one or vice versa. It seems that your chronotype is not set in stone, and it is actually a trainable characteristic.
So, if you are forced to train at a time that doesn’t feel natural, stick with it, and you’ll eventually get used to it. Any decline in performance will gradually vanish, and the time of day won’t affect your training results.
Best Time to Work Out – FAQs
Do you have questions about the best time to work out for muscle growth? That’s okay because we’ve got the answers!
1. So, what IS the best time to work out for muscle growth?
While some studies indicate that training later in the day is better for muscle growth, others suggest that workout timing doesn’t really matter. Instead, it’s more of a personal choice and depends on whether you are a morning person or an evening person, which is called your chronotype.
If you are the sort of person who wakes up feeling full of energy and ready for action, you will probably do well with AM workouts. But, if you feel sluggish in the morning and it takes you several hours to feel your best, PM workouts will probably suit you better.
However, it’s worth noting that you can train yourself to become a morning or evening person simply by pushing yourself through workouts at the “wrong” time. Gradually, you’ll get used to training at a different time of day.
So, ultimately, the best time of day to work out for muscle growth is a) when you feel best and b) whenever you can train reliably and consistently. The so-called right time could be the wrong time if you cannot stick to it.
2. What should I eat before an early morning workout?
One of the main benefits of training later in the day is you can eat several times before you hit the gym. This ensures your muscle glycogen levels are maxed out, so you can train as hard and as long as you want to.
Unless you get up several hours before your workout, this is not possible with early morning workouts.
One way around this is to consume your pre-training meal the night before. Just make sure you eat a good balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and you’ll be good to go.
You can then top up your energy with a fast-acting snack shortly after rising, such as a sports drink, energy bar, or energy gel. Alternatively, a small bowl of breakfast cereal or a ripe banana will suffice.
You can also ingest some caffeine which, studies suggest, can boost your energy during early-morning workouts (3) and may even reset your circadian rhythm, helping you to become more of a morning person.
3. Do early morning workouts burn more fat?
Studies suggest you may burn more fat when you do cardio on an empty stomach, i.e., fasted (8). However, if training on empty reduces your workout duration or intensity, this benefit is lost.
That said, strength training uses more glycogen than fat, so lifting weights while fasted probably won’t help you burn more fat. In fact, it could impair your performance, making your workout less effective for building muscle and strength.
By all means, give fasted strength training a try, but if you are serious about building muscle, you’ll probably have a better workout with some fuel in the tank.
4. Are early morning workouts safe?
Early morning workouts are perfectly safe, provided you take a few small precautions. For example, after sleeping for the night, your spine is slightly elongated and relaxed. As such, you should warm up thoroughly before loading it, i.e., doing heavy squats or deadlifts.
Also, your blood glucose may be a little lower than usual, which could lead to symptoms of mild hypoglycemia, e.g., feeling weak, dizzy, or nauseous. You could also be slightly dehydrated. These problems can be avoided by drinking plenty of water before and during your workout and having a fast-acting high-carb snack before you hit the gym.
If you are unused to early morning workouts, ease yourself in by reducing exercise intensity and duration for your first few training sessions. You can work harder and longer as your body gets used to your new routine.
5. Is working out at different times on different days okay?
While a consistent workout schedule is usually easier to maintain, it is not always possible. For example, working rotating shifts, family commitments, or school projects may mean you have to train early some days and later on others.
If this is the case, you’ll have to roll with the punches and make the best of your situation. However, you should avoid doing an intense training session one night and another tough workout the following morning. This might be too much to recover from, especially if you are sleep-deprived.
Ultimately, even a less-than-perfect training schedule will work if you stick to it and is preferable to missing workouts.
Closing Thoughts
Many exercisers are guilty of majoring in the minors. In other words, they spend too much time worrying about barely relevant details while ignoring the big picture. Some spend so long comparing and researching their workout and diet options that they don’t have any time left to go to the gym!
So, while some studies may suggest that training later in the day can improve your hypertrophic results, the benefits are marginal. Interestingly, other studies even indicate that there is no difference between AM and PM training.
With that in mind, you should stop worrying about the benefits and drawbacks of AM vs. PM training and work out at the time that suits you. For some, morning workouts are best, while others will prefer to train later in the day.
What matters most is that you work out hard and often. After all, that’s what builds bigger, stronger muscles.
