Tag: training
IGF-1 Insulin-Like Growth Factors in Bodybuilding
Unleash the power of IGF-1 in bodybuilding to maximize your muscle growth, recovery, and performance. Discover the benefits of IGF-1 LR3, the recommended dosages for beginners, intermediate, and advanced bodybuilders, and how to safely incorporate this potent growth factor into your bodybuilding journey. Unlock your full potential and achieve optimal results with the help of IGF-1.
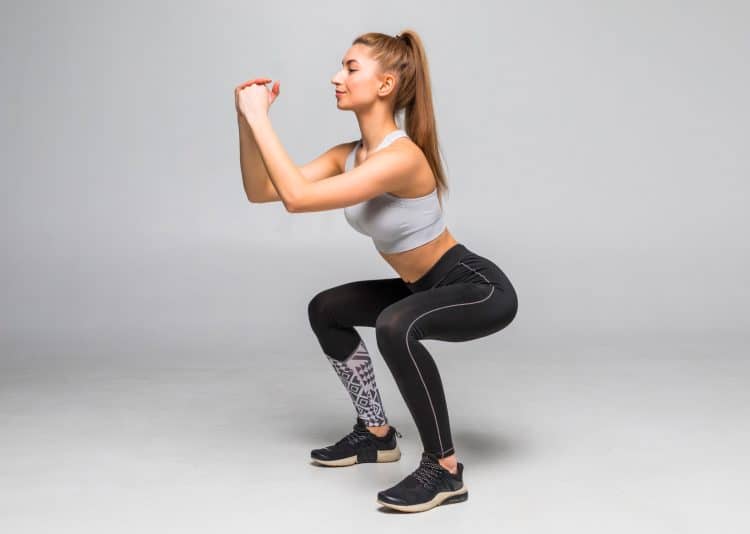

3 Best Beginner Leg Workouts: Turn Your Chicken Legs Into Tree Trunks
Leg workouts are the most skipped workouts in a resistance training routine. It’s almost as if most lifters think that leg workouts are optional. So many lifters have such polarizing views about leg workouts because they had a shaky start with lower-body training.
Many beginners try to do too much too soon in their leg workouts; it gives them suboptimal results and increases their risk of injury. One of the most common mistakes a beginner lifter can make is to incorporate advanced exercisers, such as the Bulgarian split squat and the Jefferson squat, in their training regimen. Although these exercises look dope and can help induce hypertrophy, these lifts are best left to advanced trainers.
Starting the leg workouts on the right foot will set you on the correct trajectory toward your fitness goals. An effective beginner leg workout will help you drill the basic movements and make you look forward to your lower body workouts every week.
In this article, we go over the three best beginner leg workouts to unlock new strength and muscle gains. We also cover the advantages of performing leg workouts as a beginner and the tips to get the best bang for your buck.
Best Beginner Leg Workouts
This article contains three beginner-friendly workouts that will help you build bigger wheels.
But why three and not one, you ask?
A complete beginner should always begin with a bodyweight workout and stick to it for four to eight weeks. The first workout in this article will be a bodyweight workout to help you master the basic movements. The third workout introduces additional resistance to the mix.
What about the second workout? That’s a surprise!
The first workout will help you develop the necessary muscle mobility and strength to perform the exercises using weights with a full range of movement.
Although the bodyweight beginner leg workout might sound boring, it is a must for newbie lifters as it will help you build the necessary bone, tendon, ligament, and muscle strength to support weights for the more advanced workouts.
Bodyweight Beginner Leg Workout
Beginners must begin their lower body training journey with compound (multi-joint) exercises as it helps ignite strength and muscle gains while improving overall functionality, which boosts their physical performance in everyday tasks.
Here is how to perform each exercise with the correct form:
Air Squat
The squat is the king of leg exercises and should be a part of each lower-body training session. It helps develop strength and muscle mass, improve balance and mobility, and build a solid core. There are enough squat variations to keep your workouts interesting.
Steps:
Stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance.
Turn your toes outward slightly for a more comfortable ankle position.
Hold your hands in front of your chest throughout the exercise.
Push your hips back and down to lower yourself into a deep squat.
Pause at the bottom.
Explode back to the starting position while driving through your heels.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Maintain the natural curvature of your spine throughout the movement. Avoid bending forward, as it will strain your lower back.
Check out our complete air squat guide here!
Step-Up
The step-up is a lunge variation. It is a potent booty builder and will help improve your mobility as it involves moving through a more extensive range of motion than the conventional lunge.
Steps:
Stand tall, facing an elevated platform, such as a flat bench or a plyo box. The height of the box should be at least 20 inches.
Lift your right foot off the floor and plant it on the elevated platform.
Drive through the right foot to lift your left leg off the floor. Place your left foot beside your right foot.
Return to the starting position.
Start with your left foot for the next rep.
Alternate between sides for the recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Avoid using your rear leg to push yourself off the floor. Further, keep an upright torso throughout the exercise.
Check out our complete step-up guide here!
Lateral Lunge
The lateral lunge is one of the most overlooked lower body movements. It is excellent for improving your hip mobility. The lateral lunge will boost your performance in leg exercises, especially those that require a wide stance, such as the sumo squat and deadlift.
Steps:
Stand erect with a hip-width stance.
Hold your hands in front of your chest.
Take a big step to your right while keeping your left foot planted on the floor.
Bend your right knee to lower yourself toward the floor. Your right thigh should at least be parallel to the floor at the bottom.
Forcefully push off from your foot to return to the starting position.
Repeat on the left side.
Alternate between sides for the recommended reps.
Pro Tip: As you gain more experience, you can achieve more depth by lifting the toes of the planted foot off the floor.
Check out our complete lateral lunge guide here!
Glute Bridge
This exercise targets your glutes and hamstrings. The glute bridge might look inconsequential but will leave you with a muscle-ripping pump.
Steps:
Lie on the floor on your back. Your arms should be at your sides.
Bend your knees and plant your feet flat on the floor.
Lift your hips toward the ceiling. Your body, from knees to head, should be in a straight line at the top.
Pause and contract your glutes at the top.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Place the soles of your feet together for a greater emphasis on the outside of your glutes.
Check out our complete glute bridge guide here!
Stability Ball Leg Curl
The stability ball leg curl will smoke your hamstrings. This exercise also requires decent core strength to perform correctly.
Steps:
Lie supine on the floor with your feet on top of an exercise ball.
When your legs are extended, your ankles should be on top of the ball. This will be your starting position.
Raise your hips off the floor, keeping your weight on your shoulder blades and feet.
Bend your knees to bring the ball as close to your butt as possible.
Pause and contract your hams at the top.
Return to the starting position.
Pro Tip: You could start with a heavy wall ball if doing this exercise using an exercise ball feels too difficult.
Standing Calf Raise
Calves are often overlooked in a bodyweight training regimen. However, this is no ordinary training program.
Steps:
Place your toes on the edge of an elevated object, such as an aerobic step.
Place your hands on a wall for stability.
Lower your heels as close to the floor as possible.
Lift your heels as high as possible.
Pause and contract your calves at the top.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Pro Tip: Imagine getting on your toes like a ballerina at the top of the movement for optimal gastrocnemius muscle stimulation.
Check out our complete standing calf raise guide here!
Bodyweight HIIT Leg Workout For Beginners
Beginners can ramp up the intensity of the bodyweight leg workouts using the HIIT (high-intensity interval training) protocol. HIIT workouts involve short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. Besides helping build muscle mass and strength, HIIT workouts can improve cardiovascular health, increase metabolic rate, and promote weight loss. Furthermore, since this type of workout takes less time to complete than conventional workouts, it is more suitable for people on a tight schedule. [1]
We’ll program the bodyweight beginner leg workout exercises into a HIIT format. Perform three rounds of the following circuit. Do each exercise for 45 seconds. You are allowed a 15-second rest after each exercise and a two-minute rest after finishing each round. This workout will take you 21.25 minutes to complete.
Weighted Beginner Leg Workout
The weighted beginner leg workout includes basic lower body exercises; these will help add size and strength to your wheels.
After doing the bodyweight leg workout for four to eight weeks, you can switch to the weighted beginner leg workout. It includes a balance of compound and isolation exercises to ignite new growth. Use a weight that allows you to reach muscle failure in the 8-12 rep range to boost muscle hypertrophy. Also, limit your rest duration between sets to 60-120 seconds to keep your training intensity high. [2]
Below is the form breakdown of each exercise:
Barbell Squat
The barbell back squat is a variation of the air squat and involves holding a bar across your shoulders while performing the lift.
Steps:
Stand erect with a hip-width stance with a barbell placed across your shoulders.
Keeping an upright torso, lower yourself into a squat by pushing your hips back and down.
Lower toward the floor until your thighs at least break parallel.
Explode back to the starting position.
Pro Tip: Keep your core and glutes braced throughout the exercise for better balance and stability.
Check out our complete barbell squat guide here!
Walking Lunge
The barbell walking lunge is more challenging than the forward or reverse lunge as it demands greater balance and core stabilizer engagement.
Steps:
Stand upright with a barbell placed across your shoulders.
Step forward with your right foot.
Lower until your left knee touches the floor and your right thigh is parallel to the floor.
Bring your left foot next to your right foot.
Alternate between sides for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Use a weight that you can handle comfortably. You can switch to dumbbells if you’re having difficulty maintaining your balance with a barbell.
Check out our complete walking lunge guide here!
Leg Press
The leg press is one of the most abused training equipment. Most lifters load more weights onto the machine than they can handle and end up moving the sled only a few inches. Ensure you follow a full range of motion for optimal muscle stimulation.
Steps:
Load an appropriate weight onto the leg press machine.
Take a seat on the machine while maintaining the natural curvature of your spine.
Plant your feet shoulder-width apart on the foot platform.
Unrack the sled and unhook the safety bars.
Slowly lower the sled until your thighs are a few inches away from your chest.
Extend your legs while driving through your whole foot.
Avoid locking out your knees at the top.
Repeat for recommended reps.
Pro Tip: Use different foot positions to target your legs from different angles. A wider-than-shoulder-width stance targets your inner thighs, whereas a narrow foot placement targets your quad sweeps.
Check out our complete leg press guide here!
Leg Extension
The leg extension is a staple in most leg workouts. It is an isolation exercise that focuses on your quads.
Steps:
Sit on the leg extension machine and place your ankles behind the foot pad.
While keeping your hips glued to the seat, extend your knees so your legs are in a straight line.
Pause and contract your quads at the top.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Train to failure on this exercise to achieve a quad-ripping pump.
Check out our complete leg extension guide here!
Leg Curl
Similar to how the machine preacher curl targets the biceps, the leg curl targets and strengthens the hamstrings.
Steps:
Lay face down on the machine.
The ankle pad should be just above the back of your ankles.
Squeeze your hamstrings and curl the weight. The pad should touch your hips at the top of the movement.
Pause and contract your hams at the top.
Slowly return to the starting position.
Repeat for reps.
Pro Tip: Keep your toes pointed during this exercise for better hamstring isolation.
Check out our complete leg curl guide here!
Seated Calf Raise
While the standing calf raises stimulate the gastrocnemius muscle, the seated calf raise works the soleus muscle.
Steps:
Sit on the calf raise machine. Place your toes on the foot platform and the bottom of your quads under the thigh pads.
Unrack the machine and lower your heels as close to the floor as possible.
Raise your heels as high as possible.
Contract your calves at the top.
Pro Tip: Calves can be a stubborn muscle group to develop. Increase your training volume by doing more sets and reps if you have lagging lower legs.
Check out our complete seated calf raise guide here!
Benefits of Beginner Leg Workout
Here are the advantages of doing the beginner leg workout:
Builds Strength and Muscle Mass: These beginner leg workouts will help you pack on muscle mass and strength. It will also improve your overall physique symmetry and balance.
Helps Builds a Solid Foundation: Leg workouts can help build a solid foundation by increasing your overall strength, improving your posture, and boosting your athletic performance.
Improves Balance and Stability: Lower body exercises, especially unilateral movements like the lunge, can improve your balance and stability. It will also strengthen your stabilizer muscles.
Boosts Functionality: Most exercises in beginner leg workouts are compound movements that will improve your overall functionality and make you perform better in daily activities.
Burns More Calories: Leg workouts involve training half your body in a single workout, which results in greater calorie burning than training other smaller muscle groups.
Develops a Strong Mindset: Leg workouts demand more grit and determination than any other muscle group. Going hard and heavy in leg workouts will help you develop a killer mindset.
Tips To Consider During a Beginner Leg Workout
Use the following tips to make the most of your lower body training sessions:
Warm-Up: Spending 5-10 minutes warming up will improve your mobility and flexibility and lower your injury risk.
Cool Down: Stretching after a leg workout is an excellent way to kickstart your recovery process.
Mobility: You must have decent overall mobility to perform leg workouts. Poor mobility will limit your range of motion and make achieving depth in exercises like the squat and leg press uncomfortable.
Progressive Overload: You must consistently challenge your muscles by increasing your training intensity and volume to ensure constant growth and limit the risk of hitting a plateau. Increase the weights, number of sets, reps, and exercises, or reduce the rest between sets to progressively overload your muscles. You could also use advanced training techniques like super sets and drop sets to achieve this feat.
Diet and Recovery: Whether you are training to build muscle mass or strength, you must follow a macro-focused diet and sleep for at least seven to eight hours each night to speed up your recovery and get the best bang for your buck.
Wrapping Up
The three beginner leg workouts detailed in this article are an excellent starting point for those looking to build strength and size in their lower bodies. These will also help boost your overall functionality, improve your balance and stability, burn more calories, and develop a killer mindset.
You must start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the workouts. Seek expert help to nail down your training form and limit your risk of injury. Finally, back up the beginner leg workouts with balanced diet and recovery programs to unlock stellar gains. Best of luck!
References
Ito S. High-intensity interval training for health benefits and care of cardiac diseases – The key to an efficient exercise protocol. World J Cardiol. 2019 Jul 26;11(7):171-188. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v11.i7.171. PMID: 31565193; PMCID: PMC6763680.
Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.

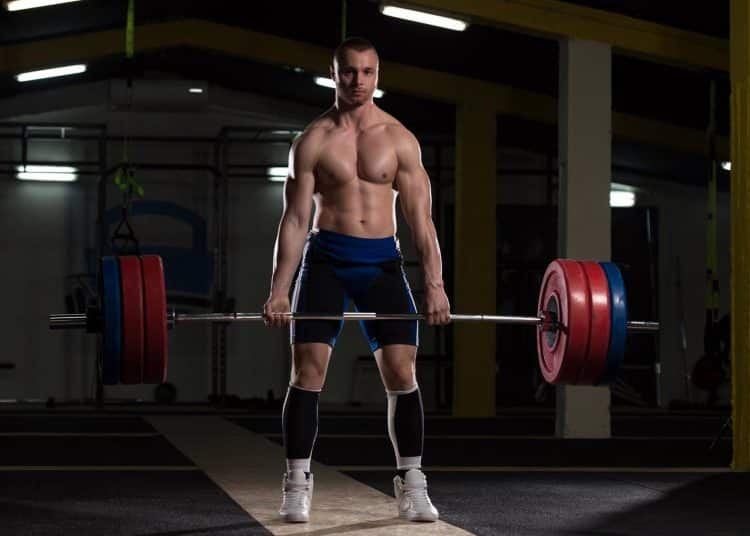
Get Super-Strong with The Best Powerlifting Exercises + Workout
Powerlifting is all about getting strong in the squat, bench press, and deadlift. Between them, these three exercises test and develop your entire body. As such, powerlifters are among the strongest people on the planet. Many famous strongman competitors started as powerlifters, and some continue to compete in both disciplines.
Most gymgoers are familiar with squats, bench presses, and deadlifts and do them as part of their leg, chest, and back workouts. However, these movements are the priority in powerlifting, and all other exercises are secondary, chosen to improve their performance.
In this article, we take a look at the squat, bench press, and deadlifts and reveal the best accessory exercises you can use to increase your strength in these key lifts. We’ve also got a powerlifting-inspired training program for you to try.
Powerlifting Exercises – The Big Three
Russel Orhii / Instagram
The competitive lifts in powerlifting are often called “the big three” and are the barbell back squat, bench press, and deadlift. Each powerlifting exercise is governed by rules so that all competitors perform each exercise in a similar fashion. This ensures that performances can be compared and judged fairly.
Needless to say, the squat, bench press, and deadlift should always be at the top of any list of powerlifting exercises.
Barbell Back Squat
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors, core.
Powerlifting meets start with the barbell back squat. Lifters have three attempts and perform a single rep. For their squat to count, powerlifters must descend until their thighs are at least parallel to the floor. This is deeper than many recreational exercisers squat and takes flexibility, mobility, and practice.
Because of the danger of failing a rep, squats should always be performed in a power rack or with strong spotters on hand.
Steps:
Rack and hold your barbell across your upper back. It should not rest on your neck. The lower you can hold the bar, the shorter the lever from the weight to your hips will be, and that means less stress on your lower back. This is called a low-bar squat.
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, toes turned slightly outward.
Pull your shoulders down and back, brace your core, and inhale deeply.
Bend your knees and hips and squat down until your thighs are parallel to the floor. Push your knees out as you descend. Take care not to round your lower back, as doing so can lead to injuries.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand up straight. Exhale as you ascend.
Rerack the bar or reset your core and do another rep.
Tips:
Experiment with your stance width to see what feels strongest and most comfortable.
If squats hurt your neck, you’re resting the bar too high. Move it further down your back so it’s resting on a pad of muscle and not directly onto bones.
Wear knee sleeves to support and protect your joints if necessary.
Use a lifting belt to increase intra-abdominal pressure and support your lumbar spine.
Wear hard-soled shoes to increase your stability and balance, e.g., weightlifting shoes.