References:
Crawford ED, Poage W, Nyhuis A, Price DA, Dowsett SA, Gelwicks S, Muram D. Measurement of testosterone: how important is a morning blood draw? Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31(10):1911-4. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1082994. Epub 2015 Sep 11. PMID: 26360789. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26360789/
Küüsmaa M, Schumann M, Sedliak M, Kraemer WJ, Newton RU, Malinen JP, Nyman K, Häkkinen A, Häkkinen K. Effects of morning versus evening combined strength and endurance training on physical performance, muscle hypertrophy, and serum hormone concentrations. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016 Dec;41(12):1285-1294. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0271. PMID: 27863207. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27863207/
Mora-Rodríguez R, García Pallarés J, López-Samanes Á, Ortega JF, Fernández-Elías VE. Caffeine ingestion reverses the circadian rhythm effects on neuromuscular performance in highly resistance-trained men. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033807. Epub 2012 Apr 4. PMID: 22496767; PMCID: PMC3319538. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3319538/
Mirizio GG, Nunes RSM, Vargas DA, Foster C, Vieira E. Time-of-Day Effects on Short-Duration Maximal Exercise Performance. Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 11;10(1):9485. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66342-w. PMID: 32528038; PMCID: PMC7289891. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32528038/
Vitale JA, Weydahl A. Chronotype, Physical Activity, and Sport Performance: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2017 Sep;47(9):1859-1868. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0741-z. PMID: 28493061. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28493061/
Grgic J et al. The effects of time of day-specific resistance training on adaptations in skeletal muscle hypertrophy and muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chronobiol Int. 2019 Apr;36(4):449-460. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30704301/
Pengelly M, Elsworthy N, Guy J, Scanlan A, Lastella M. Player Chronotype Does Not Affect In-Game Performance during the Evening ( >18:00 h) in Professional Male Basketball Players. Clocks Sleep. 2021 Nov 29;3(4):615-623. doi: 10.3390/clockssleep3040044. PMID: 34940023; PMCID: PMC8700237. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8700237/
Aird TP, Davies RW, Carson BP. Effects of fasted vs. fed-state exercise on performance and post-exercise metabolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 May;28(5):1476-1493. doi: 10.1111/sms.13054. Epub 2018 Feb 23. PMID: 29315892. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29315892/
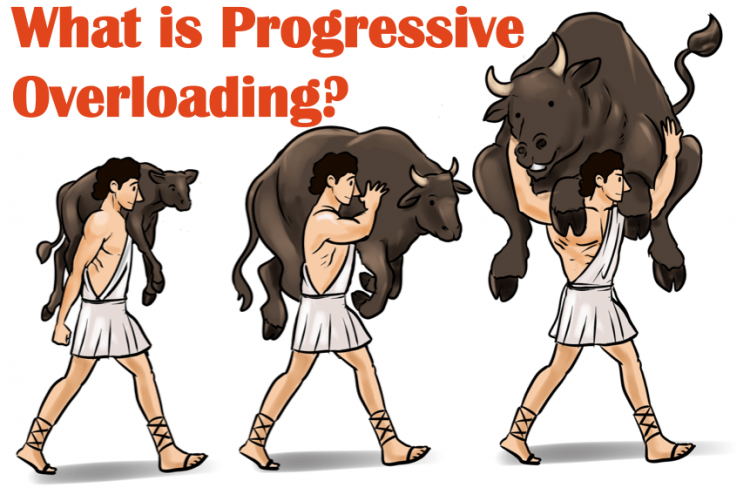

Progressive Overload: The Science Behind Maximizing Muscle Growth
If you have been in the iron game for a while, “progressive overload” might not be something new. It’s a common phrase to help explain what is needed for effective training.
The idea is pretty simple. Training must present progressively larger stressors over time for continued progress. However, as straightforward as it is, there are a ton of misconceptions. Progressive overload is about more than just adding weight to the bar. Yes, lifting heavier is part of it, but it is not the only way to progressively overload the muscles.
In this article, we will address some common fallacies and more as we dig into progressive overload and the science behind maximizing muscle growth.
What is Progressive Overload?
All talk on progressive overload, for better or worse, starts with the story of Milo of Croton. Milo was an ancient Greek wrestler who was known as quite the stud. As legend has it, Milo began lifting a tiny calf on his shoulders daily. As the calf grew, Milo k
ept lifting it until one day, the baby calf grew into a full-grown bull. As a result, Milo grew too.