Bench press
Target muscles: Pectoralis major, triceps, deltoids, rotator cuff.
Most exercisers are very familiar with the bench press as it’s a popular chest exercise. However, the powerlifting bench press is slightly different, as the aim is not to build muscle but to lift as much weight as possible.
A lot of powerlifters, especially in the lighter divisions, bench press with a very pronounced back arch. This reduces the distance the weight has to travel, which saves energy and should lead to a bigger lift. In powerlifting, the bar must briefly touch your chest, and you cannot press it back up until the referee tells you to.
Steps:
Lie on the bench so your eyes are directly under the bar. Grip the bar with a slightly wider than shoulder-width grip.
Push your upper back into the bench and drive your feet into the floor. Pull your shoulders back and down, inhale, and lift your chest up toward the barbell. Brace your core. Make sure your entire body is tense.
With help from a spotter, unrack the bar and hold it over your chest.
Without moving your feet, bend your arms and lower the bar to the highest point of your chest. Tuck your elbows in as the bar descends. Pause for 1-2 seconds with the weight touching but not resting on your chest.
Drive the bar up and slightly back until your elbows are straight, letting your arms flare out slightly as the weight ascends.
Rerack the bar or reset and do another rep.
Tips:
Use wrist wraps to support your wrists when lifting very heavy weights.
Move your feet closer to your hips to increase your arch, making sure you keep your butt on the bench.
Squeeze the bar as hard as possible to increase upper body tension and strength.
Try to push the bar up as fast as you can to blast through your sticking point.
Imagine pulling the bar apart to maximize upper back engagement and increase stability.
Deadlift
Target muscles: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, quadriceps, latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, biceps, forearms, core.
Powerlifting competitions end with the deadlift. In many instances, the result of the meet hangs on the deadlift. Powerlifters have a choice between conventional and sumo deadlifts. While the muscles involved in these exercises are similar, stance width affects how much work they have to do.
Narrow-stance conventional deadlifts involve more back, glutes, and hamstrings engagement, while wide-stance sumo deadlifts hit the quads and glutes more.
Prospective powerlifters should try both types of deadlifts to see which one they prefer.
Read more about Sumo vs. Conventional Deadlifts here.
Sumo deadlift steps:
Position your barbell so it’s roughly nine inches from the floor. Stand behind the bar and adopt a wide stance so your feet are close to the weight plates. Turn your toes out slightly. The bar should be almost touching your shins.
Hold the bar with a shoulder-width overhand or mixed grip. Your back should be slightly arched, arms straight, shoulders down and back, and hips higher than your knees. Brace your core and inhale.
Drive your feet into the floor and extend your knees, keeping the bar close to your legs. Do not round your lower back.
As the bar passes your knees, push your hips forward to finish the lift.
Stand up straight but do not lean back or bend your arms, which could cause injury.
Push your hips back, bend your knees, and lower the weight back to the floor.
Release the bar and stand up, or reset your core and grip and perform another rep.
Conventional deadlift steps:
Position your barbell so it’s roughly nine inches from the floor. Stand behind it with your toes under the bar, feet about hip to shoulder-width apart.
Reach down and hold the bar with an overhand or mixed grip.
Straighten your arms, pull your shoulders down and back, and brace your abs. Your lower back should be slightly arched, with your hips lower than your shoulders.
Without bending your arms or rounding your lower back, drive your feet into the floor and stand up. Push your hips forward as the bar passes your knees.
Stand up straight but do not lean back or bend your arms, which could cause injury.
Push your hips back, bend your knees, and return the weight to the floor.
Release the bar and stand up, or reset your core and grip and perform another rep.
Tips:
Use lifting chalk to maximize your grip and prevent slipping.
Wear flat-soled shoes or lift barefoot for increased stability.
Use a weightlifting belt to support your lumbar spine.
Imagine you are jumping with a weight in your hands to blast past your sticking points more easily.
Do at least some of your sets with a double overhand grip and with your mixed grip reversed to avoid developing muscle imbalances.
Powerlifting Exercises – Accessory Lifts
While you can get big and strong doing nothing but squats, bench presses, and deadlifts, this is not the ideal way to maximize your performance. Powerlifters use accessory exercises to improve their performance in the big three lifts.
Accessory, sometimes called assistance, exercises help strengthen the weak links that might otherwise hold you back. These exercises are usually performed after the main lift for the day, or during a separate workout.
You should choose your accessory exercises according to your weaknesses. For example, if you round your lower back during squats and deadlifts, you need to strengthen your spinal erectors and core to prevent this problem.
These are the best powerlifting accessory exercises for the squat, bench press, and deadlift.
1. Paused squat
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors, core.
Paused squats involve stopping at the midpoint of each rep for 3-5 seconds. This breaks the eccentric/concentric stretch-shortening reflex, which forces you to work harder on the ascent. This is a good exercise for improving speed out of the hole and reinforces proper squat depth.
Steps:
Adopt your normal squat stance.
Descend smoothly and then pause with your thighs parallel to the floor. Hold this position for 3-5 seconds, maintaining tension throughout your body.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand up as powerfully as possible.
Reset your core and repeat.
Tips:
Start light and increase weights gradually; this exercise is harder than it looks.
Do not relax during the pause. Instead, stay tight and keep your chest up and knees out.
Try to explode out of the pause to increase muscle power and engage your muscles fully.
2. Box squats
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors, core.
Like paused squats, box squats break up your descent and ascent, so you have to work harder to stand up. However, resting on a box means you also have to control the speed of your descent and have a depth target to aim for. If you sometimes find yourself squatting too shallow, this exercise could help.
Steps:
Stand with your back to a knee-high bench or box and adopt your normal squat stance.
Push your hips back, bend your knees, and descend until your butt touches the platform. Keep your chest up.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand back up.
Rest your core and repeat.
Tips:
Place to foam pad on your box to avoid shock-loading your spine.
Stay tight on the box – do not relax.
Lower the height of the box as your mobility and flexibility improves.
3. Leg press
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors.
Leg presses allow you to strengthen your legs without using your core or back muscles. Needless to say, strong legs are critical for a big squat! If your back and core are tired after squats or deadlifts, a few sets of leg presses will allow you to continue strengthening your legs. However, your primary focus should always be squats and squat variations. Leg presses are not one of the big three!
Steps:
Sit on your leg press machine with your lower back and butt pressed into the seat. Place your feet on the footrest, shoulder to hip-width apart.
Unrack the weight, bend your knees, and descend as deeply as you can without rounding your lower back.
Push the weight back up and repeat.
Rerack the weight on completion.
Tips:
Experiment with the position of your feet to determine what feels the most comfortable and effective.
Keep your core braced and your lower back pressed into the seat throughout. Do not allow your lower back to round, as doing so can cause severe injuries.
Leg press machine designs vary, so ensure you know how to use the machine in your gym. Ask an instructor if you are unsure.
4. Bulgarian split squat
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors.
Barbell back squats are a bilateral or two-legged exercise. However, it’s common to have one leg stronger than the other. Slight strength imbalances are no problem, but more significant differences can lead to injuries and could hurt your performance. Bulgarian split squats are an excellent exercise for fixing left-to-right strength imbalances and improving balance and hip mobility.
Steps:
Stand with your back to a knee-high bench. Bend one leg and place your foot on the bench with your laces facing downward. Hop forward into a split stance.
Bend your legs and lower your rear knee down to within an inch of the floor.
Stand back up and repeat.
Switch legs and do the same number of reps on the other side.
Tips:
Hold dumbbells or use a barbell to make this exercise harder.
Pause at the bottom of each rep to make this exercise more challenging.
Lean forwards slightly from your hips to increase glute and hamstring engagement.
5. Squat jumps
Target muscles: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, abductors, adductors.
While powerlifting squats are invariably performed slowly, your intention should always be to move fast. Trying to explode up out of the hole increases muscle recruitment and helps you avoid stalling partway up. As such, it makes sense to include low-load but high-speed exercises in your powerlifting squat workout.
Steps:
Stand in your normal squat stance.
Bend your legs and descend down to parallel.
Using your arms for added momentum, jump up as high as possible.
Land on slightly bent knees to absorb the shock of landing and repeat.
Try to minimize ground contact time between jumps – imagine the floor is hot.
Tips:
Do this exercise on a mat for comfort and safety.
Increase the load by holding dumbbells in your hands or a barbell on your back.
End your set when your jump height starts to decrease.
6. Paused bench press
Target muscles: Pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps.
Competition-style bench presses involve pausing with the bar touching your chest. This stops lifters from bouncing rather than pushing the bar up. Paused bench presses prepare you for powerlifting meets and also increase your strength off your chest, which is a common sticking point for many lifters.
Steps:
Adopt your usual bench press position and unrack the weight.
Bend your arms and lower the bar to your chest.
Pause with the bar touching your chest for 3-5 seconds.
Drive the weight back up and repeat.
Tips:
Use less weight than usual, as pausing makes the load feel heavier.
The longer you pause, the more difficult this exercise becomes.
Do not relax with the bar on your chest. Instead, stay tight like a compressed spring.
7. Close grip bench press
Target muscles: Deltoids, pectorals major, triceps.
While bench presses are usually described as a chest exercise, the triceps are equally involved. However, because the triceps are smaller and weaker than the pecs, invariably, they fail first. Close grip bench presses emphasize your triceps and can help make them less of a liability. Stronger triceps usually mean a bigger bench press.
Steps:
Lie on your bench and hold the bar with a shoulder-width grip. Plant your feet on the floor, push your upper back into the bench, and lift your chest.
Unrack the bar and hold it over your chest.
Bend your arms and lower the bar to your sternum. Keep your upper arms tucked into your sides throughout.
Drive the weight back up and repeat.
Tips:
Experiment with the width of your hands to see what feels most comfortable and effective.
You can also combine close grip bench presses with a pause to make them more demanding.
Avoid doing very close grip bench presses, which can be hard on your wrists, elbows, and shoulders.
8. Wide grip bench press
Target muscles: Pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps.
Wide grip bench presses emphasize your pecs, which are the engine that drives your bench press. Isolation exercises like dumbbell flys and cable crossovers are great for building bigger pecs but won’t do much for your strength. Wide grip bench presses are a critical accessory exercise if you want to press more weight.
Steps:
Lie on your bench and hold the bar so your hands are about six inches wider than your regular grip.
Plant your feet on the floor, push your upper back into the bench, and lift your chest.
Unrack the bar and hold it over your chest.
Bend your arms and lower the bar to your sternum. Keep your upper arms tucked into your sides throughout.
Drive the weight back up and repeat.
Tips:
Keep your upper back engaged to take stress away from your shoulders.
Do this exercise with a pause for a more challenging workout.
Experiment with the width of your hands to see what feels most comfortable and effective.
Read also: Learn how to absolutely nail the wide grip bench press to push your chest muscles to the max!
9. Floor press
Target muscles: Pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps.
Bench presses can be hard on your shoulders. It’s no coincidence that many powerlifters also suffer from chronic shoulder pain. Floor presses allow you to keep working on your bench press while giving your joints a well-deserved break. They’re also excellent for increasing triceps and lockout strength.
Steps:
Lie on the floor with your legs bent and feet flat. Hold your barbell over your chest using a medium-width grip. Press your upper back into the floor and lift your chest up.
Bend your arms and lower the bar until your elbows and triceps lightly touch the floor.
Press the bar back up and repeat.
Tips:
Lower the weight slowly to avoid jarring your elbows.
You can also do this exercise with straight rather than bent legs.
Try using dumbbells instead of a barbell to see which you prefer.
10. Plyo push-up
Target muscles: Pectoralis major, deltoids, triceps.
Plyometric or plyo push-ups develop explosive strength. After pausing, it can be hard to get the bar moving off your chest, which is where your explosive strength comes in. Plyo push-ups are one of the best upper body power and speed exercises around, and you don’t need any equipment to do them.
Steps:
Adopt the push-up position with your arms, legs, and body straight. Brace your core.
Bend your arms and lower your chest to within an inch of the floor.
Explosively extend your arms and push yourself up so your hands leave the floor.
Land on slightly bent elbows, lower your chest back down to the floor and repeat.
Tips:
Do this exercise on a mat for comfort and safety.
End your set when you start losing height.
Try to minimize ground contact time between reps by imagining the floor is hot.
11. Paused deadlifts
Target muscles: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, quadriceps, latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, biceps, forearms, core.
The most common sticking point in the deadlift is as the bar passes your knees. This is because you are in a mechanically disadvantageous position, as the bar is also furthest from your base of support. Paused deadlifts address this common weakness and should help you blast through this sticking point more easily.
Steps:
Set up for sumo or conventional deadlifts as usual.
Drive your feet into the floor and pull the bar up to about knee height. Pause for 3-5 seconds.
Push your hips forward and stand up straight to complete the lift.
Lower the bar back to the floor, reset your core and grip, and repeat.
Tips:
Stay tight during the pause, and do not allow your lower back to round.
The longer you pause, the more demanding this exercise becomes.
Don’t go too heavy too soon, as paused deadlifts are far more challenging than regular conventional or sumo deadlifts.
12. Romanian deadlifts
Target muscles: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, erector spinae, rhomboids, biceps, forearms, core.
Romanian deadlifts target your posterior chain, which is the engine that drives your deadlift. Posterior chain is the collective term for your glutes, hamstrings, and lower back. Weakness in this area will not only reduce your deadlift performance but could also open you up to injuries. As such, Romanian deadlifts are doubly-important for powerlifters.
Steps:
Stand with your feet hip-width apart, knees slightly bent. Hold a barbell in front of your thighs with a mixed or double overhand grip. Brace your core and pull your shoulders back and down.
Hinging from your hips, lean forward and lower the bar down the front of your legs as far as your flexibility allows.
Stand back up and repeat.
Tips:
Do not round your lower back, as doing so can lead to injury.
Tuck your chin in and lengthen your neck to avoid stressing your spine.
Push your hips back and keep your weight on your heels to maximize posterior chain engagement.
Read also: Learn how to build a powerful posterior chain with Romanian deadlifts, or RDLs for short.
13. Good mornings
Target muscles: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, erector spinae, core.
Good mornings get their name because, when you do this exercise, it looks like you are bowing to greet a Victorian-era friend! Weird images aside, this is an excellent posterior chain exercise and, because it doesn’t involve your arms, won’t tax your already overworked forearms and grip.
Steps:
Rack and hold a barbell across your upper back like you are doing squats. Stand with your feet shoulder to hip-width apart and knees slightly bent.
Hinging from your hips, lean forward as far as your flexibility allows. Do not round your lower back.
Stand back up and repeat.
Tips:
Use a squat bar pad for comfort.
Pull the bar down onto your upper back to step it moving as you lean forwards.
Push your hips back and keep your weight on your heels to maximize posterior chain engagement.
14. Barbell hip thrusts
Target muscles: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, erector spinae, core.
This is another posterior chain exercise. However, unlike the previous few movements, it puts very little stress on your lower back, providing a welcome break for that already hard-working group of muscles. Barbell hip thrusts will improve your lockout strength and give you a better-looking butt.
Barbell Hip Thrust
Steps:
Sit on the floor with your upper back against a stable bench. Rest and hold a barbell across your hips. Bend your legs and plant your feet firmly on the floor.
Drive your feet into the floor and push your hips to form a straight line with your knees and shoulders.
Lower your butt back down to the floor and repeat.
Tips:
Use a bar pad or folded mat for comfort if required.
Drive your heels into the floor and not the balls of your feet to maximize hamstring and glute engagement.
You can also do this exercise with a dumbbell instead of a barbell or using one leg instead of two.
15. Ab wheel rollouts
Target muscles: Core, latissimus dorsi, triceps.
Your core can make or break your deadlift. Core is the collective term for the muscles of your midsection, which act like a weightlifting belt during deadlifts, squats, and most other strength training exercises. If your core fails, your midsection will collapse, and some of the force generated by your legs or arms will get lost. A rounded lower back is also weaker and more prone to injury.
Rollouts are one of the most powerlifting-specific core exercises, as they also involve your lats and triceps, both of which are very active during deadlifts.
Ab Wheel Rollouts
Steps:
Kneel down and place your ab roller on the floor in front of your legs. Hold the handles with an overhand grip. Brace your core and straighten your arms.
Push the roller away from you and lower your chest toward the floor.
Keeping your arms straight, use your core to pull the roller back up to your knees.
Tips:
Kneel on an exercise mat or foam pad for comfort.
The further you roll the wheel away from you, the more demanding this exercise becomes.
Reduce your range of motion if this exercise causes lower back discomfort.
Four-Day Powerlifting Workout
While the exercises listed above will make you stronger, you’ll get much better results from your training if you follow a more structured program. This workout plan emphasizes the big three powerlifts and also includes several complimentary accessory exercises to balance your musculature and improve your performance.
However, before beginning any of these workouts, make sure you prepare your muscles and joints with an appropriate warm-up. Begin with 5-10 minutes of easy cardio followed by dynamic mobility and flexibility exercises for the joints and muscles you’re about to use.
Finish off your warm-up with a couple of progressive sets of your first exercise to dial in your technique and get your nervous system ready for heavier weights.
Read more about warming up for strength training here.
Your Training Week
To avoid overtraining and allow adequate time for rest and recovery, this workout plan involves no more than two training days in a row and no more than two back-to-back rest days. This provides the ideal balance between work and recovery. Try not to change which days you train unless absolutely necessary.
#
Day
Exercise
1
Monday
Squat & accessory exercises
2
Tuesday
Bench press (1) & accessory exercises
3
Wednesday
Rest
4
Thursday
Deadlift & accessory exercises
5
Friday
Rest
6
Saturday
Bench press (2) & accessory exercises
7
Sunday
Rest
Workout 1 – Squat & accessory exercises
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Squat
5
5
3-minutes
2
Paused squat
3
6-8
2-minutes
3
Bulgarian split squat
3
10-12 per leg
60 seconds
4
Leg press
3
10-12
60 seconds
5
Squat jump
3
8-10
90 seconds
Workout 2 – Bench press (1) & accessory exercises
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Bench press
5
5
3-minutes
2
Paused bench press
3
6-8
2-minutes
3
Plyo push-up
3
8-10
90 seconds
4
Triceps pushdown
3
10-12
60 seconds
5
Face pull
3
10-12
60 seconds
Workout 3 – Deadlift & accessory exercises
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Deadlift
5
5
3-minutes
2
Paused deadlift
3
6-8
2-minutes
3
Romanian deadlift
3
6-8
2-minutes
4
Hip thrust
3
10-12
90 seconds
5
Ab wheel rollout
3
12-15
60 seconds
Workout 4 – Bench press (2) & accessory exercises
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Close grip bench press
5
5
3-minutes
2
Wide grip bench press
3
6-8
2-minutes
3
Floor press
3
8-10
90 seconds
4
Seated cable row
3
10-12
60 seconds
5
EZ bar skull crusher
3
10-12
60 seconds
FAQs
Do you have a question about the best powerlifting exercises or our workout? No problem, because we’ve got the answers!
1. What weight should I use for these exercises?
The one thing we can’t tell you is how much weight to use for these exercises and workouts. After all, strength is determined by many factors, including age, gender, experience, and genetics.
So, spend your first week of training estimating your training weights. If an exercise calls for 6-8 reps, increase your weight over several sets until you feel you will get close to failure within the specified range. Use your final weight the next time you repeat that workout.
Use this process for all the exercises.
Then, week by week, work at increasing the loads, even if it’s only by 2.5 to 5.0 pounds. These small but gradual increases are the key to getting stronger. This is called progressive overload.
2. How long can I follow this workout plan?
Stick with our powerlifting workout plan until you notice your big three progress starting to slow. This could be 4-8 weeks or several months. Then, as the workout loses some of its, take a one-week deload (easy training week) and try and squeeze a couple more weeks of progress out of your training.
Then, when your progress grinds almost to a halt, quit this plan and start another one.
Check out our library of powerlifting programs here.
3. What diet should I follow with this workout plan?
Training to get stronger invariably means training to build muscle mass. Yes, some strength gains are neurological and not the result of muscle growth. However, a bigger muscle is a stronger muscle. It’s no coincidence that powerlifters are big and muscular.
To build muscle, you need a calorie surplus and at least one gram of protein per pound of body weight. Use this protein calculator to determine your precise protein needs. You also need to consume plenty of carbohydrates for energy and unprocessed fats for hormonal balance and general health.
Ideally, your meals should contain plenty of unrefined foods, including vegetables, whole grains, and other natural ingredients. While the occasional junk food treat probably won’t harm you, the healthier your diet is, the healthier you will be. After all, you are what you eat.
As such, there is no standard powerlifting diet, and you can follow any meal plan that meets your needs.
4. How do I get big like a bodybuilder but strong like a powerlifter?
While powerlifters are strong, bodybuilders are often bigger and are almost always leaner with more aesthetic physiques. Because of this, and depending on their goals, most people choose to follow either a powerlifting plan or a bodybuilding plan.
However, if you want the best of both worlds, you may want to consider powerbuilding. A powerbuilding approach builds muscle mass and strength in equal measure and uses training methods from both types of workout.
You can read more about powerbuilding here.
5. Can I make changes to any of the workouts?
You certainly can, but make sure you avoid changing the exercises too much. For example, while switching barbell for dumbbell floor presses would be fine, hitting the pec deck instead of the bench press would not as the exercises are too dissimilar.
So, look at the muscles involved in the exercise you want to replace and choose a similar alternative. And don’t replace an exercise just because it’s hard – it’s those challenging exercises that are responsible for your strength gains.
6. Can I train for powerlifting even if I don’t want to compete?
While powerlifting competitions are a lot of fun and can be very rewarding, training for one requires a lot of time and dedication.
Your training will need to peak at the right time, and you may also have to lose or gain weight to qualify for your chosen class. You’ll also need to decide whether you will compete equipped or raw and in which federation. There is a risk of injury as you train with ever more weight, and you may have to take time off work and travel to find a suitable meet.
Because of these details, many people follow a powerlifting program with no intention of ever stepping into the limelight and competing. They just enjoy lifting heavy weights and getting stronger, which, for them, is rewarding enough.
The good news is that you can always compare your performance against other lifters in your demographic and compete against your previous best lifts by tracking your one-repetition maximums in the squat, bench press, and deadlift. You can also use the Wilks calculator to compare your strength against other lifters, irrespective of weight and gender.
7. Is powerlifting safe?
Like all sports, powerlifting has some inherent risks. Lifting very heavy weights, failed reps, poor form, and simple accidents can all lead to mild to severe injuries. However, using the proper equipment and correct technique, respecting your body’s need for rest, staying within your limitations, and training hard but smart will mitigate many of these risks.
In reality, powerlifting is no more dangerous than basketball, soccer, football, etc. However, there ARE safer workouts, so if you are only training for general strength and health, you should probably consider something less risky, like progressive calisthenics or general strength training.
Closing Thoughts
Powerlifting is a very accessible strength sport. Unlike competitive strongman, you don’t need lots of specialist equipment, and you can train for powerlifting in almost any commercial gym.
Based on three common gym exercises – the squat, bench press, and deadlift – powerlifting is relatively easy to learn and much less difficult to get into than Olympic lifting. Buy a squat rack, bench, barbell, and weights, and you can even do powerlifting at home.
If you are looking for a way to build muscle and get super-strong, powerlifting is a great choice. More functional than bodybuilding, powerlifting is an excellent standalone activity and compatible with many other sports.
Use the exercises and workouts in this article to get stronger than ever before!
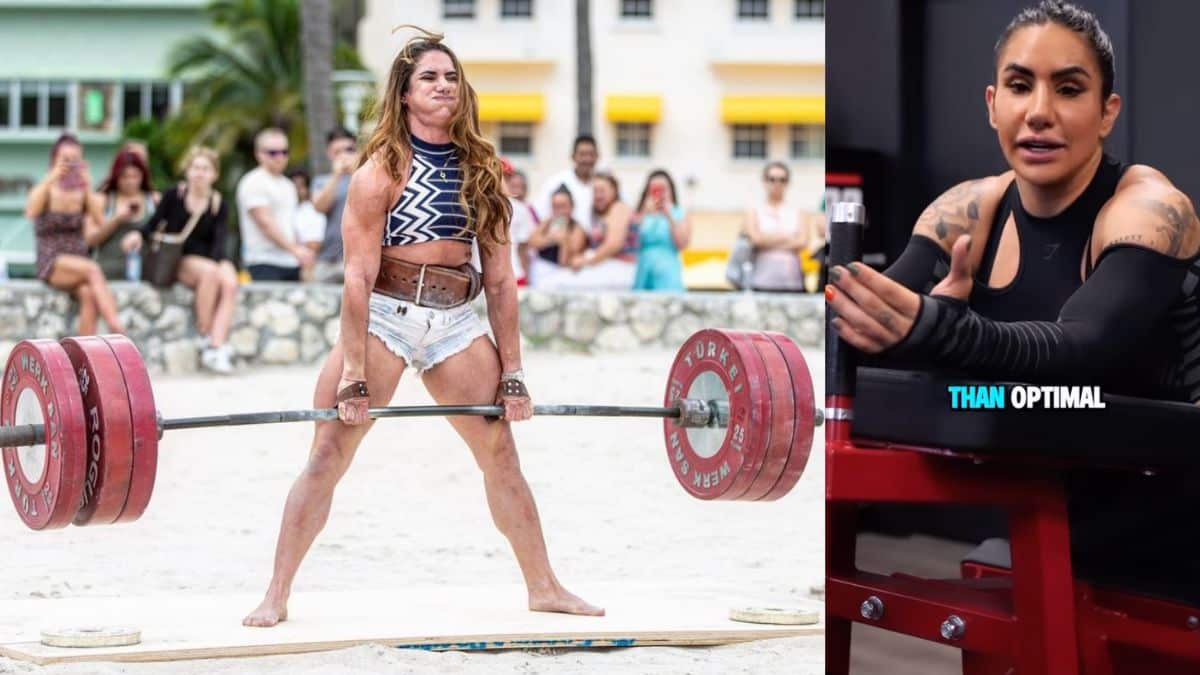

Stefi Cohen on Growing Weaker Body Parts: “9/10 Times You’re Not Performing the Exercise Correctly”
Stefi Cohen has proven herself to be a force inside the gym, having taken part in a number of different sports over the years. In a recent Instagram post, Cohen said genetics aren’t to blame for weaker body parts and shared that stubborn muscles require correct form and proper technique.
“We all have body parts that are harder to grow, but to blame it on genetics is lame. More often than not it’s a product of poor exercise selection, inadequate volume, intensity and most importantly poor execution. The moment you take accountability is the moment you’ll be able to start making progress,” Cohen shared.
From boxing, arm-wrestling, bodybuilding, powerlifting (25-time record holder), strongman, and CrossFit, there are very few athletic mountains Stefi hasn’t climbed. Far from average, she has tested her physique, strength, and endurance for years. She’s also rubbed shoulders with some of the best athletes of their respective disciplines, like former 2017 World’s Strongest Man, Eddie Hall. They teamed up for a shoulder workout and Stefi proved herself lifting alongside the legendary strongman.
As for her CrossFit skills, Cohen doesn’t shy away from a workout challenge. She recently joined Brent Fikowski, the 2017 CrossFit Games silver medalist, for a savage workout that featured intense exercises like Plyo-push-ups, kettlebell deck squats, and burpee-dumbbell snatches.
During her time in the squared circle, Stefi built a commendable combat sports record. In her Pro boxing debut, she knocked her opponent out but recently suffered the first defeat of her career last August when she lost to Devany Cuevas by unanimous decision. Given her competitive history and knack for athletics, Stefi Cohen’s knowledge of fitness makes her especially qualified to offer training advice.
‘We Tend to Blame Sub-Optimal Genectics Instead of Us Not Working Hard Enough,’ Stefi Cohen On Weaker Body Parts
According to Stefi Cohen, people are quick to blame genetics rather than their technique and intensity.
“You don’t have shit genetics. Your hamstrings don’t grow because you don’t know how to train them. And it’s not only when we’re talking about our hamstrings, it’s often the case when we’re talking about a stubborn or weak body part that we’re trying to grow, that we tend to blame it on our less-than-optimal genetics instead of admitting the simple fact which is we don’t know what we’re doing and we’re not working hard enough.
9 times out of 10 the main reason why you can’t grow that specific body part is because you are not performing the exercise correctly and you’re not choosing the right exercise either. It’s so obvious but it’s often overlooked at the expense of hyperfocusing on progressive overload, which is the notion of continuously adding more weight to the exercise that you’re performing.
Oftentimes, lifters focus on getting through the reps instead of the quality of the contraction, which compromises form, Cohen says.
“Take for example the prone hamstring curl exercise. In this exercise the goal is to stabilize our hips as much as possible so that we can stress and apply as much tension to the hamstring muscle as possible. What most people tend to do is focusing on how much weight they’re lifting with this exercise and they compromise their form,” Stefi Cohen explained.
Having made a name for herself in the fitness industry, Cohen has been subjected to a fair amount of fan animosity. So much so that Stefi has openly discussed how she handles haters online who have taken issue with muscular women. She called it ‘fit shaming’ and she highlighted that strong muscular women are common victims of this type of social injustice.
In one of her latest ventures, Cohen teamed up with fitness influencer Will Tennyson. They took part in a boxing/agility-themed workout and played a game of exercise HORSE, with the loser forced to wear a horse mask and take a punch from the winner.
This isn’t Stefi Cohen’s first time offering fans valuable workout advice. Cohen shared her most effective strategies for sculpting a six-pack of abs recently. While she accepts everyone is different, she stressed the importance of dieting and maintaining a sufficient fitness level, adding that, ‘you don’t need to do endless crunches.’ Cohen also said common movements like the deadlift and squat help build the core muscles as well.
Growing weaker body parts can be a daunting task for some, but Cohen is confident that with correct technique and proper intensity, even with bad genetics, substantial gains can still be made inside the gym.
READ MORE:
Published: 5 July, 2023 | 5:58 PM EDT

Army PRT Exercises – The Army Physical Readiness Training Drill
Watch any movie or video about Army physical training, and you’ll probably see recruits and soldiers clambering over obstacles, running with packs, doing unarmed combat, or participating in other forms of intense exercise.
However, the reality is that a whole lot of basic fitness training precedes these feats of endurance and strength. While military training is tough, it builds up gradually over time, helping to reduce the risk of injury and preventing recruits from “washing out” before their military career begins.
The Army PRT (APRT) is a series of exercises designed to prepare soldiers for more intense physical training. It’s also a great way for civilians to warm up before exercise and develop and maintain a decent all-around fitness level.
In this article, we reveal the exercises that make up the Army Physical Readiness Training Drill.
What is the Army PRT Drill?
The Army PRT Drill is a series of ten simple bodyweight exercises designed to be performed sequentially to a predetermined tempo or cadence. The Army uses it as a warm-up before more intense forms of training and also as a short-but-effective standalone workout.
Soldiers often perform the APRT daily, usually on rising. It can also be used to build the basic fitness required to pass the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT), which all soldiers must do at least twice a year.
The exercises themselves involve no equipment, so they can be done anywhere and anytime, even while on deployment.
The exercises that make up the Army PRT Drill are:
Bend and reach
Rear lunge
High jumper
Rower
Squat bender
Windmill
Forward lunge
Prone row
Bent-leg body twist
Push-up
Each exercise is typically performed for five to ten “Army reps,” which, because each movement is performed to a cadence, is actually 10-20 regular reps. You may find this challenging if you are unused to doing your exercises this way.
The aim of the Army PRT Drill is not to overload the muscles or exhaust the participant. Instead, it’s meant to increase heart rate, body temperature, joint mobility, and muscle blood flow. You should feel pleasantly energized after completing the APRT, and not tired to the bone!
The entire ten exercise sequence should take no more than 10-12 minutes, and breaks between exercises should be kept as short as possible. All major joints and muscles are involved in the Army PRT Drill, and its simplicity and low to moderate intensity level means it can be performed daily.
Many military veterans continue to perform the PRT exercises to help them stay in shape and maintain some of their hard-won Army fitness.
Army PRT Exercise Instructions
There are two ways to perform most exercises – the right way and the wrong way. Needless to say, the Army won’t tolerate sloppy exercise technique, so make sure you follow these instructions and make your physical training instructor proud!
Do 5-10 reps of the following exercises using a smooth, controlled tempo.
1. Bend and reach
Purpose: Mobilize the shoulders, hips, and spine.
The first exercise in the Army PRT Drill is the forward bend and reach. This exercise will loosen and warm up your entire posterior chain, which is the collective name for the muscles of the back of your legs, hips, and torso. Take care not to round your back too much, as doing so could lead to injury.
Steps:
Stand with your feet roughly shoulder-width apart. Pull your shoulders down and back and look straight ahead.
Brace your abs and raise your arms above your head.
Bend your knees slightly, hinge from your hips, and lean forward, reaching your hands between your feet.
Return to the starting position and repeat.
2. Rear lunge
Purpose: Mobilize the hips while improving lower body strength and balance.
Most exercisers should be familiar with lunges. After all, they’re one of the best unilateral leg exercises around. The Army does rear lunges a little differently, but they still offer many of the same benefits. This move is especially beneficial for soldiers as it helps strengthen and stretch the running muscles and builds the balance and agility needed to get behind cover and shoot from a kneeling position.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, hands on your hips. Pull your shoulders down and back, brace your core, and look straight ahead.
Take a large step backward and then stop.
Keeping your leg straight, gently press your heel into the floor and push your hips forward to feel a mild stretch in your calf, hips, and quads.
Step your foot back in and then repeat on the opposite leg.
Continue for the desired number of reps.
3. High jumper
Purpose: Improves explosive leg strength and teaches the correct takeoff and landing for jumps.
A soldier’s legs need to absorb a lot of impact when they march, run, and jump. That impact rises significantly when carrying a pack or equipment. This jumping exercise is designed to develop lower body power and teach correct jumping technique to help ward off impact-related injuries.
Steps:
Stand with your feet roughly shoulder-width apart, knees bent, and arms straight with your hands behind your hips.
Swing your arms forward and up, and jump a few inches into the air.
Lower your arms and perform a second small jump.
Next, swing your arms forward vigorously, and use this momentum to jump high into the air.
Land, lower your arms, and perform another small jump.
Continue this four-count sequence for the desired number of reps.
4. Rower
Purpose: Develop core and hip flexor strength
Core strength is important in the military. A strong core provides support for your lumbar spine, reducing the risk of back injury. A strong core is especially important for infantry soldiers, who must be able to march long distances while carrying heavy packs. This is known as rucking in Army parlance.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your arms straight and your biceps close to your ears. Brace your core.
Bend your legs, sit up, and take your arms forward so they’re parallel to the ground and outside your knees. Your feet should be flat on the floor.
Lie back down and return to the starting position.
Continue for the desired number of reps.
5. Squat bender
Purpose: Develop lower body endurance and hip/lower back mobility.
The squat bender combines bodyweight or air squats with unweighted Romanian deadlifts. Between them, these two exercises work all your major leg muscles while providing an excellent stretch for your hips and hamstrings. The bodyweight RDL also reinforces correct lifting technique.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, hands on your hips. Pull your shoulders down and back and look straight ahead.