The story is more myth than fact, but it does help illustrate the concept of progressive overload. In simple terms, progressive overload means training must get progressively more challenging over time to continue stimulating adaptation.
But let’s take a step back.
The human body is a well-balanced machine controlled by homeostasis. It’s like the body’s built-in thermostat. Blood pressure, body temperature, and blood sugar are examples of homeostasis within the body. If the body detects any changes, it takes action to return to balance. It’s why we sweat in the heat and shiver in the cold.
Building muscle is no exception.
The process of building muscle can be described as stimulus, recovery, and adaptation. Or, in a practical sense — train, recover, and then get stronger and more muscular. Lifting weights is the first domino, but the entire process must repeat for continued progress.
The key is the stimulus must represent an overload. Overload is a workload beyond what the lifter is accustomed to.
The adaptation (getting more jacked) is only a result of the overload forcing the body out of homeostasis. This is why doing the same weight for the same reps is eventually a dead end. Progress slows or stops as soon as the workout is no longer challenging, and your body can maintain homeostasis.
Bottom line: Training must get progressively challenging for the workout to continue to deliver results.
Why Progressive Overload Is Essential
The importance of progressive overload comes down to mechanical tension. Mechanical tension is the stress applied to a muscle from external resistance. It’s what happens to the muscle when we lift weights. Although there are many factors for initiating muscle growth, mechanical tension is widely considered the primary factor.
To illustrate how critical tension is for building and maintaining muscle, look no further than astronauts in space. Whether we realize it or not, we are always resisting the force of gravity. Of course, gravity on earth is a low level of tension, but its tension nonetheless.
When astronauts are up in space, they don’t have gravity, so tension is removed. In fact, minimal muscle contraction is needed. According to NASA, astronauts experience up to a 20% loss of muscle mass during spaceflights. In a weightless environment, the body doesn’t require additional muscle mass. If you don’t use it, you lose it.
You may wonder what this has to do with progressive overload and muscle-building.
The reason astronauts lose muscle in space helps explain why progressive overload is essential for progress. The body only wants as much muscle and strength as it needs to carry out daily functions.
Lifting boxes, carrying our kids, and climbing stairs are examples of enough tension to create a hypertrophy stimulus, just a minuscule amount. Once we have enough muscle and strength for these daily functions, they no longer stimulate growth.
To grow additional muscle beyond what is needed for daily functions, we must introduce the body to higher levels of mechanical tension. At first, all forms of resistance training satisfy that requirement. This is why when you first start training, progress is easy. You get bigger and stronger if you show up to the gym a few times per week, give a reasonable effort, and eat halfway decent. But, the newbie gains only last for a brief period.
The body is very good at adapting. Eventually, just showing up will not deliver results. The body adjusted to the workouts the same way it did daily activities. Most of us have experienced this as we transitioned from beginner to intermediate. It’s often called a training rut or plateau.
You must continue overloading the body to break the plateau and stimulate progress.
How to Build Progressive Overload into Your Program
So far, we have talked a lot about the concept of progressive overload but have yet to learn how to implement it. There are many ways to build progressive overload into the training plan. Here are the most common:
Increase the weight lifted: Adding weight to the bar is the easiest way to build progressive overload into any training program. Accomplish this by increasing the weights lifted over time while maintaining the same reps and sets.
Increase the repetitions performed: Another option for progressive overload is adding repetitions over time while keeping the weights and sets performed the same.
Increase the number of sets: One of the most overlooked ways to build progressive overload into your program is by increasing sets. Do this by adding sets over time while maintaining weight and reps. Adding sets is a great way to increase training volume.
Increase the number of exercises performed: Adding exercises is another way to increase training volume and progressive overload. For example, you have implemented progressive overload if you usually do three chest exercises per week and bump it up to four.
Decrease rest periods: Training density refers to the work you can do in a given time. Completing your workouts faster is another form of progressive overload. You can accomplish this by decreasing rest periods between sets. That said, be careful not to reduce rest periods too much that it limits performance. For optimal performance, rest for 1-3 minutes between sets.
Progressive Overload Misconceptions
On the surface, this all seems straightforward. However, there are some common misconceptions we need to address.