Bend your knees and squat down until your thighs are roughly parallel to the ground. Extend your arms out in front of you for balance.
Stand up and return to the starting position.
Next, hinge forward from the hips and reach down toward your toes. Take care not to round your lower back.
Finally, stand back up and return to the starting position.
Repeat the four-count sequence for the desired number of reps.
6. Windmill
Purpose: Develop mobility in the spine, shoulders, and shoulder girdle.
The windmill is an old-school calisthenic mobility exercise. It involves hip hinging and twisting, which stretches your hamstrings and waist while mobilizing your entire spine. Do this exercise slowly, as per the instructions, to avoid injury and get the most from this classic calisthenic movement.
Steps:
Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, arms raised so they’re parallel to the ground. Brace your core and look straight ahead.
Bend your hips and knees and reach down to touch the outside of your left foot with your right hand.
Extend your right arm behind you so the arms form a straight line throughout. Ensure most of the movement comes from your hips and not by rounding your lower back.
Stand back up and repeat to the opposite side.
Continue alternating sides for the required number of reps.
7. Forward lunge
Purpose: Develops balance, mobility, and leg strength.
The Army sure does love lunges! For your seventh PRT exercise, you’ll be doing alternating forward lunges with a somewhat shorter-than-normal step. This increases quads engagement and involves a larger range of motion at the knees. As such, expect to feel this exercise more in your thighs and less in your hips.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, hands on your hips. Pull your shoulders down and back and look straight ahead.
Take a small step forward, bend your legs, and try to lower your butt to your rear heel. Keep your torso as upright as possible.
Straighten your legs, step back into the starting position, and repeat on the other side.
Continue alternating legs for the duration of your set.
8. Prone row
Purpose: Strengthen the neck and upper back for greater stability and better posture.
The prone row is an excellent exercise for the neck and upper back. It helps prepare you for shooting from a prone (lying on your front) position and supporting the weight of your helmet. It’s also a good movement for increasing lower back strength and improving your posture. All in all, it’s a perfect exercise for soldiers.
Steps:
Lie on your front with your arms extended and hands a couple of inches above the floor.
Raise your shoulders and chest off the floor and pull your hands down and into your shoulders like you’re doing a lat pulldown. Clench your fists and lift your head as far as comfortable.
Next, extend your arms, open your hands, and return to the starting position.
Repeat for the desired number of reps.
9. Bent-leg body twist
Purpose: Develop core strength and spine mobility.
This exercise will help mobilize your lumber spine and increase core strength, especially in the obliques or waist muscles. Rotational strength is important for many activities in the military, including pushing, pulling, punching, kicking, and throwing.
Steps:
Lie on your back with legs bent to 90 degrees and thighs vertical. Extend your arms out to the side to form a T-shape, hands resting on the floor.
Keeping your shoulders and arms on the floor, rotate your hips and lower your knees to the left so they’re a couple of inches above the floor.
Return to the starting position and then repeat the same movement to the right.
Come back to the center and repeat, alternating sides rep by rep.
Continue for the desired number of reps.
10. Push-up
Purpose: Strengthen the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
No Army workout is complete without push-ups! This classic exercise builds upper body strength and endurance and is a staple of military training. Forget the bench press; if you want to develop a functionally strong upper body and arms, push-ups are a must.
Steps:
Adopt the front support position with your arms, legs, and body straight. Your hands should be shoulder-width apart, fingers pointing forward. Brace your core.
Bend your arms and lower your chest down until your upper arms are parallel to the ground.
Extend your arms and return to the starting position.
Continue for the prescribed number of reps.
Army PRT Exercises Pros
Not sure if the Army PRT is right for you? Consider these pros and then decide!
1. Anywhere, anytime
The exercises in the Army PRT involve no equipment and require very little space. As such, you should be able to do them almost anywhere and anytime. Because of this, you really have no valid excuse for not making the Army PRT Drill part of your daily routine.
2. A full-body workout
The Army PRT works every major muscle and joint, providing a well-rounded and comprehensive workout. Developing all your muscles and joints equally is critical for creating a balanced physique and avoiding muscle imbalances, which can lead to injuries and dysfunction.
3. Easy to learn
Despite a few unfamiliar names, the exercises that make up the Army PRT Drill are generally common and well-known. Many feature in high-school PT classes. They’re also straightforward and easy to learn. While training to a cadence may be challenging at first, you’ll get used to moving in such a controlled fashion. The Army PRT exercises are ideal for all levels, including beginners.
4. Minimal time commitment
Taking no more than 10-12 minutes to complete, doing the Army PRT should fit into even the busiest person’s schedule. Lack of time and facilities are common barriers to exercise participation, but both are no longer an issue with this short workout plan.
5. Easy to modify for all levels
The PRT Drill is usually performed for one lap of five reps done to a set cadence. However, that doesn’t mean you can’t modify it to better suit your current fitness level. For example, beginners can drop the cadence and just do regular reps, which are considerably easier. More capable exercisers can do more reps or more than a single lap.
So, the Army PRT Drill has something to offer all exercisers, from beginners to advanced.
6. Easy to make a habit
This workout is tailor-made to make habitual exercising easier. The ten exercises flow together to form an easy-to-remember routine you can do whenever you have a few minutes free.
Many people struggle to exercise regularly, but committing to doing the Army PRT Drill every day should help develop a strong exercise habit. Doing something simple every day is often better than doing something more challenging less frequently.
Army PRT Exercises Cons
The Army PRT is a safe and effective way to work out without equipment and in minimal space. However, there are a couple of disadvantages to consider, too:
1. Limited overload
The Army PRT Drill uses your body weight to develop strength, endurance, and mobility. However, if you are strong, light, or already pretty fit, this may not be challenging enough to provide an effective workout.
You can do more reps to overload your muscles, but this can become time-consuming. Alternatively, you can do the PRT wearing a weighted vest to make it more effective.
2. Not many upper body exercises
While the Army PRT Drill is undeniably a full-body program, your legs and core do most of the work. The only upper body exercises are push-ups and prone rows, and the latter is not a very challenging movement.
If you want to increase your upper body strength and endurance, you may want to include more upper body exercises in your workout routine, such as pull-ups, dips, and yet more push-ups. You could also supplement your APRT with resistance exercises such as bench presses, shoulder presses, biceps curls, and lat pulldowns.
3. Not enough training volume
Lasting no more than 10-12 minutes, the Army PRT drill may be too short to provide maximal fitness benefits. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), most adults should try to get about 150 minutes of exercise per week (1). Even if you do the PRT every day, you won’t hit this target.
As such, the PRT will probably work best when performed alongside another form of exercise, e.g., running.
Army PRT Exercises FAQs
Do you have a question about the Army PRT Drill? No worries because we’ve got the answers!
1. Can you share a follow-along version of the Army PRT Drill?
We sure can! This video takes you through the entire PRT Drill and is led by an Army physical training instructor who counts out the cadence for the entire workout. Just watch the demos and follow his lead.
2. How should I cool down after the Army PRT?
While you could just end your workout with a few cool-down stretches, the Army won’t leave you hanging and has a cool-down routine designed to be done after the PRT Drill. Comprising five exercises, this sequence of moves stretches all the muscles you have just been exercising. Follow along with the video, which again is led by an Army physical training instructor.
3. How often should I do the Army PRT Drill?
Because it’s short and not too intense, you can do the Army PRT Drill daily, which is what many soldiers do. However, if that’s too much for you, you should endeavor to do it at least every other day. Doing the APRT less often than this probably won’t produce noticeable results.
4. I’m very unfit – how can I modify the Army PRT to make it easier?
The Army PRT Drill is designed to be done as a non-stop sequence of ten exercises. However, moving quickly from one movement to the next may be too much for some people.
So, do the exercises as described but a) do fewer reps and b) take a moment between each one to catch your breath. Then, as you get fitter, make those breaks shorter until, eventually, you can do the exercises back-to-back.
You could also split the exercises into two five-movement workouts. For example, do the first five exercises one day and the second five the next. Again, as you get fitter, work toward doing the Army PRT Drill as prescribed.
5. When is the best time to do the Army PRT Drill?
The best time to do the Army PRT Drill is whenever it’s convenient. On rising works for some people, while others will prefer to do it later in the day. However, you’ll probably find it easier to create a lasting exercise habit if you do the APRT at the same time each day.
6. Will doing the PRT Drill help me prepare for boot camp?
It’s best to start training early if you plan to join the Army. While boot camp is designed to build your fitness and strength, the entire process will be more manageable if you arrive in decent shape.
So, a few months before your boot camp starts, begin doing some running and basic calisthenic exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, and squats. You should also strive to do the Army PRT Drill daily and have a couple of tries at the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT), so you can be confident that you can pass it.
Related: 5 Simple Exercises – A Daily Calisthenics Routine
7. Can I change any of the exercises in the Army PRT Drill?
You could, but you probably shouldn’t. After all, the APRT Drill was created by the US Army for soldiers, and following orders goes with the job! That said, if one of the exercises bothers an old injury, is painful, or is beyond your abilities, feel free to replace it with something similar.
However, that doesn’t mean you can switch out an exercise just because you find it hard; those are the exercises that drive your fitness improvements. So, rise to the challenge and don’t shy from it, and remember, as they say in the military, you gotta train hard if you want to fight easy.
Related:
Closing Thoughts
The Army Physical Readiness Training (APRT) Drill is a sequence of ten simple calisthenic exercises that develops basic all-around fitness, endurance, and strength. Doubling as a warm-up, this program is designed to be done anywhere and anytime.
It is ideal for serving soldiers, veterans, home exercisers, and anyone who enjoys no-frills, equipment-free workouts. It can also be used to help you prepare for the Army Physical Fitness Test, which is a prerequisite for military service.
While the Army PRT has limitations, it can combined easily with other workouts, such as running and lifting weights, to create a balanced training system.
So, if you are looking for a short, straightforward bodyweight workout that you can also use as a daily warm-up, give the Army PRT Drill a try. At less than 10-12 minutes in duration, it’s time efficient, practical, and very convenient.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: How much physical activity do adults need? https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/adults/index.htm

The Best Calisthenic Leg Workout
Friends don’t let friends skip leg day, or so the popular meme says. However, most leg day workouts involve things like squats, deadlifts, hamstring curls, and leg presses – all of which require equipment and various weights to perform.
That’s no problem if you have access and the time to get to a well-equipped gym, but that’s not always practical or possible. For example, you might be on vacation or too busy and unable to find a couple of hours spare to travel and train.
The good news is that you don’t need a large selection of workout equipment or a pile of weights to get a good leg workout. In fact, your body weight is all you really need.
In this article, we share a challenging and effective calisthenic leg workout, so you can train your lower body anywhere and anytime.
What is Calisthenics?
The term “calisthenics” comes from the Greek words for beauty (kállos) and strength (sthenos). It is a form of training that relies on using body weight for resistance and is also known as bodyweight training.
Popular calisthenic exercises include push-ups, pull-ups, sit-ups, unweighted squats and lunges, and gymnastic and functional movements, including rope climbing and handstands.
Calisthenics has always been popular but has become even more so since COVID forced many gyms to close, as most exercises require no equipment and can be performed at home. Bodyweight training is widely used in the military and by amateur and professional athletes, especially martial artists.
You can use calisthenics to achieve almost any fitness goal, including muscle building, gaining strength, fat burning, improving endurance, and increasing general fitness. There are exercises to suit all experience levels, from raw beginners to very advanced.
The Benefits and Advantages of Calisthenics
Many people are skeptical that something as simple as calisthenics can provide a comprehensive workout. Let’s put those fears to rest by examining the benefits and advantages of calisthenic training!
Convenience
While you may need some way to do pull-ups or dips, most calisthenics exercises involve no specialist equipment. As such, you are free to work out almost anywhere and anytime. You can do calisthenics at home, in your garden, at a local park or playground, or in your hotel room.
Also, because you can do calisthenics anywhere you have enough space to move, you won’t have to waste time traveling to the gym to work out. A 45-minute calisthenic training session will only take 45 minutes, and not the couple of hours that traveling to and from a gym so often takes.
Lack of time and facilities can be a real barrier to exercise participation, but with calisthenics, these barriers are removed.
Economical
With no gym fees to pay and no training equipment to buy, calisthenics training is very easy on your pocket. In fact, you don’t need to spend a single cent to start working out with your body weight.
If you train at home, you don’t even need to buy specialist workout clothes – any old T-shirt and loose-fitting pants will suffice.
That said, a few relatively cheap items can add a lot to your calisthenic training, such as pull-up and dip bars, exercise mats, gymnastic rings, and parallettes. However, these tools are optional extras and not essentials.
Joint-friendly
While some calisthenic exercises are extremely tough, others are more straightforward and easy on your joints. Calisthenic exercisers often mirror everyday activities, so they’re easy to learn, and many will already be familiar to you, as things like push-ups, jump jacks, sit-ups, and squats are often part of high school physical education classes.
Most calisthenic exercises can be modified to suit not only your fitness but your height, weight, and limb length. For example, you can move your hands or feet in or outward to make your chosen exercise as comfortable as possible. Try doing that with leg extensions or the pec deck!
This all adds up to a workout that is usually very joint-friendly. Providing you don’t try to progress too quickly, calisthenic training does not typically lead to injuries.
Improve athleticism and functionality
With no machines to guide your movements or support your body, calisthenic training is not only good for your muscles but your nervous system too. Doing calisthenic exercises will improve your balance, mobility, coordination, proprioception, athleticism, and functional fitness and strength.
In other words, the fitness you develop through calisthenics will transfer seamlessly to your life outside of training.
This helps explain why calisthenics is so popular with sportspeople and the military – it improves real-world fitness, so you’ll not only look in shape but will actually BE in shape, too.
Versatility
Contrary to what you might think, calisthenics can be adapted to meet almost any training goal, from fat burning to muscle building to improving your general health and well-being. It all comes down to your choice of exercises and how they’re programmed and performed.
For example, you could superset (perform in pairs) high-rep push-ups and squat jumps to get a great fat-burning cardio workout. Alternatively, you could do low-rep pull-ups and single-leg pistol squats to build muscle mass and strength.
So, whatever you are training for, you can probably achieve it with calisthenics.
Related: Calisthenics vs. Weight Training – Which is Best?
Calisthenics Disadvantages and Drawbacks
While calisthenics training is mostly safe and effective, there are a couple of disadvantages and drawbacks to consider, too. These include:
Difficulty isolating muscles
Bodybuilders use single-joint or isolation exercises to target individual muscles and maximize hypertrophy or growth. This is usually not possible with calisthenic training. In contrast, most calisthenic exercises are compound or multi-joint and train several muscles at once.
While compound exercises are excellent for building strength and burning calories, some lifters enjoy doing isolation exercises, using them to target individual muscles, such as the biceps, triceps, or deltoids.
For this reason, some people like to combine compound calisthenic exercises with resistance band or isometric isolation exercises.
Limited progression options
While you can progress some calisthenic exercises by modifying them to make them more challenging, the primary source of progression is doing more reps. That’s okay when you’re starting out, but as you get fitter and stronger, you may find yourself doing 50, 80, or even 100 reps of some calisthenic exercises. This can be time-consuming and boring.
In contrast, with conventional strength training, you can simply up the weight to maintain your progress.
Your body weight may be a limiting factor
Some calisthenic exercises may be too hard or even impossible if you are heavy and/or a beginner. For example, push-ups and pull-ups can be especially challenging for larger people.
This is usually less of an issue with conventional strength training, where the load can be modified more easily.
It could be too convenient
Convenience can be a double-edged sword. On the one hand, it means you can work out anywhere and anytime. However, this can also create a lack of urgency, meaning you put your workout off until later, and may even skip it entirely. “I’ll do it later” can quickly turn into “I’ll do it tomorrow,” and, as the saying goes, tomorrow never comes.
One way around this is to plan your workouts in advance and have a set time to train, e.g., on rising or before dinner. Working out on the same days and at the same time makes it easier to be consistent.
The Best Calisthenic Leg Workout – Overview
The following workout is designed to be performed as part of a split routine, where you train different muscles on different days, for example:
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
Saturday
Sunday
Legs
Upper body
Rest/cardio
Legs
Upper body
Rest/cardio
Rest
However, before starting any strenuous training, you should prepare your muscles and joints with some light cardio followed by dynamic mobility and flexibility exercises. Warming up will make your workout more comfortable and effective and could also help reduce your risk of injury.
Five to ten minutes is all you need, so don’t be tempted to skip this critical step. While not warming up may save you a few minutes, it could cost you months of lost progress if you pick up an otherwise avoidable injury.
All warmed up and ready to go? Good to hear! Here’s your calisthenic leg workout:
#
Exercise
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Reverse Nordic
2-4
Take each set to within 1-3 reps of failure.
60-90 seconds
2
Bulgarian split squat (1½ reps)
2-4
60-90 seconds
3
Glute bridge walkout
2-4
60-90 seconds
4
Single-leg Romanian deadlift
2-4
60-90 seconds
5a
Wall squat hold
2-4
N/A
5b
Squat jump
60-90 seconds
6
Single-leg calf raise
2-4
60-90 seconds
Exercises 5a and 5b are to be performed as a superset. Do the first exercise (wall squat hold), followed immediately by squat jumps. Rest a moment and repeat the pairing for the required number of sets.
The Best Calisthenic Leg Workout – Exercise Instructions
There are two ways to perform most exercises – the right way and the wrong way. The right way is safe and effective, while the wrong way is more likely to cause injuries and probably won’t produce such good results.
Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure you do all the exercises in this workout correctly.
1. Reverse Nordic
Muscles targeted: Quadriceps, hip flexors, core.
People who train in a gym can do leg extensions to target their quadriceps. Calisthenic practitioners don’t have this option, but that doesn’t mean you can’t hammer your quads and strengthen your thighs. Think of reverse Nordics as natural leg extensions – no equipment required!
Steps:
Kneel on the floor with your toes pointed and the tops of your feet pressed into the floor. Your thighs and torso should be vertical. Brace your core.
Without bending your hips, lean backward and try to touch your calves with your hamstrings.
Drive your feet into the floor and push yourself back into the starting position.
Continue for the desired number of reps.
Tips:
Kneel on a folded gym mat or foam pad for comfort.
Only lean back as far as is comfortable. Increase your range of motion as you get stronger.
Use a resistance band for assistance if necessary:
2. Bulgarian split squat (1½ reps)
Muscles targeted: Quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, hip abductors, hip adductors.
After hitting your quads hard with reverse Nordics, it’s time to work them in conjunction with your other lower body muscles with Bulgarian or rear foot elevated split squats. However, to compensate for the lack of external load, you’ll do this exercise using 1½-rep style.
Steps:
Stand with your back to a knee-high step or bench. Bend one leg and place the top of your foot on your platform. Hop forward and into a split stance.
Keeping your torso relatively upright, bend your legs and lower your rear knee down to within an inch of the floor.
Extend your leg and come halfway up.
Lower your knee back down to the floor, and then come all the way up.
That’s one rep – keep going!
Continue for the desired number of reps, and then switch legs.
Tips:
Do this exercise next to a wall and use it for balance if required.
Place a folded exercise mat under your rear knee for comfort.
Lean forward slightly to increase glute and hamstring engagement.
3. Glute bridge walkout
Muscles targeted: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, core.
With no leg curl machine to use, you may be wondering how you’re going to train your hamstrings. Well, wonder no more – this exercise is the answer! Glute bridge walkouts are a low back-friendly posterior chain exercise that will fry your hamstrings in double-quick time.
Steps:
Lie on your back with your legs bent and feet flat. Press your lower back into the floor and brace your core.
Lift your hips up toward the ceiling.
Without touching your butt to the floor, walk your feet out and away until your legs are straight.
Walk your feet back in and repeat.
Tips:
Keep your core braced and hips up throughout.
Alternate your leading leg rep by rep.
Tale small steps to keep your muscles under tension for longer.
4. Single-leg Romanian deadlift
Muscles targeted: Hamstrings, gluteus maximus, core.
Now your hammies are warmed up and ready to go, it’s time to work them a little harder with single-leg Romanian deadlifts. This exercise will also enhance your balance and mobility, making it a very functional calisthenics move.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together. Shift your weight over onto one leg and brace your core. Bend your supporting knee slightly for balance.
Hinging from your hips, lean forward and reach down the front of your leg to the floor.
Extend your other leg out behind you as a counterbalance.
Stand up straight and repeat.
Continue for the desired number of reps, and then switch legs.
Tips:
Take care not to round your lower back, as doing so could lead to injury.
Do this exercise next to a wall and use it for balance if required.
You can also do this exercise with your non-working foot still on the floor, i.e., a B-stance or kickstand Romanian deadlift.
Related: Why the Single Leg Romanian Deadlift Deserves to Be the Hero of Your Workout
5a. Wall squat hold
Muscles targeted: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings.
Wall squat holds are an isometric lower body exercise. This means your muscles generate force without producing any movement. Don’t let the static nature of this exercise put you off – it’s still a very challenging way to work your quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
Steps:
Stand with your back to a smooth wall. Lean against the wall so your feet are about 24 inches from the baseboard.
Slide down the wall until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
Push your lower back into the wall as hard as possible.
Maintain maximal muscle tension for as long as you can.
Tips:
Descend below parallel to really hit your quads hard.
Take care not to hold your breath.
Do not rest your hands on your legs – keep them out of the way to ensure you can’t cheat and make this exercise easier.
5b. Jump squat
Muscles targeted: Quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, gastrocnemius, soleus.
Doing squat jumps immediately after wall squats will set your legs on fire! However, this devilish exercise combo will also build muscle strength, size, and power without having to use a squat rack, leg press machine, or any weights. It’s low-tech but ultra-high-effect!
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, toes turned slightly outward.
Bend your legs and squat down until your thighs are roughly parallel to the floor.
Stand up quickly and leap into the air as high as possible.
Land on slightly bent knees to absorb the impact and repeat.
Tips:
Use your arms for added momentum.
End your set when your jump height starts to decrease.
Stand on a mat for a more cushioned landing.
6. Single-leg calf raise
Muscles targeted: Gastrocnemius, soleus.
No calf machine? No problem! You can get a great lower leg exercise with only your body and a sturdy step to stand on. Your calves are a small but often visible muscle group, so it’s important not to neglect them.
Steps:
Stand on a step so the ball of one foot is on the edge. Cross your other foot behind your supporting ankle.
Keeping your leg straight, lower your heel down toward the floor and get a good stretch in your calf.
Push up onto your tiptoes and repeat.
Switch legs and do the same number of reps on the other leg.
Tips:
Pause at the top and bottom of each rep to make this exercise more challenging.
Use your hands for balance as required.
Keep your glutes engaged and your core braced throughout.
Calisthenic Leg Workout – FAQs
Do you have a question about this workout or calisthenic training in general? No problem, because we’ve got the answers!
1. How many times a week should I do this workout?
While you could do this workout just once a week, you’ll get better results if you do it twice, e.g., Monday and Thursday. This provides a good balance between work and rest/recovery.
You could do it three times, but that’ll probably be too much for most people, especially if you push the sets close to failure. Remember to perform it in conjunction with a similar number of upper-body workouts.
2. What does “take each set to within 1-3 reps of failure” mean?
It’s almost impossible to tell you how many reps to do as your body weight and fitness will directly affect your performance and capabilities. So, rather than provide you with a rep range that’s too high or too low, you should simply do as many reps as you can in good form, be that 10, 20, or 30.
Just keep going until your muscles feel good and tired. Strive to do more reps as you get fitter and stronger, but never sacrifice good form for a couple more reps.
3. Is this a cutting or a bulking leg workout?
Your workout doesn’t really determine whether you are cutting or bulking. Instead, it’s your diet. To cut (lose fat), you need to have a dietary calorie deficit which forces your body to burn fat for fuel. A 500-calorie deficit will usually result in losing one pound per week.
In contrast, you need a calorie surplus to build muscle and gain weight. 500 extra calories a day should result in a one-pound weight gain per week.
So, adjust your diet according to your goals, and don’t worry too much about changing your workout for cutting or bulking.
4. Can I change any of the exercises?
Sure you can! However, make sure you use similar exercises that work the same muscle groups as those listed. For example, if you want to replace squat jumps, do something like jumping lunges, which involve all the same muscles. Stay true to the spirit of the program, and you won’t go wrong.
However, avoid swapping out an exercise just because you find it hard. It’s those challenging exercises that invariably produce the best results.
5. Is this workout suitable for beginners?
While a beginner could do this workout, it’s probably a little too challenging for most. It’s pretty long and contains some demanding movements that may be beyond the abilities of less experienced exercisers.
Do a basic calisthenic program for a few months, and then return to this plan when you feel you’re ready. Even then, just do a couple of sets of each exercise and stop before reaching failure. Doing too much too soon will undoubtedly cause severe delayed onset muscle soreness and could even lead to injury.
So, start slowly and build up gradually – getting in shape is a marathon, not a sprint!
Wrapping Up
While exercises like squats, leg presses, and deadlifts are undoubtedly effective, they’re not always practical or convenient. Going to the gym can take time many people don’t have, and gym memberships can be expensive. You COULD set up a home gym, but not everyone has the space or the budget to do so.
The good news is that you can develop a strong, muscular, well-conditioned lower body with calisthenic exercises and workouts. Using nothing except your body weight, you can train anywhere and anytime, and it won’t cost you a cent.
So, there really is no reason to skip leg day ever again. Do the workout in this article a couple of times a week to develop a lower body you can be proud of.

Two Best Love Handle Workouts For Building a Shredded Midriff
Love handles poking through your shirt can be the first sign of trouble. Most people are in denial at first when they start accumulating body fat. They blame their ‘ill-fitting’ shirts for their love handles or consistently tug on their shirts throughout the day to conceal them. Since you’re reading this article, I assume you are guilty of doing at least one of these at some point.
Ignoring these signs can worsen your spare tire situation, and it will require more work in the future to fix. Love handles can be notoriously difficult to lose. These are among the last fat stores to disappear during a fat loss program.
Before we get into the nitty gritty of love handle workouts, let’s get to the basics. Do you know how love handles got their name? I thought so.
Love handles is a colloquial expression that refers to excess fat deposits around the waistline, specifically on the sides of the abdomen and lower back. They got their name as an individual’s partner or loved ones often embrace them around the hips. Furthermore, it is often the body part your partner holds onto during a love-making session. The term ‘love handles’ will never be the same for you from this moment. You’re welcome!
In this article, we go over everything you need to know about love handles, including their causes, the associated risks, the holy grail of losing love handles, the best workouts and exercises, and the best lifestyle tips to see quick results.
What are Love Handles?
Love handles are protruding fat stores that sit above your hip bones and cover your external obliques. They are among the most stubborn areas to lose fat from. “Muffin tops” are a sign of poor physical fitness. Plus, they can hamper your physique aesthetics. The V-taper, characterized by broad shoulders and a narrow waist, is widely regarded as the epitome of aesthetic perfection. Love handles, on the other hand, hamper your shoulder-to-waist ratio.
Genetics, hormonal changes, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and overall body composition can influence love handle development. Besides their impact on your overall fitness and aesthetics, love handles can also lead to health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Contrary to what most people think, performing a few exercises in the transverse (axial) plane isn’t enough to shed the spare tire. Additionally, you cannot spot-reduce your love handles. You must follow a balanced diet and exercise regimen to achieve overall fat loss.
The love handles can be a tricky area to target with exercises. Performing the exercises with a picture-perfect form is crucial to achieving the desired results. You must also make mindful lifestyle choices to lose the love handles and keep them off.
Causes of Love Handles
Love handles develop as a consequence of weight gain. You gain weight when you are in a calorie surplus for a prolonged period, which includes consuming more calories daily than you expend. Your body converts the food into glycogen to use as fuel. However, your body stores excess glycogen as fat. Love handles tend to be the primary area where surplus fat accumulates in the body.
Besides a calorie surplus, here are the other factors that can cause weight gain — and love handles:
Genetical predisposition
Sedentary lifestyle
Hormonal changes
Age
Gender
Stress
Lack of sleep
Medication
Certain health conditions
Risks of Love Handles
While some may perceive muffin tops as endearing and dismiss them, it is important to acknowledge that love handles can have significant health implications. Here are some potential risks associated with love handles: [1]
Obesity
Increased risk of chronic diseases
Higher chances of contracting cardiovascular diseases
Insulin resistance and diabetes
Metabolic syndrome
Body image and psychological well-being
Kidney disease
The Secret To Losing Love Handles
If eating more calories daily than you can burn leads to excess fat accumulation and love handle development, guess how you can lose the spare tire? Right, by burning more calories in a day than you consume. It is known as a calorie deficit.
Many people believe they can trim their belly fat by doing abdominal exercises and do not need to change their diet. Unsurprisingly, most of these folks never achieve their weight loss goals and end up shopping for new pants and loose-fitting shirts to hide their body fat.
Weight loss ultimately comes down to calories in versus calories out. You can enter a calorie deficit by cutting your calorie intake or burning more calories through exercise. Using a combination of the two will get you the fastest results.
Two Best Workouts To Lose Love Handles
There are two popular ways of training your core. You could do it after a strength training workout to tone your midsection and develop a six-pack. The other method involves performing a high-intensity full-body workout to burn calories and increase fat loss. The HIIT workout is more prevalent among people that want to focus on losing weight, whereas the first type of core workout is favored by lifters that want to build muscle mass and strength.
Core-Strengthening Workout To Lose Love Handles
This type of workout consists of three to four exercises and is done after a resistance training session. Focus on your breathing pattern and contracting your target muscle group with each rep to get the best bang for your buck.
Here is how to perform each exercise in this workout:
Russian Twist
Sit on the floor with an upright torso, your knees bent, and heels on the ground. Lean back until your torso is at a 45-degree angle with the floor. Lift your feet off the floor and extend your arms so they are parallel to the floor and over your knees. Turn to your right side while breathing out. Contract your abs and obliques at the isometric contraction point. Return to the starting point and repeat on the other side. Alternate between sides for recommended reps. Advanced exercisers can hold onto a weight plate to make this exercise more challenging.
Woodchopper
Stand upright with a hip-width stance while holding a dumbbell with both hands in front of your hips. Interlace your fingers around the dumbbell’s handle for a firm grip. Lift the dumbbell across your body and over your right shoulder. Twist your left foot slightly during the upward motion and fix your eyes on the dumbbell. Bring down the dumbbell diagonally across your body so it is at the side of your left knee. Pause and contract your core during the downward motion. Repeat for recommended reps before switching sides.
Bicycle Crunch
Lie on your back on the floor. Hold your hands next to your ears and lift your legs so your thighs are perpendicular to the floor. Bring your left knee toward your chest while reaching across with your right elbow. Pause and contract your core. Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side.
Side Plank
Lie on your side on the floor. Place your elbow under your shoulder and stack your hips and legs. Plant your forearm on the floor so it is perpendicular to your body. Lift your hips off the floor; your body should be in a straight line from head to toe. Place your top hand on your hip. Hold this position for a minute. Without stopping for rest, repeat on the other side.
HIIT Workout To Burn Calories, Boost Fat Loss, and Get Rid of Love Handles
Given below is a full-body high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout that will spike your heart and metabolic rate. This 17-minute HIIT workout will help you shed excess fat and build a shredded core. Perform two rounds of these exercises and limit rest duration between exercises to 30 seconds. You are allowed a two-minute breathing time after completing the first circuit. Also, do not stop for rest while changing sides in the side plank pulse.
Given below are step-by-step guides to performing these exercises:
High Knees
Stand upright with a shoulder-wide stance and place your hands on your hips. Brace your core, bend one leg, and lift your knee until your thigh is roughly level with the floor. Return the leg to the ground and repeat on the other side. Establish a steady rhythm.
Mountain Climber
Assume the push-up position; your hands should be under your shoulders and legs extended behind you. Your body should be in a straight line from head to toe. Lift one foot off the floor, bend at the knee, and bring it toward your chest. Return it to the start position and repeat on the other side. Alternate between sides in a rhythm.
Plank Jack
Get into the high plank position. Place your hands on the floor under your shoulders. Extend your legs behind you and place your feet together. Maintaining the high plank, jump and place your feet wider than shoulder-width apart. Jump and return to the starting position. Repeat in a rhythm.
Side Plank Pulses
Get into the side plank position so your body is in a straight line from head to toe. Lower your hips to the floor and return to the starting position. Repeat for the recommended reps before switching sides.
Sledgehammer Overhead Strikes
Grab a sledgehammer in front of your body with your left hand at the bottom of the handle and your right hand just above it. Swing the hammer around your right side and behind and over your head. Smash the tire in the center with full force. Switch hands and return the hammer to the overhead position while swinging the hammer around your left side. Repeat for recommended reps.
Cross-Body Mountain Climber
Get into the high plank position. Maintaining your body in a straight line from head to toe, lift one foot off the floor, bend your knee, and bring it toward the opposite shoulder. Contract your core at the top. Return to the start position and repeat on the other side. Perform this exercise using a steady rhythm.
Sit-Up Twist
Lie on your back on the floor, bend your knees, and plant your feet on the ground. Hold your hands next to your ears. Contract your abs and lift your torso off the floor. Turn to your side and bring your left elbow to your right knee during the upward motion. Return to the start position and repeat on the other side.
Most Effective Love Handle Exercises
Sticking to the same exercises can get really boring, really fast. If you dread doing the same movements in every workout, we have got you covered. Below is an exhaustive list of additional exercises that will help tone your love handles. Add these movements to your exercise arsenal to keep your workouts exciting.
Standing Dumbbell Side Bend
Stand upright with a hip-width stance while holding a dumbbell in each hand at your sides. Keeping your elbows locked, brace your core, and slowly lower the right dumbbell as low toward the floor as possible. It should at least be at your knee level at the bottom. Return to the start position. Complete the recommended reps on one side before switching to the other side. Read more about standing dumbbell side bend here.
Oblique V-Ups
Lie on your right side on the floor. Stack your legs while maintaining a slight bend in your knees. Place your right arm on the floor so it is perpendicular to your torso. Hold your left hand behind your head. Lower your head and left arm to the floor behind you; this will be your starting position. In a single motion, lift your legs off the floor and raise your knees toward the ceiling while bringing your left elbow to your knees.
Cable Side Crunch
Set a cable pulley at the highest setting and attach a D-handle bar. Grab the handle with a neutral (palm facing inward) grip and take a big step away from the pulley. Place your other hand on your hip. Holding the handle to your ear, perform a side crunch. Contract your core at the bottom of the movement. Repeat for reps before switching sides.
Read more about cable side crunch.
Side Jackknives
Lie on your left side on the floor; your hips and legs should be stacked. Place your left upper arm on the floor in front of your body so it is perpendicular to your torso. Keep your right hand on your right hip. Lift your right foot toward the ceiling while performing a side crunch. Pause and contract your obliques at the top. Rinse and repeat.
Read more about side jackknives.
Side Plank Twist
Get into the side plank position. Place your top hand behind your head. Your top elbow should be in line with your shoulders at the starting position. Bring your top elbow to the floor under your shoulders while keeping your legs stacked. Contract your core during the lowering movement and hold for a two-count at the bottom. Repeat for recommended reps before switching sides.