Misconception #1: Progress is Linear
Okay, so we have established that doing more work overtime leads to progress. Awesome. Let’s do the math. If you can bench 135 pounds for five reps today and add five pounds to the bar each week for the next two years, you will be benching well over 600 pounds!
We all know it doesn’t work like that. But why?
Progressive overload is the observation of increased performance based on the adaptations that have already occurred. Put another way; you must earn the right to progressively overload your training. It’s not just the act of doing more work. It’s the result, too. Overload is limited by the positive adaptation that results from training. It can’t be forced. The limitations of muscle growth are beyond the scope of this article, but they exist.
Misconception #2: You Need to Progressively Overload Every Workout
Progressive overload does not need to occur in every training session. Beyond the beginner and early intermediate stages, this is unrealistic. However, growth will be limited if you do not add weight to the bar over time. The goal is to keep the big picture in mind.
The more advanced you get, the longer it takes to see meaningful progress. Sometimes you have to do the same thing for a couple of weeks before you can up the ante. The goal is not to do more in each workout but to push for more in each workout. Results will come if the programming is well-designed and the effort is there.
Misconception #3: It’s All About Going Heavy
The biggest misconception about progressive overload is that it’s all about lifting as heavy as possible. Yes, adding weight to the bar is an excellent way to progressive overload, but it’s not the only way. In fact, adding reps is highly effective. Research shows muscle growth occurs with low and high reps [1]. The key is pushing each set close to failure.
Misconception #4: It’s All About Volume
Over the past few years, training volume has received much attention as a primary driver of muscle growth. On the surface, this is true. Research comparing one, three, and five sets per exercise shows that multiple sets are more effective for muscle growth than a single set [2].
However, the response to volume follows an inverted “U” shape curve. What this means is, adding more volume works until it doesn’t. Eventually, volume increases to a point where it exceeds the body’s ability to recover. At that point, progress stalls and, if continued, starts to backslide. Besides, who has all day to spend in the gym?
The right amount of volume will be slightly different for everyone. Based on the current literature, ten sets per muscle group per week is a great spot to build muscle [3]. This doesn’t mean you can’t go beyond ten sets per week. You can. However, once you get beyond ten sets per week, start looking at other ways to build progressive overload into your program to facilitate progress.
Three Examples of Progressive Overload
The key to taking advantage of progressive overload is not leaving it up to chance. Here are three ways to build progressive overload into your program.
Example #1: Increase Weight
The first example is adding weight each week. Don’t be tricked by the simplicity of this setup. A basic linear load progression can be highly effective.
Week 1: 3 sets of 10 reps at 66% of 1RM
Week 2: 3 sets of 10 reps at 68% of 1RM
Week 3: 3 sets of 10 reps at 70% of 1RM
Example #2: Increase Sets
In example two, the number of sets increases weekly while the weight stays the same. Adding sets is a great way to increase volume without lifting heavier each week. Advanced lifters respond well to this style of overload.
Week 1: 3 sets of 10 reps at 68% of 1RM
Week 2: 4 sets of 10 reps at 68% of 1RM
Week 3: 5 sets of 10 reps at 68% of 1RM
Example #3: Increase Reps
The third example involves adding a rep each week while maintaining the sets and weight on the bar. Increasing reps each week is sometimes more feasible than increasing the weight.
Week 1: 3 sets of 8 reps at 70% of 1RM
Week 2: 3 sets of 9 reps at 70% of 1RM
Week 3: 3 sets of 10 reps at 70% of 1RM
Progressive Overload Principles
There are three progressive overload principles you must keep in mind.
Principle 1: Only change one variable at a time
The first principle of progressive overload is only to change one variable at a time. It’s easy to assume that if a bit of progression is good, more must be better. With progressive overload, that muddies the waters, making it hard to know what is driving progress.
Additionally, changing more than one variable at a time can cause you to push beyond your recoverability. For example, if you try adding weight and reps simultaneously, you can outpace your progress and miss reps.
Principle 2: Always maintain good technique
For progressive overload to work, we need natural progression. You can’t use a lousy technique to force weekly advancements that are not there. Adding weight or reps but allowing your form to break down differs from actual progression.
Principle 3: Keep a Training Journal
The key to progressive overload is knowing what you have done during your workouts in previous weeks. Keep a training journal and track the exercises, weights you used, sets, reps, etc. Before each training session, review the journal to know what numbers you need to beat.
Benefits of Using Progressive Overload
Regardless of your goals, there are many benefits to using progressive overload in your training.
Avoid Muscle Building Plateaus:
Once you get past the beginner stage, continuing to build muscle becomes harder. If you don’t have a strategy to build progression into your program, it’s easy to get caught in a muscle-building rut. Eventually, you will stop progressing if you continuously do the same exercises for the same weight, sets, and reps. By constantly planning ahead and building ways to stress the muscles to greater degrees, you can mitigate stalls in progress.
Gain Strength:
To gain strength, you need to lift heavy weights. There is no way around it. That said, you can’t just go to the gym and max out every time and expect to get the best results. Part of quality strength programming is gradually increasing the weights used systematically.
Save Time:
Chances are you live a busy life and can’t spend all day in the gym. Well, using progressive overload is the most time-efficient way to train. One of the problems with training programs that don’t use progressive overload is they end up with a lot of junk volume.
Junk volume is work that needs to be more challenging to stimulate muscle growth. Often this happens when working sets are not close enough to failure to produce enough tension in your muscles. People typically add more sets to make up for the abundance of junk volume. You can train for two hours at a time, but if the workout is 80% junk volume, it won’t deliver results.
Focusing on progressive overload and beating the logbook ensures your program has no wasted sets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of progressive overload?
There are many examples of progressive overload. You can increase the weight lifted, the number of sets performed, and do more reps or exercises.
Should I progressive overload every week?
In a perfect world, we could implement progressive overload every week. However, progress is only sometimes linear. As an advanced lifter, you can outpace your progress if you try to force weekly progressions. Think of progressive overload in the big picture. If week-to-week gains are too aggressive, aim for month-to-month.
Is progressive overload safe?
As long as you maintain good form, progressive overload is safe. That said, if you add weight too quickly, you can increase your risk of injury. Only use weights you can handle with good technique.
Can you grow muscle without progressive overload?
Yes, you can grow muscle without progressive overload, but only temporarily. Eventually, your muscles will stop growing unless you continuously apply more stress.
Wrapping Up
Progressive overload is one of the primary principles in strength training. Anyone can make progress for a short time, but as the iron game veterans know, long-term results are a different story. Whether you want to be as strong as possible or look great naked, your workouts must have built-in progressions.
That said, there is more to it than lifting heavier weights. Of course, always aim to get stronger, but don’t avoid the other methods of progressive overload, either. Using all the tools available is the key to long-term progress. Now all you have to do is put in the work!
References:
Schoenfeld BJ, Grgic J, Ogborn D, Krieger JW. Strength and Hypertrophy Adaptations Between Low- vs. High-Load Resistance Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Dec;31(12):3508-3523. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002200. PMID: 28834797.
Radaelli R, Fleck SJ, Leite T, Leite RD, Pinto RS, Fernandes L, Simão R. Dose-response of 1, 3, and 5 sets of resistance exercise on strength, local muscular endurance, and hypertrophy. J Strength Cond Res. 2015 May;29(5):1349-58. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000758. PMID: 25546444.
Schoenfeld, Brad J, et al. “Dose-Response Relationship between Weekly Resistance Training Volume and Increases in Muscle Mass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Journal of Sports Sciences, vol. 35, no. 11, 2017, pp. 1073–1082, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27433992, 10.1080/02640414.2016.1210197.

Does Electrical Muscle Stimulation Work? What the Science Actually Says
Electrical Muscle Stimulation isn’t A Silly Pseudoscience If you are eager to know if Electrical Muscle Stimulation, abbreviated as EMS, can help you gain muscle and recover you from workouts rapidly, then this article is tailored for you. What if shocking your muscles a little bit may help them grow […]
The post Does Electrical Muscle Stimulation Work? What the Science Actually Says appeared first on What Steroids.

How To Optimize Recovery For Maximal Muscle Growth?
Introduction
First, we will tell you why recovery matters so much, especially if you are a natural for maximal muscle growth. Then, we will give you some tips on how to optimize it, and lastly, a few supplements that can help you achieve your goals. Stay tuned!
Why Do You Need Recovery for Maximal Muscle Growth?
The process of muscle building is simple in theory: you lift weights, which causes micro-damage to the muscle fiber. Then, protein synthesis starts happening, and your body heals the damage, at the same time making the muscle bigger and stronger.