Standing Torso Twist
Stand upright with a hip-width stance. Extend your arms in front of your body so they are parallel to the floor. Interlace your fingers and turn to your right side as far as possible without bending your elbows. Twist your left leg during the turn for optimal range of motion and contract your abs and obliques. Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side. Experienced exercisers can hold onto a dumbbell or kettlebell to make this exercise more challenging.
Flutter Kicks
Lie supine on the floor with your legs extended. Place your hands under your hips for leverage. Brace your core and lift your feet a few inches off the floor. Raise your head off the floor. Without bending your knee, lift your right leg toward the ceiling while keeping your left leg in place. Return the right leg to the starting position while lifting the left leg toward the roof. Maintain a steady tempo for recommended reps. More on flutter kicks here.
Side Plank Knee Tucks
Get into the side plank position. Place your top hand next to your ear. Simultaneously, elevate your upper leg towards your chest while bringing your elbow to your knee, all in one fluid motion. Breathe out and contract your abs throughout the range of motion. Return to the start position and repeat for recommended reps before switching sides.
Standing Side Leg Lifts
Stand with your left side facing a sturdy elevated surface like a cable pulley machine. Hold on to the pulley machine with your hand. Hold your right leg slightly in front of your body. Bring the right leg toward the pulley while keeping your knee locked. Raise the leg out to your side as high as possible. Return to the starting position and repeat for recommended reps. You could also perform an oblique crunch during the concentric motion for better muscle contraction.
Side-to-Side Medicine Ball Slams
Place a medicine ball on the floor. Stand upright with a shoulder-width stance so the medicine ball is at your left foot’s side. Bend over and lift the ball off the floor. In a sweeping motion, lift the ball over your head. Raise onto the balls of your feet and slam the ball on your right side as hard as possible. Bend over and lift the ball. Alternate between sides for reps. Learn more about side-to-side medicine ball slams here.
Lateral Band Walk
Wear a loop resistance band around the bottom of your thighs. Take a wide stance so that band is engaged. Bend your knees slightly and hinge at your hips. Hold your hands in front of your chest. Take a wide step to your right side. Walk 10 steps to your right side and return to the starting position. Start with the opposite leg on the subsequent set.
Side Plank with Leg Lift
Get into the side plank position. Raise your top leg as high toward the ceiling as possible. Exhale and contract your core during the upward motion. Hold the position for a two-count. Slowly lower the leg to the starting. Repeat for recommended reps before switching sides. Experienced exercisers can wear ankle weights while performing this exercise for optimal oblique engagement. Also, perform a side crunch to target your love handles.
Side Plank Reach-Throughs
Assume the side plank position. Raise the top arm toward the ceiling so it is perpendicular to the floor; this will be your starting position. Lower your arm toward the floor and thread it between your body and the floor. Breathe out and contract your abs during this lowering motion. Repeat for reps and switch sides.
Clamshell
Lie on the floor on your side. Bend your knees while keeping your hips and legs tacked. Place your bottom arm under your head for support. Place the hand of your top arm on the floor for support. Keeping your ankles stacked, lift your top leg toward the ceiling as high as possible. Hold the contraction for two seconds. Tie a resistance band around your knees for better glute engagement.
Seated Side Bend with Dumbbell
Sit upright on an elevated surface, such as a flat bench, while holding a dumbbell in each hand. Place your feet on the floor wider than shoulder-width apart for better stability. While breathing out, lower the right dumbbell to the floor. Explode back to the starting position. Repeat for recommended reps before switching sides.
More Love Handle Exercises
Here are a few more love handle exercises that will help burn off the spare tire and give you the coveted sex lines:
Cable Woodchoppers
Stability Ball Side Bend
Side Lunge with Twist
Plank with Knee Tucks
Side Plank with Arm Reach
Crunch and Twist on Stability Ball
Side Plank Clamshells
Side Plank with Dumbbell Row
Kettlebell Windmill
Standing Side Bend with Resistance Bands
Heavy Farmer Walk
Single-Arm Dumbbell Row
Box Jump
Floor Wipers
Hanging Windshield Wiper
Tips For Losing Love Handles
Here are a few tips to speed up your fat loss and build a shredded six-pack:
Follow a Balanced and Healthy Diet
Folks serious about losing the spare tire must avoid following a cookie-cutter diet plan. You must follow a personalized diet plan that helps you lose 1-2 pounds weekly. According to the CDC, you must maintain a daily 500-1,000 calorie deficit to achieve this goal. [2]
Use this total daily calorie expenditure (TDEE) calculator to determine your goal daily calorie intake. Then, break it down into a suitable macronutrient split to lose fat and build muscle mass simultaneously.
Exercise
Although training is not mandatory on a weight loss program, it can help speed up your progress. Perform two daily cardio training sessions for optimal results — one HIIT and another low-intensity steady state (LISS).
Seeking professional help can help beginners save time and effort. A personal trainer can give you a customized training program and will teach you the correct exercise form. On the other hand, a registered nutritionist will ensure you are hitting your daily macro and micronutrient goals.
Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Losing weight and love handles and keeping them off might require a complete lifestyle change. Folks with desk jobs must add more physical activity to their days. You must choose the stairs over the elevator and bike to work when possible.
Start with a goal of walking 5,000 steps daily and slowly make your way up until you are logging 10,000 daily steps. Staying physically active will help burn calories throughout the day and keep your metabolic rate high.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking water at regular intervals can keep you satiated. Furthermore, it can help curb cravings. Drink at least a gallon of water daily to ensure optimal body functioning and overall well-being. Switch calorie-laden sugary drinks and sodas with plain water to speed up your weight loss.
Adequate hydration can also boost your metabolism. Your body is more effective at metabolizing stored fat and converting it into energy when you are hydrated. It can help improve your fat-burning process. Staying hydrated also enhances digestion and nutrient absorption, supporting your overall weight loss efforts.
Rest
Many people tend to overexert themselves while trying to lose weight and love handles, which can be counterproductive. Remember, you lose weight while you are asleep, and you must give your body enough to recover. Sleep at least seven to eight hours each night for optimal results.
Also, learn to listen to your body. If you are very sore after a workout, it is best to skip a training session and allow your body time to recuperate. Pushing too hard in the gym can lead to overtraining, which can negatively impact your central nervous system.
Avoid Stress
Your cortisol levels rise when you are under stress, which can increase your appetite, slow down your metabolism, and increase fat storage. Chronic stress can lead to greater inflammation, emotional eating, and impaired sleep.
Elevated cortisol levels can make it more challenging to lose weight, even when you are following a balanced diet and training program. Meditation, yoga, and journaling can help deal with chronic stress. However, you must consult a healthcare professional if these three methods don’t work for you.
Set a Goal and Track Your Progress
Starting your transformation journey with a specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound goal can increase your chances of success. Having a deadline will also motivate you to stick to your fitness regimen.
You must have long-term and weekly goals. Track your progress every week to ensure you are on the right path. Stick to your regimen if the progress is favorable. Conversely, make necessary adjustments if the needle is not budging in the right direction.
Stay Consistent and Dedicated
Love handles can be a stubborn muscle group. Depending on your current and goal physique, it might take you weeks, if not months, to achieve your objective. Nonetheless, you must stick to your fitness regimen with military discipline and ensure you never miss a training session or meal.
You must also consistently challenge yourself by increasing your training intensity and volume to avoid hitting a plateau. Establishing healthy habits will reduce the friction in your training regimen and help you stick to the fit lifestyle for the long term.
FAQs
Can I lose love handles without exercise?Yes. The love handles vanish when there is a reduction in your overall body fat, which requires you to be in a calorie deficit. You can lose your love handles by limiting your calorie intake. That said, adding exercise to your fitness regime can help speed up your results.
Is it possible to have a flat stomach and love handles simultaneously?Some skinny individuals can also develop love handles, known as skinny fat. Skinny fat can result from several factors, including genetics, sedentary lifestyles, medication, or certain health conditions.
How much time will it take for me to lose my love handles?It will depend on your starting physique and ultimate objective. You cannot spot-reduce your love handles and must work toward overall body fat loss. A 500-1,000 daily calorie deficit can help you lose 1-2 pounds weekly.
Note: The content on Fitness Volt is for informative purposes only. Do not take it as medical advice to diagnose, prevent, or treat health problems. If you’re suffering from a health issue, are pregnant, or are under 18 years old, you should consult your physician before starting any new supplement, nutrition, or fitness routine.
Wrapping Up
Love handles can be stubborn, requiring dedication, determination, and consistency to burn them off. Avoid falling into the spot-reduction trap and focus on reducing your overall body fat to see quick, favorable results.
This article has two highly effective workout routines specifically designed for strength trainers and those engaged in full-body HIIT exercises to effectively target and eliminate love handles. So, what are you waiting for? Lace-up your shoes and get moving. Best of luck!
References
Patel P, Abate N. Body fat distribution and insulin resistance. Nutrients. 2013 Jun 5;5(6):2019-27. doi: 10.3390/nu5062019. PMID: 23739143; PMCID: PMC3725490.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Losing Weight. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/losing_weight/index.html

The Best Over 40 Training Tips and Workout Plan for Men
I’ve been lifting weights since I was 15 years old – I’m now 55. During that time, I’ve kept meticulous records, and looking back over my training diaries it’s interesting to see how much my workouts have changed.
Some of these changes were due to my goals at the time. I’ve trained for bodybuilding, powerlifting, and to complement whatever sport I was into, all of which required different workout approaches.
Other changes are the result of old injuries and, sadly, getting older. Simply put, I can’t train like I did when I was in my 20s and 30s. The mind is willing, but time has taken its toll on my body.
However, as the saying goes, winners never quit, and quitters never win, and I have no intention of giving up training anytime soon.
In fact, my mission in life is to preserve my strength and muscle mass for as long as possible, and I plan on being the strongest, most buff old dude in the retirement home!
So, how do you get and stay in shape in your fourth decade?
In this article, I share my top tips for working out in your 40s and provide you with a tried-and-tested age-appropriate workout to follow.
The Challenges of Working Out in Your 40s and Beyond
Advancing age is NOT a reason to give up working out. In contrast, exercise becomes more important as you get older. Regular workouts can help reduce the risk of:
Age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia)
Age-related bone loss (osteopenia)
Coronary heart disease
Type II diabetes
High blood pressure
Age-related weight gain
Cognitive decline
Some cancers
All-cause mortality
So, while there are no guarantees, getting and staying in shape as you age could help you live longer. And even if you don’t get to celebrate your 100th birthday, you will be able to enjoy a more active, fulfilling, and independent life, making the most of whatever time you have left.
However, getting older is unavoidable, and the changes in your body mean that you probably won’t be able to work out like you did in your 20s and 30s. That’s not to say you have to quit lifting weights and take up tai chi! But you will need to modify your training to make it sustainable and safe.
Some of the challenges facing exercisers in their 40s and beyond include:
Slower recovery between workouts
The older you get, the longer it takes to recover from bouts of intense exercise. As such, you’ll need to pay as much attention to rest and recuperation as you do your workouts. Getting enough sleep is a must, and you should also alternate between intense and less intense workouts.
You’ll also need to accept that there will be days when you’re not firing all cylinders simply because you’re still tired from your last workout. Be prepared to dial things back and take it easy, as pushing on regardless could lead to overtraining and injuries.
You can still train hard in your 40s, but you’ve got to train smart, too.
Joint issues
Like a car with high mileage, older exercisers tend to accumulate wear and tear. Joints are especially prone to aches and pains. Knees, hips, shoulders, elbows, your lower back – it’s not unusual to experience discomfort in some or all of these areas.
The good news is that training can help make these issues less impactful and preserve joint function as you age. However, you may need to make allowances for your joints, replacing high-stress exercises with movements that are more joint-friendly.
Injuries take longer to heal
As a young athlete, I had no problem either training through injuries or taking a week off and coming back healed and ready for more. Nowadays, even a slight strain can take several weeks or even months to heal. Needless to say, this can be VERY frustrating!
With this in mind, a lot of your over-40 training should revolve around preventing injuries in the first place. Warm-ups and prehab are the name of the game if you want to avoid injuries. Plus, you should probably stop chasing new one-repetition maximums and focus on other performance metrics, such as rep records or movement quality.
Mobility and flexibility issues
Muscles tend to shorten and tighten as you get older. This can affect everything from your posture to your squat depth. Trying to force your limbs to bend further than is comfortable is a recipe for injuries which, as you know, will take longer to heal than when you were younger.
As such, you should a) do all that you can to maintain or even improve your mobility and flexibility and b) avoid exercises that take you into extreme ranges of motion. There is no need to treat your body like a fragile antique, but you should do what you can to avoid unnecessary injuries.
Related: The Best Morning Stretches for Men
Hormonal changes
Testosterone and human growth hormone levels peak in your 20s and early 30s. After that, the production of these anabolic or muscle-building hormones gradually decreases.
These hormonal changes can cause reductions in muscle mass and strength, lowered motivation, slower recovery, and less energy. All these things can affect your ability to train and recover from your workouts.
Sure, you could ask your doctor about testosterone replacement or HGH therapy, but there are risks and financial costs associated with these treatments. The good news is that regular exercise and a healthy diet can help boost testosterone and growth hormone naturally.
Lack of time
Life can get pretty hectic when you’re in your 40s. You’ll need to balance your work and home life while finding the time and energy you need for training. In many cases, when time is short, the first casualty will be your workouts.
Initially, you’ll probably plan on rescheduling, but, more likely, you’ll skip more workouts than you complete. Being in your 40s means you can’t shirk your responsibilities to go and train.
Most guys in their 40s don’t have the luxury of hitting the gym for two hours a day, six days a week. Thankfully, you don’t need to train for hours at a time to preserve or gain muscle.
Related: Two Exercise Workouts for Time-Pressed Bodybuilders
These are the realities of training in your 40s. Sure, some fitness influencers and ex-bodybuilders seem to have been able to avoid the effects of aging, but they are in the minority and are probably on TRT. It would be a mistake to judge your progress against such people because there is a massive difference between being natural and boosting your performance with anabolic steroids, even if they have been prescribed by a doctor.
Workout Tips for Men in Their 40s
Avoid the pitfalls and problems that could derail your training with these tried-and-tested workout and fitness tips for men in their 40s:
Warm up like a boss
Warm-up Exercise Bike
Warming up is important whatever your age, but the older you are, the more critical it becomes. Older bodies tend to be stiffer, more immobile, more damaged than younger ones, and more prone to injury, too.
Make your workout as enjoyable, safe, and comfortable as possible by warming up thoroughly before you begin. Extra time spent on your warm-up will pay dividends in the future.
Related: How to Warm Up for Strength Training
Train with lighter weights and higher reps
Younger men tend to put a lot of stock in how much weight they can lift. Plates on the bar equal bragging rights, and, as the saying goes, if the bar ain’t bending, you’re just pretending!
However, injuries are more common when you lift heavy loads. They stress not only your muscles but your joints too.
Avoid injuries and unnecessary wear and tear by training with lighter weights and higher reps. Contrary to what many lifters believe, you can still build strength and muscle mass with weights below 50% of your 1RM (1).
This means you no longer have to feel trapped by the 6-12 rep range and can do as many as 25-30 reps per set. Needless to say, this will be far less stressful for your already hard-worn joints. Muscle strains are also less of a risk.
Do fewer sets
With your somewhat compromised recovery ability, doing high-volume workouts could lead to overtraining. So, instead of seeing how many sets per muscle group you can tolerate, try to find out how few you need to do to get the results you want.
You’ll probably find it’s not as many as you first thought.
Try keeping your workout volume down to about 8-12 sets per muscle group per week. This is significantly less than most bodybuilding programs recommend but more than enough to build muscle and strength. Focus more on training quality than quantity; make every exercise, rep, and set count!
Do each exercise with perfect form
There are two ways to do any exercise – the right way and the wrong way. The wrong way may allow you to lift more weight or do more reps, but it usually comes with an increased risk of injury while taking work away from the muscles you want to develop.
In contrast, the right way is invariably harder, but it’s also safer and usually more effective.
So, check your ego, dial back the weights, and do every exercise in your program with perfect technique. Try to make your reps as smooth and controlled as possible to take stress off your joints and keep it on your muscles. Lift and lower with purpose.
Choose low-risk exercises
While training is good for everybody’s body, some exercises are riskier than others. As injuries tend to take longer to heal when you’re in your 40s and beyond, you should build your workouts around the safest exercises.
For example, you could do push-ups instead of bench presses, goblet squats instead of back squats, or box jumps instead of power cleans.
So, think about what you want from your workout, then choose the safest exercises for that goal. If the risks outweigh the benefits, you should think twice about doing that exercise.
It’s better to play it safe and be able to continue training than do a dangerous exercise, get hurt, and spend the next two months waiting to heal.
Make flexibility and mobility a training priority
While mobility and flexibility training are far from exciting, the older you get, the more critical they become. Older muscles and joints tend to be less elastic and mobile than their younger counterparts. Previous injuries can also take their toll.
Mobility and flexibility tend to be worse the more sedentary you are. Most older men have relatively inactive jobs and lifestyles, so they’re even more likely to be tight and immobile.
Complement your workouts with daily mobility and flexibility training to keep you supple and flexible. Just because you are in your 40s doesn’t mean you have to be as stiff as a proverbial board!
Related: How Sitting is Bad For You and What To Do About It
Strengthen your core
A large and growing number of men suffer from lower back pain, and the risk of back pain increase with age. Some types of back pain are unavoidable and are linked to things like disc degeneration and general wear and tear. However, other types of back pain can be attributed to weak core muscles.
Core is the collective term for the muscles of your midsection, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis. These muscles contract inward to create intra-abdominal pressure and support your lumbar spine from within.
Spending a lot of time sitting in a chair can weaken your core muscles, increasing your risk of suffering back pain. So, make sure you include core and anti-core exercises in your workout routine to keep the risk of back pain to a minimum.