Obviously, for this to happen, you need to exercise, you need protein, and you need to rest as the process only gets triggered in the gym, but the muscles grow while you recover.
This process of repairing the damage lasts 24-48 hours post-workout, depending on many factors such as muscle groups affected, training intensity, current fitness level, etc.
The Dangers Of Overtraining
Athletes and gym fanatics often make a mistake by having following the “one more rep!” approach, always trying to force themselves to do more. That kind of mindset looks at recovery as something subhumans do, which can often lead to overtraining.
The obvious risk of overtraining is not letting your body fully recover from the damage, which can have many negative effects all over your body. These range from injuries, suboptimal gains, but can also affect your immune system, neurological issues, mood changes, and endocrinological changes. The overtraining syndrome is a real issue and is something you don’t want to mess with.
But, that doesn’t mean that you will become overtrained if you chain 3-4 workouts in consecutive days. Overtraining develops over a prolonged period of high volume + high intensity activities.
If you notice that you are becoming lethargic, stressed, anxious, that your immune system is weaker, or that you are losing sex drive, loss of appetite, and are continually feeling sore, it is probably time to slow down.
Body Parts Matter Too
When talking about gym workouts that are aimed towards hypertrophy and strength, it is important to note that the 24-48h rule of rest between workouts is important only when working one body part. However, training the opposite (antagonist) body part won’t cause overtraining. This is why you often have Push/Pull workouts, or body part splits such as Chest/triceps-Back/biceps-Legs/shoulders/abs, and similar. By manipulating your training this way, you are still giving each of your body parts an adequate 24-48 hour rest between workouts, which will allow optimal growth.
And remember, compound movements that involve the hip joint (squats and deadlifts, and their variations), as well as pullups and presses tax the body much more than isolations that only target one muscle group. Therefore, never train squats and deadlifts on consecutive days, and if you can, put them at least 3-4 days apart. Monday for deadlifts, Friday for squats.
It Is Important To Have Off Days
Although you can arrange your workouts so that your body parts are activated interchangeably, there’s one thing that is always on – your CNS. When working out hard every day, your body gets taxed a lot, as it has to go through the recovery process over and over again. To make sure it does recover fully, it is essential to have at least one day off every week. Only one day is an option if you are following a classic “bro split,” where you only focus on one muscle group per day. But, if you are training several groups, two days per week off might be a better idea. If you are training full-body, you should do it three times per week, with four off days.
Of course, nothing is set in stone, these are recommendations for most people. But, it is best to stick to them and see how you feel and then adjust accordingly.
Don’t Forget To Recover Between Sets
Recovering between sets will allow your muscles to perform optimally and enable you to reach your goals faster. There are different theories, and rest times between sets differ based on your goals. If your goal is strength, you should aim as long as you need to between sets, as you are going to try singles anyway. Therefore, 3-5 minutes, or even more, between sets is not unusual.
If you are training for size, you are usually somewhere in the 8-12 rep range. That means you are using less weight, but are still going reasonably heavy, and close to failure. In this case, resting 2-3 minutes is optimal.
If you are training for endurance or looking to lose fat via weight training, you are probably doing higher reps with lighter weights. If that is the case, 1-2 minutes between sets is enough. Or, you can choose two opposite exercises and do supersets, one after another.
8 Hours Of Goodness
People, you need to worry about your sleep schedule, just as much as you worry about your workout programs. There’s no going around it, if you lack sleep, your gains will suffer.
Sleep is responsible for energy levels, of course, and if you are drowsy, your workout quality will drop. But, sleep also has essential roles in normal hormone production. Fail to sleep enough, and you will start gaining fat, even if you are not in a surplus. Also, HGH is released during sleep, which is another important factor in muscle growth.
Related Article:: The Importance of Sleep for Bodybuilders
How much sleep is enough? You already know that 8 hours is optimal for most people. There are exceptions, of course, but most will need 7-8 hours of quality sleep. If you can’t do it all at once during the night, it is OK to have an afternoon nap, as long as you reach your goal. Just remember to have an afternoon and not an evening nap, as it can mess with your night sleep if you do it too late.