Include unilateral exercises in your workouts
Unilateral or single-limb exercises are a godsend for older exercisers. For starters, they’re great for preserving your balance, which often declines with age. Secondly, they let you train hard without resorting to bone-crushing weights. For example, single-leg Romanian deadlifts are MUCH more lower back-friendly than regular RDLs.
While there is nothing wrong with bilateral or two-limbed movements, every over-40s exerciser should include unilateral exercises in their workouts.
Get your body composition under control
Younger lifters often want to get bigger and stronger, which they usually achieve through bulking. Bulking involves strategic overeating to create a significant calorie surplus. These extra calories go to fuel muscle growth but also lead to fat gain.
Older exercisers often experience fat gain, too, but not because they’re bulking. Instead, gaining weight gain in your 40s is usually the fault of moving less and eating more. This weight gain even has a name – middle-aged spread.
Gaining weight as you age can increase your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other insidious illnesses. Being overweight when you’re young is dangerous, but it can be fatal in your 40s and beyond.
Now is the time to get your weight under control and lose the fat you’ve been accumulating since high school. There is no need to crash diet or try to lose it in a month; such intense interventions are seldom successful.
Instead, aim to lose half to one pound a week for the next few months. This time next year, you could be a whole new man.
Do your cardio
Younger lifters are all about getting buffed and ripped. They want big veiny biceps and cannonball delts. They aren’t thinking about the future – just looking their best on the beach.
As a man in your 40s, your risk of heart disease is considerably higher, so you must start doing more cardio to keep your heart and circulatory system in tip-top shape.
We’re not saying you need to quit lifting and take up jogging. However, you do need to complement your strength training workouts with more cardio. Aim to do at least three 20-minute cardio workouts per week to keep the old ticker fit and strong.
Big biceps are great, but you need a healthy heart if you want to keep on truckin’.
Make sure your diet supports your training
As a younger man, you could probably eat whatever you wanted and still feel fine; cold pizza for breakfast, a takeout burger for lunch, and beer and cereal for dinner. Now you’re in your 40s, the expression, “You are what you eat,” has never been truer, and if you fill up on junk food, that’s exactly how you’ll feel.
If you want to look and perform at your best, your diet needs to not only support your training but it also needs to be healthy. So, make friends with fruit and vegetables, eat more heart-friendly whole grains, pump up the lean protein, and enjoy some healthy fats.
In short, now you are in your 40s, it’s time to eat like an adult and not the kid you once were.
Related: Fix Your Diet in Six Weeks
Respect your body’s need for rest and recovery
It’s time to pay as much attention to rest and recovery as you do your workouts and diet. Training takes a lot out of your body, and now you are in your 40s, it’ll be longer before you can do it all again.
So, make sure you get plenty of sleep, preferably 7-9 hours a night, and use these recovery strategies to put back into your body what your workouts take out.
Finally, recognize then an extra rest day might be more beneficial than a workout. It’s usually best to train consistently, but if you are still tired from your last workout, a day off might do you more good.
Forget what you used to do and focus on what you can do
I used to be a powerlifter and have pulled three times my bodyweight in competition, and my squat wasn’t far behind. However, that’s what I used to do, and it has no bearing on my training now I’m in my 50s.
Nowadays, I rarely use barbells or dumbbells, and I find bodyweight and isometric exercises are better for my battered joints. I’m still in shape and probably fitter than I was 20 years ago. However, my entire training outlook has changed over the last decade, and so should yours. Trying to relive or hold onto your glory years is an exercise in futility.
It doesn’t matter that you used to be a football player in college or a bodybuilder in your late 20s. It’s what you do now that matters.
So, don’t judge today’s you on what you achieved in the past. As a man in your 40s, your body has changed, and training like you did as a younger man is a recipe for disaster. It’s time to start training for the future and not the past.
Set yourself goals based on where you want to be in five, ten, or 20 years. Look forward, and not back. Be proud of your achievements, but don’t dwell on them or let them determine your current or future workouts.
The Best Over 40 Workout Plan for Men
You’ve now got all the information to design your very own workout plan for men over 40. But, to save time, we’ve written one for you.
This plan involves four workouts per week – two upper body and two lower body – which provides a good balance between training and recovery. It also leaves some time for cardio and mobility training, which, as you know, are critical for men in their 40s.
Try to avoid lifting weights more than two days in a row, and also avoid resting more than two days in a row. While that might sound like a logic problem, it’s actually pretty easy if you structure your workout week like this:
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
Saturday
Sunday
Workout 1
Workout 2
Rest/cardio
Workout 3
Rest/cardio
Workout 4
Rest/cardio
Remember, though, before you lift, you need to warm up, as failing to do so could lead to injury or, at least, a low-quality training session. That 10-15 minutes spent warming up could save you from spending months on the injured list and unable to train.
Workout 1 – Upper Body
We kick off our over-40s workout plan with an upper-body workout emphasizing the horizontal plane, i.e., chest and upper back. Dividing your body into planes rather than individual muscle groups makes it easier to develop structural balance, which is critical for functionality and joint health.
#
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Incline dumbbell bench press
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
2
Single-arm dumbbell row
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Push-up
2-4
AMRAP*
60-90 seconds
4
Face pull
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
5
Cable crossover
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Reverse cable fly
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
7
EZ bar biceps curl
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
8
Dumbbell concentration curl
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
*AMRAP = As Many Reps as Possible – just rep out to failure, regardless of how many you can do.
Workout 2 – Lower Body
Friends don’t let friends skip leg day, even if they’re in their 40s! Strong legs are critical, as they’re the engines that carry and support the rest of your body. Losing leg strength can have a profound effect on your mobility and stability. This leg workout is quads-centric, emphasizing your knee extensors. There is also some core work toward the end of the program.
#
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Goblet box squat
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
2
Rear foot elevated split squat
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Leg extension
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
4
Standing calf raise
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
5
Pallof press
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Kneeling cable crunch
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
Workout 3 – Upper Body
Workout three takes us back to the upper body. However, this time you’ll be working in the vertical plane, emphasizing your shoulders and lats. The workout ends with a couple of exercises for your triceps. After all, even guys in their 40s deserve a ticket to the gun show!
#
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Pull-up/Chin-up*
2-4
AMRAP**
60-90 seconds
2
Standing barbell press
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Lat pulldown
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
4
Seated dumbbell press
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
5
Straight arm pulldown
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Cable lateral raise
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
7
Dumbbell skull crusher
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
8
Cable triceps pushdown
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
*Do band or machine-assisted pull-ups/chin-ups if necessary.
**AMRAP = As Many Reps as Possible – just rep out to failure, regardless of how many you can do.
Workout 4 – Lower Body
Your final workout is another leg session. However, this time, you’ll be working mainly on your glutes and hamstrings. But, as before, there are also a couple of core exercises toward the end of the program.
#
Exercises
Sets
Reps
Recovery
1
Rack pull
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
2
Single-leg Romanian deadlift
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
3
Leg curl
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
4
Seated calf raise
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
5
Side plank leg lift
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
6
Reverse crunch
2-4
12-20
60-90 seconds
Over 40 Training – FAQs
Do you have a question about working out in your 40s and beyond? No problem, because we’ve got the answers!
1. I’m 39. Are you saying I have to change my workouts after my next birthday?
Aging is a gradual process – the changes discussed in this article don’t happen overnight. So, changing your workouts does not have to coincide with celebrating your 40th birthday.
However, as you move into your mid-40s and beyond, you’ll invariably see and feel your body start to change, and you need to make allowances. Driving on regardless could bring your training to a crashing halt.
So, listen to your body, and adjust your workouts as and when you need to. This could be in your mid to late 40s, your 50s, or even your 30s – it all depends on you.
2. Can a man in his 40s still gain muscle?
You can gain muscle at almost any age – even in your 80s. However, how much depends on how far you are from your genetic potential and your current level of muscularity. For example, if you are in your 40s and have never trained before, you have the most potential for muscle growth.
However, if you’ve been training for 20 years and are already pretty muscular, you probably won’t gain much more muscle, although some increases should still be possible.
Finally, rates of muscle gain tend to be slower once you’re in your 40s and beyond, so don’t expect to pack on ten pounds in a month. That sort of progress only really happens when you’re in your 20s.
3. I’m in my 40s and have trained all my life; do I need to change my workouts?
If your current training plan works for you, there is no compelling reason to change your workouts, even if you are in your 40s.
However, if you are experiencing more aches and pains than usual, are finding it hard to recover from training, or aren’t enjoying your workouts as much as you used to, it may be time to think about making some changes.
Clinging to your old workouts when they no longer suit your aging body is a mistake. However, a few minor changes could be all you need to keep on training well into your 50s, 60s, and 70s.
4. What is the best diet for men in their 40s?
The best diet is the one that a) supports your training, b) is healthy, and c) you enjoy and can stick to. For some, this will be something like intermittent fasting or paleo. However, arguably the healthiest and tastiest diet comes from countries like Greece, Italy, and France – the Mediterranean diet.
Built around vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, this diet is good for your heart, brain, and waistline. The Mediterranean diet is considered by many to be the most nutritious eating plan in the world.
Read more about the Mediterranean diet in this article.
5. I’m 40 and out of shape – is this workout suitable for me?
While this program is designed for men in their 40s, it assumes you are currently exercising and in reasonable shape. Some of the exercises are pretty challenging, and the volume and frequency are moderately high. As such, it’s probably too much for someone who is out of shape or a beginner.
If it’s been a year or more since you exercised regularly, you should start getting back in shape with a basic full-body training plan and regular cardio. This will create a solid foundation for more demanding workouts in the future.
Then, after 6-9 months, of consistent training, you’ll be ready to start this workout plan.
6. What weights should I use for these workouts?
Unfortunately, this is the one question we can’t answer. After all, we have no way of knowing how strong you are.
So, instead, pick a light to moderate weight and rep out to within 1-3 reps of failure. If you can’t do 12 reps, your chosen load is too heavy. Conversely, the weight is too light if you can do more than 20 reps. Adjust the load until you’re in the sweet spot of 12 to 20 reps.
Remember, though, you must also try to make your subsequent workouts more demanding. You can do this by performing more reps or lifting slightly heavier weights. This is called progressive overload, one of the keys to successful strength training.
7. Can I make changes to the workout plan?
The exercises selected offer the best results with the lowest risk of injury. This is based on over 30 years of training and coaching experience. However, if you want to change any of the movements, you are welcome to do so.
That said, make sure you choose similar exercises so you stay true to the spirit of the program. For example, while doing trap bar deadlifts instead of rack pulls is an acceptable change, doing cable hip abductions is not, as they’re very different exercises.
Closing Thoughts
A lot of men think that, when they hit their 40s, their best years are behind them and that middle-aged spread and muscle loss are compulsory. This is not necessarily the case!
While you may not be able to train as you did in your 20s and early 30s, you can still get and stay in great shape when you’re in your 40s, 50s, and beyond.
While your progress might not be as dramatic, and you’ll need to pay more attention to your diet, rest, and recovery, you can still build muscle and get fit and lean.
Age does not have to be an unbreakable barrier.
Use the tips and program to get in the best shape of your life, even if you are a man in his 40s.
References:
Lasevicius T, Ugrinowitsch C, Schoenfeld BJ, Roschel H, Tavares LD, De Souza EO, Laurentino G, Tricoli V. Effects of different intensities of resistance training with equated volume load on muscle strength and hypertrophy. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018 Jul;18(6):772-780. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1450898. Epub 2018 Mar 22. PMID: 29564973. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29564973/
The 17 Best Standing Abs Exercises for All Fitness Levels
We love floor-based abs exercises as much as the next guy, but sometimes it’s nice not to have to lie on a sweaty gym mat or dirty floor to bust out some sit-ups or crunches.
Also, floor-based abs exercises are not exactly functional. After all, apart from sitting up in bed, when was the last time you used your abs to pull your torso upright? Floor abs exercises are often hard to load, too. You’ve got to rely on the weight of your upper body or legs to hit your abs. Depending on your body size and strength, this may be too much or too little weight to work your abs.
The good news is that there are LOTS of great abs exercises you can do while standing. Some are easy and ideal for beginners, while others are hardcore and perfect for more advanced exercisers.
In this article, we reveal the 17 best standing abs exercises for all fitness levels.
Abs Anatomy 101
When most exercisers talk about abs, they actually mean their core. The core is the collective term for all the muscles of the midsection. Some functional fitness experts also like to include additional muscles in their core collective, including the lats and glutes. However, that just complicates an already complex subject!
So, for the purposes of this article, when we say abs, we actually mean the core, and that covers the following muscles:
Core Muscles Anatomy
Rectus abdominus
The rectus abdominis is the long, flat muscle on the front of your stomach. It’s divided into vertical halves and horizontal sections by lines of ligamentous tissue, giving it that famous six-pack appearance.
However, you’ll need to be pretty lean to see these lines, typically below ten-percent body fat for men and under 15 percent for women.
The functions of the rectus abdominis are flexion and lateral flexion of the spine.
Obliques
The obliques are basically your waist muscles, and there are two sets – the internal and the external obliques. These muscles rotate and laterally flex your spine. However, when both sides co-contract, they also play a part in flexion and work alongside your rectus abdominis.
Transverse abdominis
Known as the TVA for short, this muscle encircles your midsection like a weightlifting belt. When you brace your abs, it contracts inward and compresses your internal organs. This creates intra-abdominal pressure, which helps to support your lumbar spine.
So, while you won’t be able to see your TVA working, you will be able to feel it. The TVA is involved in all standing abs exercises.
Erector spinae
The erector spinae is a group of three muscles, each of which is divided into three sections. These muscles run up either side of your spine and are involved in extension and lateral flexion. Many standing core exercises also involve the erector spinae, despite the fact they’re technically back muscles. In most cases, the erector spinae act as stabilizers.
All standing abs exercises involve all of these muscles. However, depending on the movement performed, some will be working harder than others. Therefore, in the exercise descriptions, we’ll list the muscles in order of which are doing most of the work.
The Benefits of Standing Abs Exercises
While there is nothing wrong with floor-based abs exercises, standing abs exercises offer some noteworthy advantages and benefits. These include:
Increased functionality
Your core plays a critical role in most human movements. In some situations, it acts as a stabilizer to prevent unwanted movement of your spine. In others, the core is responsible for generating force, e.g., pushing, pulling, and throwing.
Regardless of what they are doing, most of these activities occur when you’re on one or two legs and not lying on your back. Therefore, standing abs exercises are often more functional than their supine counterparts.
Comfort
Standing abs exercises are often more comfortable than similar exercises performed lying on the floor. An exercise mat will help, but one may not be available. With no pressure on your lower back, standing abs exercises are usually more comfortable than floor-based movements.
Convenience
Not everyone trains in a well-equipped gym. Some people prefer to work out in playgrounds, parks, or other large open spaces. Sure, you COULD take a mat with you for abs exercises, but that’s unnecessary if you do standing abs exercises.
With no mat required and often very little equipment, you can do some standing exercises anywhere and anytime, making them the perfect excuse-free workout.
No more mobility issues
Older exercises and people with mobility issues may find getting down on the floor to do sit-ups, crunches, etc., awkward. Getting back up may present an even more significant challenge. Many standing abs exercises are ideal for older exercises and anyone who finds getting down to floor level difficult.
Standing Abs Exercise Drawbacks
Standing abs exercises are generally safe and effective. However, there are a couple of drawbacks to consider, too:
Limited loading
While there are numerous standing abs exercises that utilize an external load, other movements rely on your body weight for resistance. Because of the direction of gravity, this may mean there is very little tension on the muscles you’re training.
You can contract the target muscles harder to get a better training effect, but, even then, some exercises will be too easy if you already have a well-conditioned core.
Lack of understanding
Standing abs exercises are a trending topic right now (#standingabs). Unfortunately, this means a lot of wannabe fitness experts are posting standing abs exercises with little understanding of how the core muscles work.
For example, holding a weight in your hands and then twisting your torso does NOT load your obliques. The force is vertical, whereas the obliques work in the transverse plane, i.e., horizontally. In essence, there is no resistance to rotation.
It doesn’t matter if you hold a 20-pound weight or a 100-pounder; twisting with a weight in your hands won’t challenge your obliques. However, your arms will probably get a good workout!
Similarly, doing standing crunches are all but pointless, as the weight (your upper body) is pulling your spine into flexion – your abs aren’t doing much, if any, of the work.
So, don’t make poor exercise choices. Remember that some self-certified fitness influencers are nothing but a pretty face with a six-pack and a loud voice and don’t actually know what they’re talking about.
Instead, think about the function of the muscles you want to engage, perform movements that work that muscle, and then apply a load, if necessary, to make that movement more challenging.
The 17 Best Standing Abs Exercises
Now you know the pros and cons of standing abs exercises and the muscles these movements work. So, it’s time to reveal the 17 best standing abs exercises for all fitness levels!
1. Standing cable crunch
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
The key to an effective crunch is shortening the distance between your sternum and pelvis. Making a discernable C-shape with your spine ensures that your abs do the work, not your hip flexors. If you can’t feel this exercise in the front of your abdomen, there is a good chance you are flexing your hips more than your spine.
Steps:
Fix a rope handle to a high cable pulley machine. Take one end in each hand and take a step backward to tension the cable.
Pull the handles down so your hands are in front of your shoulders.
Stand with your knees slightly bent, feet shoulder-width apart.
Flex your spine and draw your sternum down toward your pelvis.
Lift your chest to get a stretch in your abs, and repeat.
Benefits:
Easy to scale by reducing or increasing the load.
More effective than the kneeling variation of this exercise.
A very lower back-friendly core exercise.
Tips:
Exhale as you contract your abs to increase muscle engagement.