Tips To Optimize Sleep:
Have a sleep schedule, and try to go to bed and wake up at the same time, whenever possible
Don’t drink coffee, pre-workouts, or anything caffeinated 6 hours before bed
Sleep in a dark and quiet room, use dark curtains, eye covers, and earplugs if you have to
Feed Your Muscles during Recovery
To grow muscle, you need exercise, and you need protein. Muscles are built in the process of protein synthesis, therefore, this macronutrient is essential.
Whey protein is always the best choice if you are aiming to increase your protein intake through supplementation. Whey has the best absorption and will go to the muscles very quickly.
Find it Whey ➢ HERE
If you need something that is going to feed your muscles slower, but over a longer period, Casein protein is your best choice. This is a classic “slow” protein that is most often used before sleep, to give the necessary aminos to your muscles while you sleep. Of course, if you are vegan, or you just can’t tolerate dairy products, plant proteins are a good option too. They will give you all that you need and are usually organic and free of toxins.
Eat Carbs Too
Many gym bros often treat carbs like enemies, as they think carbs ruin those hard-earned abs instantaneously. Yes, it’s true that most junk food like candy and soda is filled with sugar, but that doesn’t mean carbs are bad. It only means that junk food is junk.
Find it Orgain ➢ HERE
But, when you work out super hard, your body’s glycogen gets depleted, which is the main fuel used for highly intensive activities. Glycogen is a form of sugar that is available in the muscles themselves and is used first during the intense activities, as it is already there. So, the best way to refill your glycogen reserves is to eat carbs, which will make sure your body is fully ready for your next hardcore session.
Read more about:: How To Bulk Up Without Getting Fat
Up Your Caloric Intake
This one is not for everyone, but, in some cases upping your caloric intake is worth considering. If you are training super hard, going very heavy and doing it frequently, this can cause a caloric deficit on its own. So, if your plan is to lose weight and you are in a deficit anyway, this can be too much. Therefore, if you are feeling lethargic, or especially achy, it is a good idea to up your calories on non-workout days, so that you can recover well. Also, if you want to go extra hard, upping your carbs on workout days will give you the necessary kick.
Find Casein ➢ HERE
Incorporate Light, Non-Lifting Days
We know that you are hardcore, but if you want to avoid overtraining, you should plan some light days into your schedule. These can be anything from taking a walk, a slow-paced bicycle tour, stretching and foam rolling, going for a swim, or signing up for a yoga class. Anything that is low-intensity but promotes circulation is a good option, as the blood flow will help the muscles heal up better. Plus, you are probably very tight anyway, and doing some yoga poses won’t kill you.
Use Deload Weeks for Recovery
Deloads are controversial, as many claim that they don’t work. But, if something can potentially prevent overtraining, we say it is a good idea to consider it. A deload week is a week where you cut back on total weight use, training volume, or frequency, or all three. So, you can go for 50% of your 1RM, just going through the motions. Or, you can keep the weight, but reduce the number of sets you do. Alternatively, you can replace exercises, doing simpler and easier versions. For example, instead of the bench press, you can do pushups.
The idea is to recover by working, so you don’t get lazy, and your muscles still get a fair amount of stimuli and circulation. But, in the deload weeks you don’t redline them. Athletes who favor deloads say they help them go through plateaus, prevent injuries, and feel much better overall. Athletes who hate deloads claim that they are a waste of time. Try it, and see what works for you.
If You Are Juicing, You Still Need To Worry About Recovery
It is a common thing to hear how steroid users don’t need to worry about recovery, as being enhanced means having much better recovery on its own. That is not exactly so.
While being enhanced does mean that you will recover better, that also means you will train more, and that you will still need recovery. Think about it logically – juicing will let you train harder and more frequently. If you want to do that and maximize your enhanced gains, you will still need to take care of your sleep, nutrition, supplementation, and everything else we described in the article above. If you8 don’t want to maximize your gains, then why are you taking steroids at all?
Must read:: How Long Does Recovery of Natural Testosterone Take After a 12 Week Steroid Cycle Plus PCT?
Conclusion
As you can see, recovery is extremely important for Maximal Muscle Growth. Taking care of it is not hard, but it is not very fun, as it requires you to be idle. This is the central reason why many gym fanatics ignore recovery, as it is not something you put on your Instagram story.
But, even though it sounds boring and unimportant, ignoring it is all but smart and can lead to injuries and health issues. Yes, sometimes it is better to take it slow and easy, if you want to maximize gains, even if you are a hardcore gym maniac.