Hold the handles in one hand only to work the obliques more.
You can also do this exercise with a resistance band:
2. Pallof press
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
The Pallof press was invented by Bostonian physical therapist John Pallof. This is an anti-core exercise, meaning you’ll be using your midsection to prevent unwanted movement. This is how your core often has to work in nature, making Pallof presses a very functional abs exercise.
Steps:
Attach a D-shaped handle to a cable machine set to mid-chest height.
Stand side-on to the pulley with the handle in both hands. Your feet should be about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Brace your core.
Pull your hands into your chest and step away from the machine.
Without moving your hips or shoulders, extend your arms out in front of you.
Bend your arms and return your hands to your chest.
Repeat for the required number of reps and then switch sides.
Benefits:
Minimal lower back stress.
Very scalable – just add or subtract weight according to your needs.
An excellent exercise for integrating the upper and lower body with the core.
Tips:
The narrower your stance, the more challenging this exercise becomes.
Vary the height of your arms to work your core from different angles.
Do this exercise with a resistance band for home workouts.
3. Overhead Pallof press
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Where regular Pallof presses are an anti-rotation exercise, this version is an anti-extension exercise, so it hits your anterior abs more than your obliques. This challenging exercise is basically a standing, moving plank.
Steps:
Attach a rope handle to a high pulley. Grab the handle and then turn your back to the machine. Hold your hands at shoulder height and brace your core. Adopt a split stance for balance.
Without leaning forward or backward, press your arms above your head.
Return your hands to your shoulders and repeat.
Benefits:
A full-body standing abs exercise.
Good for increasing core and upper body stability.
Can be made as hard or as easy as required by adjusting the weight
Tips:
You can also do this exercise with a resistance band.
The closer/narrower your feet, the more challenging this exercise will be.
Exhale as you raise your arms to increase core engagement.
4. Dumbbell side bend
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Many people do this exercise with a dumbbell in each hand – don’t be one of them. Using two weights means one dumbbell counterbalances the other, rendering the exercise useless. Use one dumbbell only, and you’ll get a much better core workout.
Steps:
Hold a dumbbell in one hand, arm by your side. Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back.
Lean to the side and lower the weight down the outside of your leg.
Stand upright and repeat.
Benefits:
An effective dynamic oblique exercise.
Good for increasing lateral mobility.
A useful forearm and grip strengthening exercise.
Tips:
Keep your hips and shoulders squared – no twisting.
Use a kettlebell instead of a dumbbell if you wish.
Hold a weight in one hand only!
5. Landmine full-contact twists
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, obliques, transverse abdominis.
A landmine is a simple device that turns a barbell into a functional workout machine. You can do many exercises with a landmine, and they’re all excellent. No landmine? No problem! Just wedge the end of your barbell into a corner or against the bottom of a squat rack. Full contact twists are an excellent standing core exercise.
Steps:
Place one end of your barbell in the landmine, and grab the other in both hands.
Lift the bar and hold it above your head with your hands close together, palms facing inward.
Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back. Press the bar forward and down into the landmine.
Maintaining your core tension, rotate your shoulders and arms and lower the bar down to one side. Turn your hips in the same direction as your arms.
Lift the weight back to the center and repeat on the opposite side.
Continue alternating sides for the duration of your set, driving your arms forward and down throughout.
Benefits:
An excellent exercise for athletes.
Can be performed with heavy weights to develop a strong, powerful core.
A full-body, functional, total core strength exercise.
Tips:
Raise the weight explosively but lower it slowly to make this exercise as effective as possible.
Don’t just use your arms for this exercise; put your entire body into each rep.
Keep flexing your abs throughout.
6. Saxon side bend
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
The Saxon side bend is named after old-school professional strongman Arthur Saxon. As a strongman performer, Saxon did incredible feats of strength live onstage, often in front of enormous crowds. The Saxon side bend was one of his favorite exercises for developing core strength.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Hold and raise a weight above your head, e.g., a medicine ball or a single dumbbell.
Without twisting your shoulders or hips, lean from one side to the other to challenge your core.
Adjust your range of motion according to your flexibility and mobility.
Benefits:
You don’t need heavy weights for this exercise; a little goes a long way.
Good for improving lumbar spine lateral mobility.
An effective shoulder stability exercise.
Tips:
Don’t go too heavy too soon – this exercise is more strenuous than it looks!
Hold the weight in front of your chest to shorten the lever and make this exercise easier.
Do not allow your hips or shoulders to twist, as doing so makes this exercise less effective.
7. Cable high-to-low woodchop
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
This exercise is so-called because, when you do it, you look a little like you are chopping wood. The cable woodchop is an effective oblique strengthener and teaches you how to integrate your upper and lower body with your core.
Steps:
Attach a D-shaped handle to a high cable machine. Hold the handle in both hands and then stand sideways onto the pulley. Take 1-2 steps away to tension the cable.
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent.
Keeping your arms straight, turn your upper body through 180 degrees so your hands travel diagonally downward to hip height.
Return to the starting position and repeat.
Do the same number of reps on each side.
Benefits:
Easy to modify for all levels of exerciser.
Teaches you how to brace your core while using your upper and lower body.
A very lower back-friendly exercise.
Tips:
You can also do this exercise with horizontal arms or working from low to high.
Try shifting your weight from one leg to the other as you rotate your upper body.
No cable machine? Do this exercise with a resistance band attached to a sturdy anchor.
8. Standing oblique crunch
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Not all standing abs exercises use cables or weights to strengthen your core. This movement might not be overly challenging, but it provides your abs and obliques with a pleasant workout. Best of all, you can do it anywhere and anytime, as no equipment is involved.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart. Clasp your hands behind your head and press your elbows out and back to open your chest. Brace your core.
Bend one leg and lift your knee out and up. Simultaneously lean sideways and lower your elbow down toward your need.
Lower your leg, stand back up, and repeat.
Do the required number of reps and then switch sides.
Benefits:
A standing, equipment-free abs exercise you can do anywhere and anytime.
Ideal for beginners.
A good way to mobilize your hips and lower back as you work your abs.
Tips:
Do this exercise with an alternating action if preferred.
Make this exercise harder by wearing ankle weights.
Pause at the mid-point of each rep to maximally contract your abs and make this exercise more effective.
9. Standing bicycle crunch
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, obliques, transverse abdominis.
Regular bicycle crunches are an excellent, if highly challenging, abs exercise. This standing version is far more accessible, making it ideal for beginners. It’s also a useful teaching exercise before attempting full bicycle crunches and can also be used as a warm-up. However, the overload on your abs is pretty low, so make sure you contract your muscles hard to gain any benefits.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together, knees slightly bent for balance. Place your hands on your temples. Brace your abs.
Bend one leg and lift your knee up and across the front of your body. Simultaneously lean forward and lower your opposite knee to your elbow.
Stand up straight, lower your foot to the floor, and then repeat on the other side.
Continue alternating sides for the duration of your set.
Benefits:
A good standing abs exercise for beginners.
An excellent hip and spine mobility exercise.
A good move to prepare you for full bicycle crunches.
Tips:
Do not clasp your hands behind your neck, as you are more likely to pull with your arms if you do.
Pause at the midpoint of each rep for maximum effectiveness.
Drive your supporting foot into the floor to make balancing on one leg easier.
10. Single-arm dumbbell press
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
While dumbbell presses are usually viewed as an upper-body exercise, they also provide an effective abs workout. Done standing, the single-arm dumbbell press is as good for your abs as it is for your shoulders.
Steps:
Hold a dumbbell in one hand at shoulder height. Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent. Brace your core.
Without leaning sideways, press your weight up and overhead to arm’s length.
Lower the weight back to your shoulder and repeat.
On completion of your set, swap sides and repeat.
Benefits:
An effective and accessible lateral core exercise.
A great time-saver – work your core, deltoids, and triceps simultaneously.
An excellent way to integrate your core with your upper body.
Tips:
Do the same number of reps on both sides.
Stand with your feet closer together to make this exercise harder.
You can also do this exercise with a barbell instead of a dumbbell:
11. Suitcase deadlift
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
When most people do deadlifts, they do them to build full-body strength or a bigger, more muscular back. However, this variation is a very effective if challenging standing abs exercise. You’ll need to use all your core muscles to maintain a neutral spine, so your abs will be acting as stabilizers. This is how your core usually works in nature, so this is a very functional movement.
Steps:
Place a kettlebell or dumbbell on the floor and stand next to it so the handle is parallel to your feet.
Bend down and hold the handle with a neutral or palms-in grip.
Pull your shoulders down and back, brace your core, and look straight ahead.
Drive your feet into the floor and stand up straight. Do not lean sideways or round your back.
Lower the weight back to the floor, allow it to settle for 1-2 seconds, and repeat.
Turn around and do the same number of reps on the opposite side.
Benefits:
A very functional exercise.
Teaches you how to safely lift heavy objects off the ground.
Helps identify and fix left-to-right strength imbalances.
Tips:
Use gym chalk to prevent your hands from slipping.
Perform this exercise in front of a mirror to ensure you don’t lean to the side.
You can also do this exercise with a barbell.
12. Single-arm farmer’s walk
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
This is another standing core exercise that many people do for an entirely different reason. Farmer’s walks are a well-known grip and general conditioning exercise. However, when performed using just one weight, it quickly becomes a very challenging abs workout.
Steps:
Hold a heavy dumbbell or kettlebell in one hand with your arm by your side. Brace your core and set your hips and shoulders so they are level.
Without leaning to either side, walk around your training area.
Having completed the required distance, lower the weight to the floor, swap hands, and repeat.
Benefits:
A very functional standing abs exercise.
An excellent way to spot and fix left-to-right strength imbalances.
A challenging grip-building exercise.
Tips:
Use chalk to stop your hands from slipping.
Keep your shoulders down and back throughout.
Lower the weight to the floor as you feel your grip starting to give out. Don’t drop the weight.
13. Standing ab wheel rollout
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Standing abs exercises don’t come much more challenging than the infamous rollout. This exercise combines extended planks with a pull-over arm action, making it one of the most brutal core exercises around. Only attempt this move if you have mastered the kneeling ab wheel rollout.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart. Hold your ab wheel with an overhand grip.
Brace your core, bend your knees slightly, and lean forward to place the ab wheel on the floor in front of your feet.
Keeping your arms straight, push the roller out and away, lowering your body toward the floor. Extend your arms as far as you can without losing core tension.
Pull the wheel back toward your feet, lifting your hips up as you do so.
Continue for the prescribed number of reps.
Benefits:
Probably the most challenging standing abs exercise.
Provides an effective lat-building workout.
An ideal exercise for home workouts.
Tips:
Do this exercise facing a wall to prevent the wheel from rolling too far.
Only extend your arms as far as comfortable to avoid injuring your lower back.
Rest on your knees to make this exercise easier.
14. TRX Hip drops
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
The TRX was invented by a Navy SEAL who wanted a portable training device he could take on deployment. TRXs can be used to replicate many machine and dumbbell exercises, and there are several unique bodyweight movements you can do with this type of suspension trainer. TRX hip drops are an especially challenging lateral core exercise.
Steps:
Attach your TRX to a high anchor point. Hold the handles on both hands and raise your arms above your head so your body is straight.
Lean your hips out to the side so your body forms a distinct C shape.
Pull your hips back to the center and repeat.
Continue for the prescribed number of reps and then switch sides.
Benefits:
An excellent exercise for home workouts.
A very functional, challenging standing abs exercise.
Easy to change the difficulty by varying your range of motion.
Tips:
Place your feet closer together to make this exercise harder.
The longer the straps, the more challenging this exercise becomes.
You can also do this exercise with gymnastic rings and other types of suspension trainer.
15. Single-arm cable chest press
Muscles targeted: Rectus abdominis, obliques, transverse abdominis.
No, we haven’t included this exercise by mistake. Despite its name, the single-arm chest press is actually a terrific standing abs exercise. You’ll need to use all your core muscles to stabilize your midsection as you extend and bend your arm. But yes, it’s also a great chest exercise!
Steps:
Attach a single handle to a chest-high cable machine. Hold the handle and turn your back on the pulley so the wire runs outside or under your arm.
Step forward into a split stance for balance. Brace your core.
With your hips and shoulders still, press your arm forward and out to full extension.
Return the handle to the side of your chest, and repeat.
Switch sides and do the same number of reps with the opposite arm.
Benefits:
Teaches you how to stabilize your spine while moving your arms.
An excellent exercise for athletes.
An easy exercise to modify for all fitness levels.
Tips:
Bring your feet closer together to make this exercise more challenging.
Use your core to make sure your torso doesn’t twist.
Pair with single-arm cable rows to work your abs from the front and back.
16. Single-leg Romanian deadlift
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Single-leg Romanian deadlifts are an excellent exercise for your glutes and hamstrings. However, you’ll also need to use your core to stabilize your spine and prevent your upper body from twisting. As such, it’s also a great standing abs exercise.
Steps:
Stand with your feet together and a dumbbell or kettlebell in your left hand. Shift your weight onto your right foot. Brace your core and pull your shoulders down and back.
Hinging from your hips, bend forward and lower the weight down the front of your leg. Lift your left leg out behind you for balance.
Stand back up and repeat.
Rest a moment and then change legs, remembering to switch hands, too.
Benefits:
Teaches you how to integrate your core with your upper and lower body.
A very lower back-friendly exercise.
An excellent balance-building workout.
Tips:
Do this exercise next to a wall and use your free hand for balance if required.
You can also keep your non-supporting foot resting lightly on the floor for balance, i.e., a kickstand or B-stance Romanian deadlift.
Keep your supporting knee slightly bent throughout.
17. Kettlebell around the world
Muscles targeted: Obliques, rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis.
Many of the best standing core exercises work one side of your abs at a time. This one is slightly different as it works your entire core in one straightforward movement. Done with light weights, this exercise is an excellent warm-up for your whole midsection. But, done with greater loads, it’s a challenging yet fun total abs exercise.
Steps:
Stand with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent for balance. Brace your abs. Hold a kettlebell in front of your hips.
Swing the weight around your waist, transferring from one hand to the other behind your back and in front of your hips.
Use your core muscles to resist being pulled toward the weight.
Continue for the desired number of reps, rest a moment, and then switch directions.
Benefits:
A very time-efficient exercise.
Very little lower back stress.
An excellent way to mobilize your shoulders and activate your deep core muscles before more demanding exercises.
Tips:
Keep your feet planted firmly on the floor to maintain your balance.
Lift your chest and set your shoulders down and back throughout.
Use gym chalk to stop the kettlebell handle from slipping out of your hands.
Standing Abs Exercises – FAQs
Do you have a question about standing abs exercises or core training in general? That’s okay because we’ve got the answers!
1. Will these standing abs exercises give me a six-pack?
While many of these exercises involve your six-pack muscle – the rectus abdominis – there is no guarantee that doing them will give you six-pack abs. That’s because, for the contours of your abs to be visible, you need to have a low body fat percentage. This is typically ten percent or less for men and below 15 percent for women.
It’s entirely possible to have well-develop abs but for them not to be visible because they’re hidden under a layer of fat.
So, while these standing abs exercises COULD lead to a six-pack, your results hinge on your diet as much as your workouts.
2. How many reps and sets should I do of these exercises?
You can do anywhere from 5 to 30 reps to train your abs. Low reps with heavy weights are best for building brute strength, while higher reps and lighter loads are better for endurance, hypertrophy, and general fitness.
However, some exercises lend themselves to higher or lower reps. For example, suitcase deadlifts work well with bigger loads, while standing bicycle crunches are more suitable for higher reps.
Very high reps, i.e., more than 30, are not recommended as they are largely a waste of time and not challenging enough to be effective.
Regardless, you should take each set to within a couple of reps of failure. Easy sets won’t have much of an effect on the condition of your abs.
Regarding the number of sets, 2-4 should be sufficient for most people. If you feel you need to do more than this, you probably aren’t training close enough to failure, or you are resting too long between sets.
3. XYZ exercise hurts my back – what gives?
While the majority of these standing abs exercises are very lower back-friendly, some will put a strain on your lumbar spine. Others can cause back pain when performed incorrectly or with too much weight.
So, if any of these exercises hurt your back, firstly, make sure you are performing them correctly. Perfect form is critical for a safe and pain-free workout. Then dial back the weight a little to see if that helps.
If you still feel your lower back, skip that movement and do something else. It could be that the exercise in question just doesn’t suit you.
4. Are standing abs exercises better than those performed lying down?
While standing abs exercises offer several advantages, that doesn’t mean they’re better than more traditional lying abs exercises. Ultimately, the best exercises for you are the ones you like, and that meet your workout needs.
If you want to isolate your abs, lying exercises are often best, as they don’t involve many additional muscle groups. But, if you want a more functional workout, standing exercises are arguably the better choice.
Or, you could just combine standing and lying abs exercises and enjoy all the benefits these two different types of training provide. There is no need to choose between them.
5. Will these exercises burn belly fat?
Many people think that doing lots of abs exercises will burn belly fat. Sadly, this is nothing but an old exercise myth. Your body stores and then burns fat from all over your body, not just from the areas you train. As such, if you want to burn fat and get lean, you need to work your entire body and not just where you want to lose the fat from.
So, sorry, these exercises will NOT burn belly fat.
Closing Thoughts
There is no need to head straight to the floor to train your abs. In fact, there are plenty of standing abs exercises that are every bit as effective as the ubiquitous crunches, sit-ups, and leg raises.
Movements like cable high-to-low woodchops, Saxon side bends, standing cable crunches, and standing bicycle crunches are ideal for those times when you don’t want to lie down or just want to hit your abs from a different, more functional angle.
Are standing abs exercises better than ab exercises done on the floor? Not necessarily. However, they may be more suitable for some exercisers and are worth including in any well-balanced core workout plan.

